Energy & Economics
The Economic Effects of the Gaza War on Palestine and Israel

Image Source : Shutterstock
Subscribe to our weekly newsletters for free
If you want to subscribe to World & New World Newsletter, please enter
your e-mail
Energy & Economics

Image Source : Shutterstock
First Published in: Jun.02,2025
Jun.02, 2025
I. Introduction
Since October 7, 2023, when the Hamas attacked Israel, the Gaza war has entered its third year. Palestinians continue to endure an unprecedented level of violence, trauma, economic hardship, and uncertainty. The war has resulted in a staggering number of casualties and widespread displacement, in addition to massive destruction of physical assets in Gaza, significant reduction of economic output, increased violence in the West Bank, and widespread collapse of basic service provision across the entire Palestinian territories.
As of May 7, 2025, according to Wikipedia and Gaza’s Ministry of Health, 55000 fatalities (53,253 Palestinians and 1,706 Israelis) and more than 110,00 injuries have been reported in Gaza. More than half of the casualties are women, children, and the elderly. An estimated 1.9 million people, approximately 90 percent of Gaza’s population, are currently internally displaced. Seventy percent of Gaza’s Road network, more than 80 per cent of commercial facilities, and close to 90 percent of housing units in Gaza have either severely damaged or have been destroyed.
Since October 7, 2023, the UN has documented over 1,500 clashes between Israeli settlers and Palestinians in the West Bank, resulting in property damage, casualties, and displacement. Over 1,600 Palestinians, half of whom are children, have been displaced due to increased settlers’ violence and access restrictions. Additionally, existing fiscal constraints and growing security concerns have disrupted service provision in the West Bank.
On the macroeconomic front, the Gaza and West Bank face a collapse, which is unmatched in recent memory. The Palestine economy has faced significant contraction, evidenced by a reduced production, sharp decline in gross domestic product (GDP), and soaring unemployment rates.
On the other hand, the Gaza war has had significant negative impacts on Israel. The economic and financial costs of war consist of the direct cost of military operations as well as the indirect losses that extend over the medium and long term. One of the most direct costs of the Gaza war was the recall of about 300,000 reservists in the early days, which meant that the Israeli government would bear the cost of conscription, and the Israeli economy would bear loss of output due to their absence from the workforce.
Given these situations, this paper analyzes the economic effects of the Gaza war on Palestine and Israel.
II. Literature on the Effects of Wars
Wars have the potential to alter the parties and “transform the future” of belligerents (Ikle 1991) and they also bring about fundamental changes to the international system (Gilpin 1981).
Scholars in Economics have provided considerable analysis of the macroeconomic effects of a conflict across spatial levels: locally, nationally, regionally, and internationally. Some studies have examined the effects of specific wars such as the Syrian civil war (Kešeljević and Spruk, 2023) or the Iraq war (Bilmes and Stiglitz 2006). For example, an analysis estimated that the Russian invasion of Ukraine had an economic cost of 1% of global GDP in 2022 (Liadze et al. 2023)
Others have examined the effects of war in general. For instance, Reuven Glick and Alan Taylor (2010) examine bilateral trade relations from 1870 to 1997 and find large and persistent negative impacts of wars on trade and hence on national and global economic welfare. Similarly, Vally Koubi (2005) investigates the effects of inter- and intrastate wars on a sample of countries and finds that the combined prewar, contemporaneous, and postwar effects on economic growth are negative.
A “war ruin” school emphasized that the destruction caused by wars is accompanied by higher inflation, unproductive resource spending on the military, and war debt (Chan 1985; Russett 1970). By contrast, a “war renewal” school argued that there can be longer-term positive economic effects from war because war can lead to increased efficiency in the economy by reducing the power of rent-seeking special interests, triggering technological innovation, and advancing human capital (Organski and Kugler 1980).
