Defense & Security
An analysis of European Diplomatic Efforts to Support Ukraine’s Territorial Integrity. Challenges and Opportunities.

Image Source : Shutterstock
Subscribe to our weekly newsletters for free
If you want to subscribe to World & New World Newsletter, please enter
your e-mail
Defense & Security

Image Source : Shutterstock
First Published in: Sep.05,2025
Sep.05, 2025
Abstract
This analysis examines European diplomatic efforts to support Ukraine’s territorial integrity amid the ongoing Russia-Ukraine war, highlighting the EU’s evolving role as a security actor. The August 18, 2025, White House summit marked a key moment, with EU leaders pledging "ironclad" security guarantees modelled after NATO’s Article 5, without formal NATO membership for Ukraine, and proposing a "reassurance force" of European troops post-ceasefire. The EU commits to unrestricted Ukrainian military capabilities, sustained economic and military aid, and intensified sanctions against Russia.
While the EU aims to bolster Ukraine’s self-defence and facilitate peace talks, challenges persist, including funding, coordination with the U.S., and Russia’s rejection of guarantees involving Western troops. The EU’s approach reflects a strategic shift toward a more assertive Common Foreign and Security Policy, though institutional limitations remain. The guarantees are intertwined with Ukraine’s EU accession ambitions, carrying significant geopolitical and financial implications for the European security architecture and regional stability.
Key Words: Ukrainian War, European Security, EU, U.S., Russia
Introduction
The ongoing war in Ukraine likely marks the end of the post-Cold War security environment in Europe and the rest of the world. The old international system, based on the benign hegemony of the United States and its dominance in international institutions, is witnessing the vanishing of the pretence of the leading role of international law and international regimes before our eyes. What is emerging brings back memories of the 19th-century Concert of Europe, where the great powers of Europe— Austria, France, Prussia (later Germany), Russia, and the United Kingdom —came together to maintain the European balance of power, political boundaries, and spheres of influence. This time around, however, there are fewer players, and the gameboard is genuinely global. The U.S., China and Russia do not leave much space for other players, at least in the global context. The EU declares itself to be a global player, matching the influence of the big three, but in all honesty, it is not treated as such by them.
This analysis looks at the latest developments regarding the ongoing war between Russia and Ukraine (a proxy war between NATO and Russia) and specifically at the role of the EU and its proposed security guarantees offered to Ukraine.
The August 18 Meeting
On August 18, 2025, a meeting took place at the White House. It included U.S. President Donald Trump, Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy, and leaders from Germany, France, Italy, the UK, Finland, the European Commission, the European Council, and NATO. They talked about ways to stop Russia's invasion of Ukraine. A key topic was security guarantees for Ukraine. The EU promised strong protection for Ukraine's independence and borders. This is intended to prevent future Russian attacks, even though Ukraine is unlikely to join NATO soon. These promises build on earlier security agreements but demonstrate a more unified European effort, with the U.S. providing support but not leading with troops or NATO membership.