III. Economic Effects of the Gaza War
1. Casualties
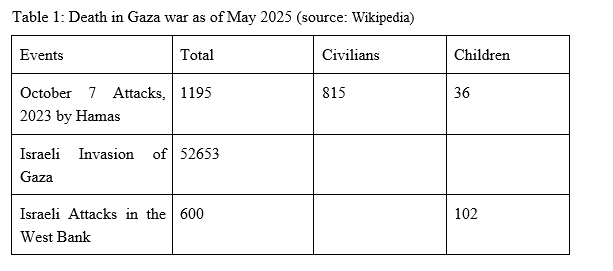
As Table 1 shows, since the Hamas attacked Israel on October 7, 2023, 55,000 people (as of May 7, 2025, 53,253 Palestinians and 1,706 Israelis) have been killed in the Gaza war according to the Gaza Health Ministry. Scholars have estimated that 80% of Palestinians killed are civilians. A study by OHCHR (The Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights) found that 70% of the Palestinians killed in residential buildings or similar housing were children and women.
The majority of casualties have been found in the Gaza Strip. The Gaza Health Ministry’s total casualty count is the number of deaths directly caused by the war.
The 7 October attacks of the Hamas on Israel killed 1,195 people, including 815 civilians. A further 806 Palestinians have been killed in the occupied West Bank (including East Jerusalem).
2. Economic Effects of the Gaza War on Palestine
As Figure 1-1 shows, since October 7, 2023, Palestine’s economy has significantly contracted as a result of continued warfare. As Figure 1-2 shows, economic downturn started from the fourth quarter of 2023. In 2024, Palestine's GDP contracted by 27% compared to the previous year. The decline was driven by a 27% drop in industrial output in the Gaza Strip due to the ongoing Israeli occupation and attack. Especially, economic contractions were recorded in construction (-14.5%), services (-11.0%), financial and insurance activities (-5.3%), information and communication (-3.2%). However, Palestine’s economy began to recover in the fourth quarter of 2024, although it still marked a negative growth.
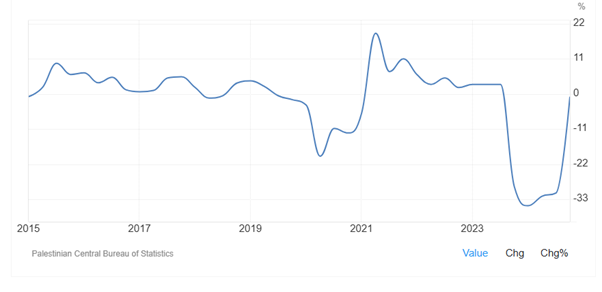
Figure 1-1: Palestine economic growth rate
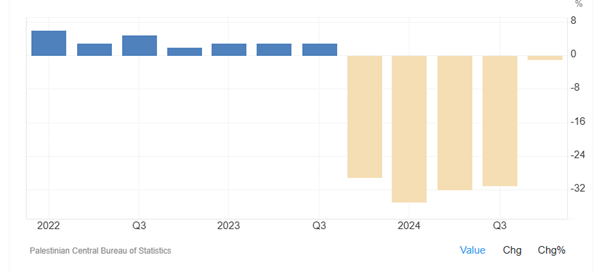
Figure 1-2: Palestine economic growth (quarterly)
As Figure 2 shows, industrial production in Palestine significantly decreased in 2024 as war has continued between Israel and Hamas. Industrial production in Palestine has been low, averaging -7.62 percent from 2012 until 2025. However, it reached a record low of -29.77 percent in June of 2024. Then industrial production in Palestine increased to 2.1 percent in March of 2025 over the same month in the previous year.
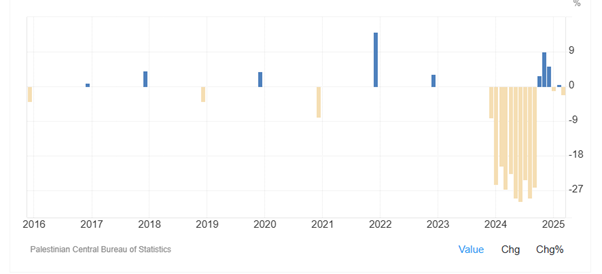
Figure 2: Industrial production in Palestine
As Figure 3 shows, inflation rate in Palestine has significantly increased in 2023 and 2024, reaching all time high of 88.93 percent in November of 2024. High inflation resulted from resource shortages as a result of continued warfare and significant production decline. And then inflation rate in Palestine dropped to 1.88 percent in March and -2.51 percent in February of 2025. Inflation rate in Palestine averaged 4.95 percent from 1998 until 2025.
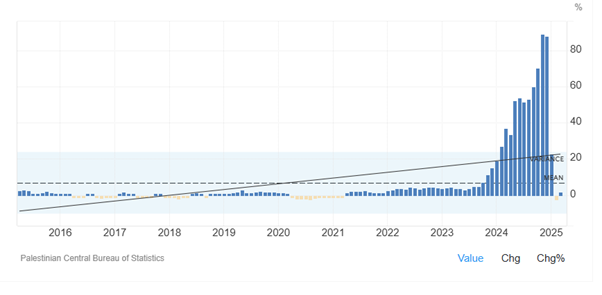
Figure 3: Inflation rate in Palestine
As Figure 4-1 shows, unemployment rate in Palestine significantly increased after October 7, 2023, as economy continued to shrink and industrial production fell. Unemployment rate in Palestine increased to 35.20 percent in the first quarter of 2024 from 24.1 percent in the third quarter of 2023. It then dropped to 31.1 percent in the second quarter of 2024 and 28.8 percent in the fourth quarter of 2024. Unemployment Rate in Palestine has been remarkably high, averaging 24.07 percent from 1995 until 2024, reaching an all-time high of 35.60 percent in the third quarter of 2002 and a record low of 8.80 percent in the second quarter of 2000.
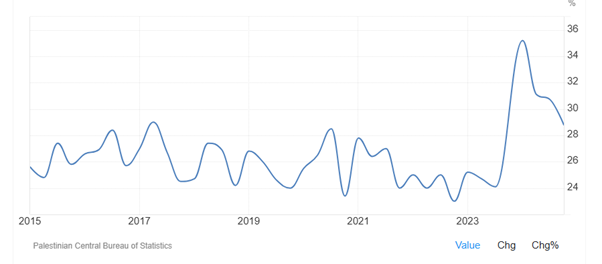
Figure 4-1: Unemployment rate in Palestine
As Figure 4-2 shows, youth unemployment rate in Palestine increased from 38.40 percent in the first quarter of 2023 to 45.70 percent in the first quarter of 2024 and then slightly dropped to 42.60 percent in the third quarter of 2024 and 38.6 percent in the fourth quarter of 2024. Youth unemployment rate in Palestine has been remarkably high, averaging 41.85 percent from 2009 until 2024, reaching an all-time high of 49.90 percent in the second quarter of 2018 and a record low of 32.90 percent in the first quarter of 2011.
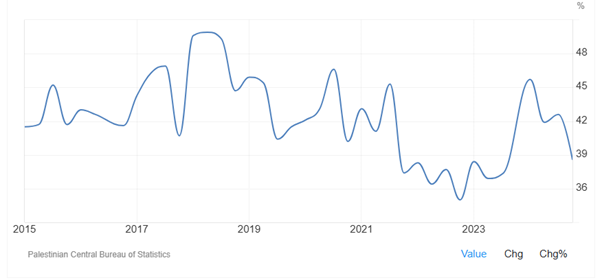
Figure 4-2: Youth unemployment rate in Palestine
As Figure 4-3 shows, full-time employment in Palestine plunged to 628000 persons in the first quarter of 2024 from 1143800 persons in the third quarter of 2023. Then it increased to 705700 persons in the fourth quarter of 2024. Full-time employment in Palestine averaged 888133 persons from 2010 until 2024, reaching an all-time high of 1143800 persons in the third quarter of 2023 and a record low of 67900 persons in the first quarter of 2010.