Ironclad Security Guarantees Equivalent to NATO's Article 5 (Collective Defence)
The EU promised to give firm, long-term security promises to Ukraine, similar to NATO's Article 5. This means an attack on Ukraine would be seen as an attack on those who promised to help. However, these promises would not be part of NATO to avoid upsetting Russia or requiring all NATO members to agree. European leaders, including those from the "Coalition of the Willing," are prepared to deploy a "reassurance force" or peacekeepers to Ukraine once the fighting ceases. This force would comprise troops from different European countries, taking turns to monitor and enforce any peace agreement, with a primary focus on preventing new attacks. EU officials stated that Russia cannot halt these plans or Ukraine's future aspirations to join the EU and NATO. Trump said the U.S. will work with Europe and might provide air support, but will not send American ground troops, making Europe the "first line of defence." Meanwhile, the U.S. will support by selling weapons.[1]
No Restrictions on Ukraine's Military Capabilities
EU leaders want Ukraine's military to have no limits on size, type, or actions. This means Ukraine can make weapons at home and get more from Western countries without Russia stopping them. The aim is for Ukraine to have a strong army for many years. Europe will also increase its own military production to help. Ukraine plans to buy $90 billion in U.S. weapons, mostly paid for by Europe. This includes planes, air defence systems, and drones. A formal agreement is expected within 10 days of the meeting.[2]
Sustained Economic and Military Support, Including Sanctions
The EU has pledged to continue providing Ukraine with military, financial, and humanitarian assistance until a lasting peace is achieved. They will also increase sanctions and economic actions against Russia to maintain pressure. Leaders say they will support Ukraine as long as the fighting continues, and they will not force Ukraine to give up any land. Only Ukraine can decide about its territory. Europe is prepared to undertake most of this effort and may allocate an additional €40 billion for weapons if necessary. They will work with the U.S. to get support from Trump.[3]
Facilitation of Further Talks and Peace Efforts
EU leaders aim to facilitate a meeting between Trump, Zelenskyy, and Putin. They say any agreement must include Ukraine's views and protect Europe's safety. They are glad Trump is pushing for peace, but say a ceasefire is not needed for security promises. Moscow's complaints, like those about NATO forces, will not stop their plans. This shows Europe is united. Leaders like Ursula von der Leyen and António Costa have stated that there will be no official changes to borders, and they fully support Ukraine's membership in the EU.[4]
There were concerns that Trump might pressure Ukraine to make concessions during his meeting with Putin on August 15, 2025, in Alaska. European leaders quickly organised a meeting at the White House to influence Trump. This was seen as a way to win him over. Russia does not want NATO or Western troops in Ukraine, seeing it as a threat. Some experts argue that there is a "security guarantee paradox": if the protection is too weak, it will not benefit Ukraine; if it is too strong, Russia may not agree to any deal.[5] EU officials are hopeful, but they face several challenges. These include securing funding (Europe will cover most costs), managing rotating forces, and ensuring the U.S. remains committed after Trump's term.[6]
Recent Military and Diplomatic Developments
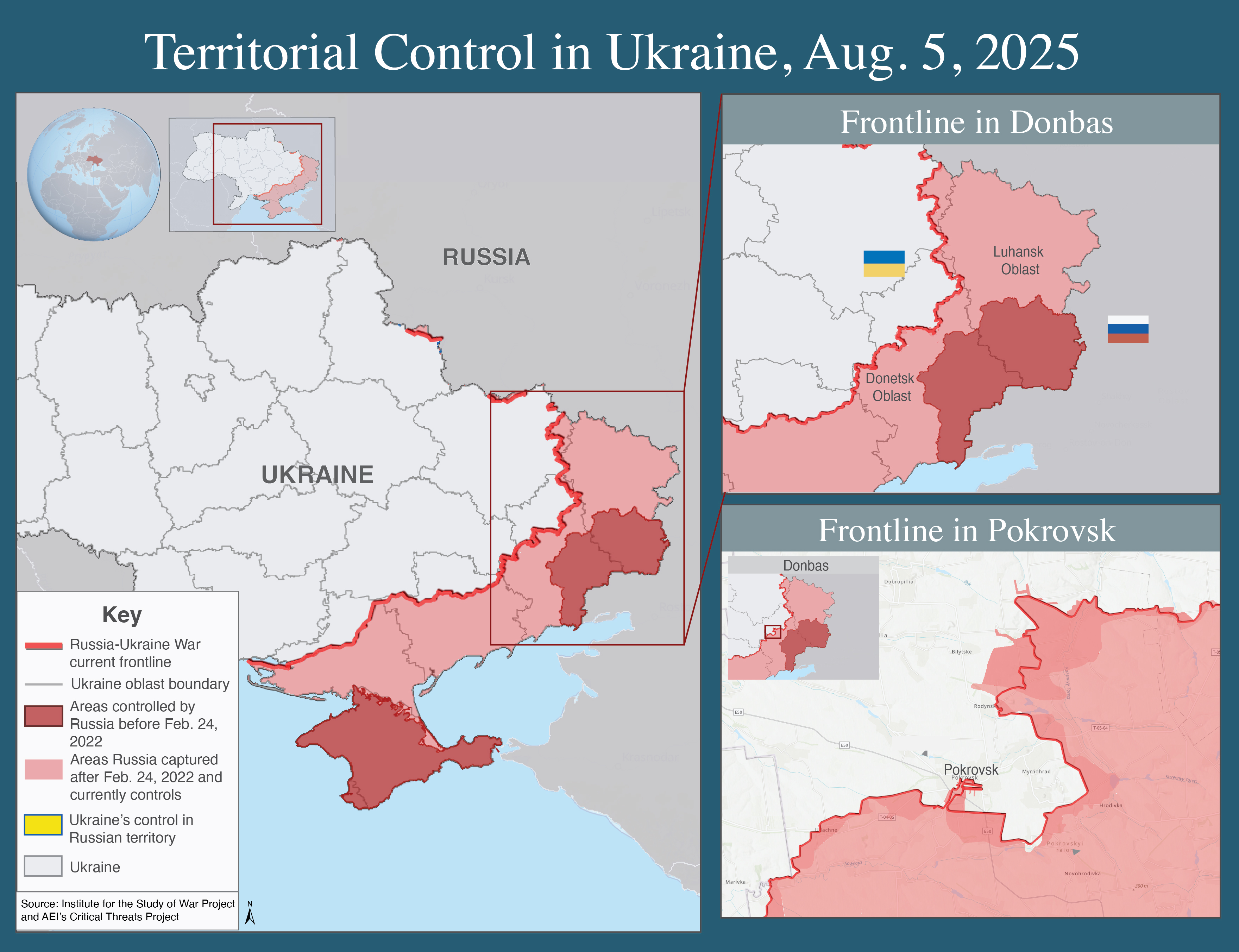
The Russia-Ukraine war started in February 2022. In August 2025, fighting and diplomatic talks increased. Russian troops are moving forward in eastern Ukraine, especially in Donetsk, with many attacks. Ukraine is hitting Russian targets. U.S. President Donald Trump is leading peace talks after meeting Russian President Vladimir Putin in Alaska on August 15. Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskyy and European leaders are also involved. However, significant disagreements persist regarding land, security, and ceasefires. There is no quick solution yet.
Russian Advances and Territorial Gains
Russian forces have concentrated on Donetsk and taken more land. From July 8 to August 5, 2025, Russia gained 226 square miles, continuing its slow progress in the area.[7] By mid-August, Russia controls large parts of Donbas and continues to advance, even though Ukraine is fighting back.[8]
On August 19, Russia launched its most significant attack of the month, using drones and missiles against Ukrainian targets, resulting in civilian casualties and infrastructure damage.[9] On August 18, there were similar long-range attacks. On August 19, Ukraine and Russia swapped the bodies of dead soldiers. Ukraine has increased attacks on Russian energy sites to cut off war funding.[10]
After the Trump-Putin meeting in Alaska, Trump met with Zelenskyy and leaders from the EU and UK on August 18 to discuss peace. Trump seems to support giving some Ukrainian land, like parts of Donbas, to Russia for peace. He also suggests U.S. air support as a security promise. A U.S. envoy stated that there is progress: Putin has agreed to U.S. security guarantees for Ukraine and has relinquished some territory.[11]
Plans for direct talks are being made. Putin suggested Moscow as the meeting place, but this has not been confirmed yet (as of August 20).[12] European leaders, including EU figures, seem to welcome these efforts but insist on continued sanctions against Russia and reject Budapest (Hungary) as a site due to past failed assurances.[13 ]
In the meantime, Ukraine demands robust security guarantees (e.g., deterrence against future attacks) and $90 billion in aid.[14 ] Russia, however, rejects European guarantees, insists on territorial concessions, and maintains unchanged objectives. As of now, no ceasefire has been agreed upon; however, Russia claims to be open to one.[15 ]
Where Does the EU Stand in General?