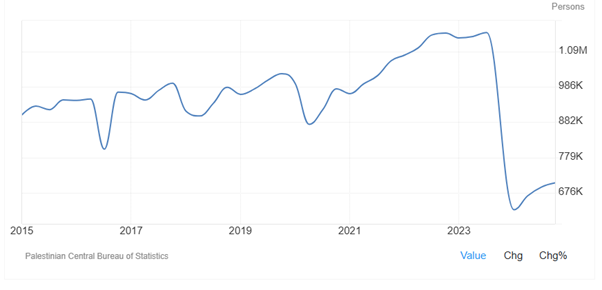
Figure 4-3: Full-time employment in Palestine
Despite the continued warfare in Gaza, as Figure 5 shows, exports in Palestine did not significantly decrease. On the contrary, exports in Palestine increased from 148.3 USD Million in August 2023 to 164.20 USD Million in December of 2024. Exports in Palestine averaged 68.15 USD Million from 2001 until 2025, reaching an all-time high of 164.20 USD Million in December of 2024 and a record low of 15.92 USD Million in April of 2002. Exports in Palestine maintained pre-war level in 2025, recording 140.70 USD Million in January of 2025. Top exports of Palestine in 2023 were scrap iron ($68.6M), tropical fruits ($53.8M), pure olive oil ($10.9M), and building stone ($7.56M).
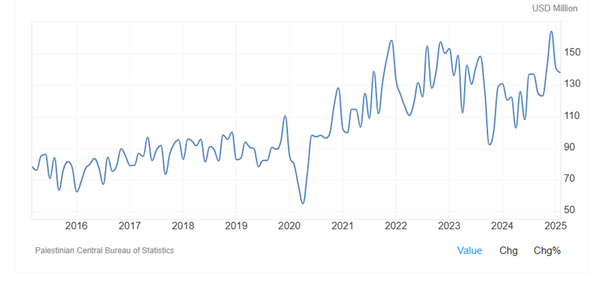
Figure 5: Exports in Palestine
Figure 6 shows, imports in Palestine significantly dropped in 2024 as warfare continued in Gaza. Imports in Palestine decreased to 420.30 USD Million in April 2024 from 747.20 USD Million in August 2023. Imports in Palestine averaged 370.00 USD Million from 2001 until 2025, reaching an all-time high of 750.60 USD Million in November of 2022 and a record low of 82.71 USD Million in April of 2002. According to media reports, there are severe food shortages in Gaza, but there is no information about the imports of food after 2023.
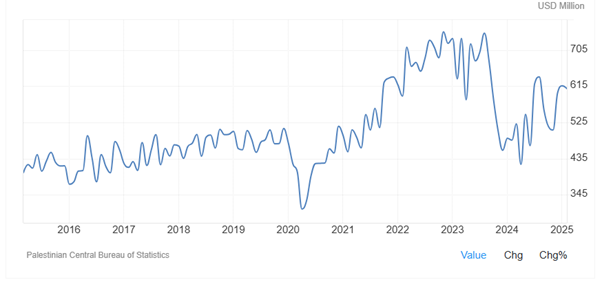
Figure 6: Imports in Palestine
As Figure 7 shows, since October 7, 2023, government spending in Palestine has significantly declined in 2023 and early 2024, hitting a record low of 461.20 USD million in the first quarter of 2024. And then government spending in Palestine increased to 666.70 USD million in the fourth quarter of 2024 from 616.50 USD million in the third quarter of 2024. Government spending in Palestine averaged 797.95 USD million from 2011 until 2024, reaching an all-time high of 974.90 USD million in the fourth quarter of 2016 and a record low of 461.20 USD million in the first quarter of 2024.
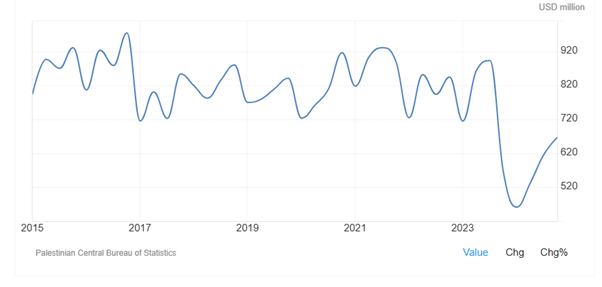
Figure 7: Government spending in Palestine
3. Economic Effects of the Gaza War on Israel
As Figure 8 shows, since October 7, 2023, when the Hamas attacked Israel, government spending in Israel significantly increased as Israel government conducted massive military operations against the Hamas. Government spending in Israel increased from 84100 ILS (Israel new shekel) Million in the third quarter of 2023 to 97973 ILS Million in the fourth quarter of 2023 and 97018 ILS Million in the fourth quarter of 2024. Government Spending in Israel averaged 58676 ILS Million from 1995 until 2024, reaching an all-time high of 97973 ILS Million in the fourth quarter of 2023 and a record low of 39524 ILS Million in the third quarter of 1995.