EU leaders stress that a strong Ukraine is the best guarantee against Russia. According to the statement of 12 August, issued by the European Council and the Council of the European Union: “The European Union, in coordination with the U.S. and other like-minded partners, will continue to provide political, financial, economic, humanitarian, military and diplomatic support to Ukraine as Ukraine is exercising its inherent right of self-defence. It will also continue to uphold and impose restrictive measures against the Russian Federation. A Ukraine capable of defending itself effectively is an integral part of any future security guarantees. The European Union and its Member States are ready to further contribute to security guarantees based on their respective competences and capabilities, in line with international law, and in full respect of the security and defence policies of certain Member States, while taking into account the security and defence interests of all Member States. The European Union underlines the inherent right of Ukraine to choose its own destiny and will continue supporting Ukraine on its path towards EU membership”.[16]
According to EU top diplomat, Kaja Kallas (High Representative/Vice-President (2024-2029) responsible for Foreign Affairs and Security Policy),[17] the idea of letting Russia keep Ukrainian territories (proposal as signalled by Trump) was a "trap that Putin wants us [the EU] to walk into".[18] She stressed that Russia has offered no concessions and that credible security measures, such as bolstering Ukraine's military, are essential—though specifics on contributions remain up to individual member states. In a like-minded fashion, French President Emmanuel Macron rather hawkishly and not very diplomatically echoed this, describing Putin as a "predator, and an ogre at our [Europe] doorstep" and expressing "the greatest doubt" that he would be willing to work towards peace.
In short, the foremost European leaders are still ready to challenge Russia. They enjoy peace at home while using Ukraine as a battleground. Their new ideas about Ukraine's safety and Europe's security are bold and raise concerns about possible problems.
The “Devil Lies in Details”
The European Union is part of the "Coalition of the Willing" due to its key members. According to Wikipedia, this group comprises 31 countries. They have promised to support Ukraine more strongly against Russia than the Ukraine Defence Contact Group. They are ready to join a peacekeeping force in Ukraine by sending troops or providing other forms of support.[19] The peacekeeping force is envisaged to be deployed only once Ukraine and Russia sign a "comprehensive ceasefire agreement" or "peace deal" to settle the ongoing Russo-Ukrainian War. The initiative, led by the United Kingdom and France, was announced by British Prime Minister Sir Keir Starmer on 2 March 2025, following the 2025 London Summit on Ukraine under the motto "securing our future".[20]
The EU has been developing plans for Ukraine's security in the aftermath of the war. The primary goal is to stop future Russian attacks, short of offering NATO membership to Ukraine. Recent plans include military, diplomatic, and financial help, with the EU and U.S. working together. These plans are still changing due to ongoing talks, Russian objections, and questions about their enforcement. The focus is on helping Ukraine defend itself and providing additional support, including air and sea protection.
The EU wants Ukraine to be able to defend itself. This is important for any promises they make. The EU and its member states are ready to provide assistance based on their capabilities. They will follow international law and their own defence rules.[21] This includes ongoing military aid but does not specify sending troops or creating new plans. In this context, European Council President Antonio Costa has called for faster work on "NATO-like" guarantees. These could be similar to Article 5, where an attack on Ukraine would lead to talks and actions from allies.[22]
NATO and European leaders are discussing a new plan similar to "Article 5." This plan would prompt allies to discuss within 24 hours in the event of an attack. They would work together on responses, such as increasing military forces and providing aid for rebuilding. This idea is similar to agreements with countries like the UK and France, which focus on building strength and recognising borders.[23] EU accession for Ukraine could trigger the bloc's mutual defence clause, offering a "strong guarantee" in principle, although its practical enforcement is debated.[24]
Air and sea security are important. A "sky shield" is planned to protect the air over western and central Ukraine, including Kyiv. European fighter jets, with possible U.S. support, will enforce this. The jets might be stationed in Poland or Romania. There will be rules for dealing with Russian actions, like missile attacks. In the Black Sea, measures will prevent Russian naval threats and keep shipping safe from ports like Odesa using intelligence and patrols.[25]
Some countries, such as France and the UK, may deploy a small number of troops. These troops could help with training in cities like Kyiv or Lviv, or they might help secure ports and airbases.[26] Sending large numbers of troops is not feasible due to Ukraine's vast size and Russia's demands. Instead, the focus is on training, sharing information, managing supplies, and equipping Ukraine's military with weapons.
Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelenskiy said that guarantees might be ready by August 29, 2025. These include U.S. assistance, valued at $90 billion, which includes weapons such as planes and air defences. Europeans will be the "first line of defence," with the U.S. helping in other ways. However, there are concerns: Russia wants to be part of the talks and does not want foreign troops. Some reports also question the coalition's strength and clarity, particularly in the absence of firm U.S. promises.
Possible Broader Geopolitical Ramifications
First, supporting Ukraine’s borders could strengthen the EU’s role in European security. This would indicate a shift towards a stronger EU foreign and security policy, as well as a more unified European defence system. However, the EU’s current tools, such as Article 42(7) TEU and PESCO, are not particularly robust. They have limitations in how they operate and face financial and organisational problems. This makes it challenging for the EU to establish itself as a strong security force without assistance from NATO and the U.S.[27]
Second, the EU’s security guarantee to Ukraine is likely to intersect closely with NATO’s role, as the EU’s defence efforts currently complement but do not replace NATO’s collective defence framework. The EU remains dependent on NATO (especially the U.S.) for significant military capabilities, and the guarantee could deepen cooperation but also create institutional competition or overlap. The transatlantic alliance’s unity and the U.S. continued engagement are critical factors in the guarantee’s effectiveness.[28]
Third, an EU guarantee of Ukraine’s security could also send a strong geopolitical signal to Russia, potentially deterring further aggression and affirming the EU’s commitment to the European security order. However, it may also escalate tensions with Russia, which views such guarantees as a threat to its sphere of influence.[29] This dynamic affects not only Ukraine but also other countries in the EU’s neighbourhood, such as Georgia, which is vulnerable to Russian pressure and exclusion from security arrangements.[30]
Fourth, guaranteeing Ukraine’s security is linked to its EU accession ambitions. While Ukrainians see EU membership as essential recognition of their sovereignty and security, many Europeans view it as a component of a future negotiated settlement with Russia. The EU’s guarantee thus has implications for the pace and nature of enlargement, potentially affecting the EU’s cohesion and its relations with neighbouring countries.[31]
Fifth, the EU’s security guarantees would likely entail substantial financial commitments, including military aid, reconstruction support financed through mechanisms such as the European Peace Facility (EPF), and the utilisation of frozen Russian assets. These financial undertakings have implications for EU budgetary policies, fiscal solidarity, and the development of a European defence industrial base, which is currently fragmented and underfunded.
Conclusion
The EU declares itself to be a global player and consequently engages as a broker in preparing peace talks with Russia. Moreover, it envisions itself as a guarantor of peace on the European continent and Ukrainian security, as well as its territorial integrity. Two important questions, however, remained unanswered.
First, given the EU's engagement against Russia alongside Ukraine, as well as its most prominent member states' support for the Ukrainian war effort, one would be correct to question the intentions of at least some European political leaders. On one hand, the openly adversarial stance against Russia may produce some deterrence-like effects (although, in all honesty, it is difficult to prove). On the other hand, it definitely does prolong the conflict at the expense of Ukraine and its people.
Second, the following analysis will examine the extent to which the EU's guarantees for Ukraine are in reality. Political declarations and paper documents can convey a wide range of statements, including the most hawkish and resolute. The real test, however, always involves actual acting in the face of challenges and dangers. Will Europeans actually be ready to back their words with actions? Will they be able to perform at the required level militarily and economically? The 20th-century experience would suggest otherwise.
References
1 Roth, A., & Sauer, P. (2025, August 19). Trump rules out sending US troops to Ukraine as part of security guarantees. The Guardian. https://www.theguardian.com/world/2025/aug/19/european-leaders-ukraine-russia-trump
2 Magramo, K., Kent, L., Lister, T., Edwards, C., Chowdhury, M., Sangal, A., Hammond, E., & Liptak, K. (2025, August 18). Trump meets Zelensky and European leaders at White House. CNN. https://edition.cnn.com/politics/live-news/trump-ukraine-zelensky-russia-putin-08-18-25
3 Europe must shoulder ‘lion’s share’ of Ukraine’s security, Vance says. (2025, August 21). AlJazeera. https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2025/8/21/europe-must-shoulder-lions-share-of-ukraines-security-vance-says
4 Mangan, D., Breuninger, K., Doherty, E., & Wilkie, C. (2025, August 18). Trump-Zelenskyy meeting paves the way for Ukraine security guarantees, trilateral talks with Putin. CNBC. https://www.cnbc.com/2025/08/18/trump-zelenskyy-ukraine-putin-live-updates.html
5 Rutland, P. (2025, August 22). The ‘security guarantee’ paradox: Too weak and it won’t protect Ukraine; too robust and Russia won’t accept it. The Conversation. https://theconversation.com/the-security-guarantee-paradox-too-weak-and-it-wont-protect-ukraine-too-robust-and-russia-wont-accept-it-263518
6 Schwartz, F., Barigazzi, J., & Webber, E. (2025, August 13). Trump tells European leaders US could provide security guarantees for Ukraine. Politico. https://www.politico.com/news/2025/08/13/trump-european-leaders-security-ukraine-00508598
7 The Russia-Ukraine War Report Card, Aug. 6, 2025. (n.d.). Russia Matters. Retrieved August 21, 2025, from https://www.russiamatters.org/news/russia-ukraine-war-report-card/russia-ukraine-war-report-card-aug-6-2025
8 A timeline of territorial shifts during Russia’s war on Ukraine. (2025, August 18). PBS News. https://www.pbs.org/newshour/world/a-timeline-of-territorial-shifts-during-russias-war-on-ukraine
9 Ukraine hit by multiple Russian strikes amid US-led push for end to war. (2025, August 19). Aljazeera. https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2025/8/19/ukraine-hit-by-multiple-russian-strikes-amid-us-led-push-for-end-to-war
10 Harvey, A., Mappes, G., Novikov, D., Sobieski, J., Young, J., Barros, G., Kagan, F. W., & Trotter, N. (2025, August 19). Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, August 19, 2025. Institute for the Study of War. https://www.understandingwar.org/backgrounder/russian-offensive-campaign-assessment-august-19-2025
11 Smolar, P. (2025, August 19). War in Ukraine: Diplomatic efforts intensify ahead of possible Zelensky-Putin meeting. Le Monde. https://www.lemonde.fr/en/international/article/2025/08/19/war-in-ukraine-diplomatic-efforts-intensify-ahead-of-possible-zelensky-putin-meeting_6744508_4.html
12 Magramo, K., Yeung, J., Lau, C., Kent, L., Edwards, C., Chowdhury, M., Powell, T. B., Sangal, A., & Hammond, E. (2025, August 20). August 19, 2025: White House says Putin-Zelensky meeting plans are ‘underway’ following Trump meetings. CNN. https://edition.cnn.com/world/live-news/trump-ukraine-russia-zelensky-putin-08-19-25
13 European Union Leaders’ Statement on Ukraine. (2025, August 12). European Council, Council of the European Union. https://www.consilium.europa.eu/en/press/press-releases/2025/08/12/statement-by-european-union-leaders-on-ukraine/
14 Hatton, B., & Davies, K. M. (2025, August 19). Despite a flurry of meetings on Russia’s war in Ukraine, major obstacles to peace remain. AP. https://apnews.com/article/russia-ukraine-war-trump-europe-next-steps-527983fab40e58208e9e18c943de696a
15 Westfall, S., & Ilyushina, M. (August 19). Here’s what Russia and Ukraine have demanded to end the war. The Washington Post. https://apnews.com/article/russia-ukraine-war-trump-europe-next-steps-527983fab40e58208e9e18c943de696a
16 European Union Leaders’ Statement on Ukraine. (2025, August 12). European Council, Council of the European Union. https://www.consilium.europa.eu/en/press/press-releases/2025/08/12/statement-by-european-union-leaders-on-ukraine/
17 See more at: https://commission.europa.eu/about/organisation/college-commissioners/kaja-kallas_en
18 Wilson, T., & Lau, S. (2025, August 22). Proposed Ukraine land concessions are Putin’s trap, EU’s top diplomat tells BBC. BBC. https://www.bbc.com/news/articles/cp8zdezm507o
19 Coalition of the willing (Russo-Ukrainian War). (n.d.). Wikipedia, the Free Encyclopedia. Retrieved August 22, 2025, from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Coalition_of_the_willing_(Russo-Ukrainian_War)
20 Martin, D. (2025, March 2). Britain and France to lead ‘coalition of the willing’ to save Ukraine. The Telegraph. https://www.telegraph.co.uk/politics/2025/03/02/britain-france-lead-coalition-willing-save-ukraine/
21 European Union Leaders’ Statement on Ukraine. (2025, August 12). European Council, Council of the European Union. https://www.consilium.europa.eu/en/press/press-releases/2025/08/12/statement-by-european-union-leaders-on-ukraine/
22 Tidey, A. (2025, August 19). EU and allies must “accelerate” work on Ukraine’s NATO-like security guarantees, Costa says. Euronews. https://www.euronews.com/my-europe/2025/08/19/eu-and-allies-must-accelerate-work-on-ukraines-nato-like-security-guarantees-costa-says
23 Webber, M. (2025, August 20). Ukraine war: what an ‘article 5-style’ security guarantee might look like. The Conversation. https://theconversation.com/ukraine-war-what-an-article-5-style-security-guarantee-might-look-like-263475
24 Is EU accession a security guarantee for Ukraine? (2025, August 22). The New Union Post. https://newunionpost.eu/2025/08/21/ukraine-security-guarantee-eu-accession/
25 Gardner, F. (2025, August 19). What security guarantees for Ukraine would actually mean. BBC. https://www.bbc.com/news/articles/cx2qr08l1yko
26 Harding, L. (2025, August 19). What security guarantees might Ukraine get in return for a peace deal? The Guardian. https://www.theguardian.com/world/2025/aug/19/what-security-guarantees-might-ukraine-get-in-return-for-a-peace-deal
27 Genini, D. (2025). How the war in Ukraine has transformed the EU’s Common Foreign and Security Policy. Yearbook of European Law. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1093/yel/yeaf003
28 Genini, D. (2025). How the war in Ukraine has transformed the EU’s Common Foreign and Security Policy. Yearbook of European Law. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1093/yel/yeaf003
29 Beta, S., Hetherington, K., Contini, K., Zajda, M., Smyrnova, H., Bidnyi, I., Lipska, N., Bahno, M., Tsios, I., Lysenko, L., & Zimmerman, L. (2025, February 5). The Legal Basis for EU Security Guarantees for Ukraine. PILPG. https://www.publicinternationallawandpolicygroup.org/lawyering-justice-blog/2025/5/2/xebqjexqu8ccgsvbo2rmcv4w5an13q
30 Brotman, A. (2025, August 22). The Importance of Security Guarantees for Ukraine and Europe. Geopolitical Monitor. https://www.geopoliticalmonitor.com/the-importance-of-security-guarantees-for-ukraine-and-europe/
31 Brotman, A. (2025, August 22). The Importance of Security Guarantees for Ukraine and Europe. Geopolitical Monitor. https://www.geopoliticalmonitor.com/the-importance-of-security-guarantees-for-ukraine-and-europe/
First published in :
World & New World Journal

Dr. Śliwiński Krzysztof, Feliks is an Associate Professor at the Department of Government and International Studies of Hong Kong Baptist University (https://gis.hkbu.edu.hk/people/prof-krzysztof-sliwinski.html) and Jean Monnet Chair.
He received his doctorate from the University of Warsaw's Institute of International Relations in 2005. Since 2008, he has been employed at Hong Kong Baptist University. He has regularly lectured on European Integration, International Security, International Relations, and Global Studies. His primary research interests include British Foreign Policy and Security Strategy, Polish Foreign Policy and Security Strategy, Security and Strategic Studies, Traditional and Non-traditional Security Issues, Artificial Intelligence and International Relations, European Politics and the European Union, Theories of European Integration, Geopolitics and Teaching and Learning.
Unlock articles by signing up or logging in.
Become a member for unrestricted reading!