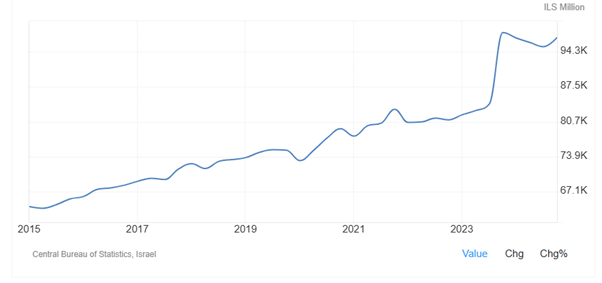
Figure 8: Government spending in Israel
As Figure 9 shows, as Israel government conducted massive military operations against the Hamas, military expenditure in Israel increased to 46505.30 USD Million in 2024 from 27498.50 USD Million in 2023. Military expenditure in Israel averaged 7742.87 USD Million from 1951 until 2024, reaching an all-time high of 46505.30 USD Million in 2024 and a record low of 57.60 USD Million in 1954.
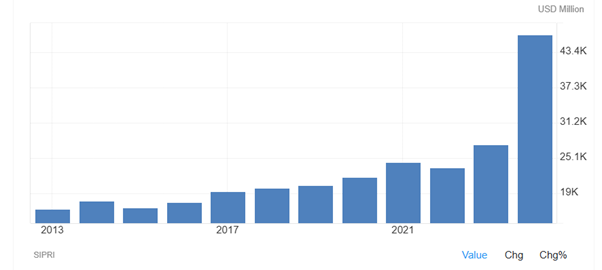
Figure 9: Military expenditure in Israel
As Figure 10 shows, Israel recorded a government budget deficit of -33793.00 ILS Million in December of 2023 from 14100 ILS Million in January 2023 because government spending, in particular military expenditure significantly increased. Government budget value in Israel averaged -3405.71 ILS Million from 2005 until 2025, reaching an all-time high of 22839.00 ILS Million in January of 2025 and a record low of -33793.00 ILS Million in December of 2023.
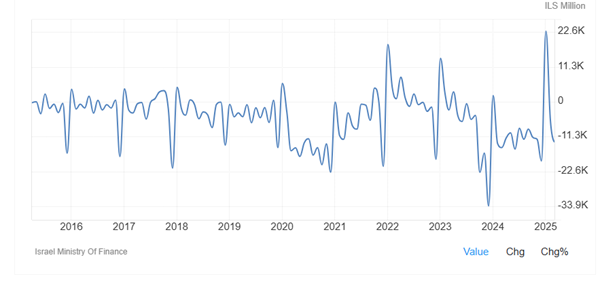
Figure 10: Budget Balance in Israel
As Figure 11-1 & 11-2 show, Israel's economic growth plunged to -4.32 percent in the fourth quarter of 2023 from 3.44% in the third quarter of 2023. Israel experienced consecutive negative growth until the third quarter of 2024 as the ongoing conflict with the Hamas had taken a significant toll on economic activity. This marked the weakest growth since 2020, when the covid-19 pandemic severely impacted the economy. However, the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) in Israel expanded 5.46 percent in the fourth quarter of 2024 over the same quarter of the previous year. GDP annual growth rate in Israel averaged 3.73 percent from 1996 until 2024, reaching an all-time high of 16.27 percent in the second quarter of 2021 and a record low of -8.37 percent in the second quarter of 2020.
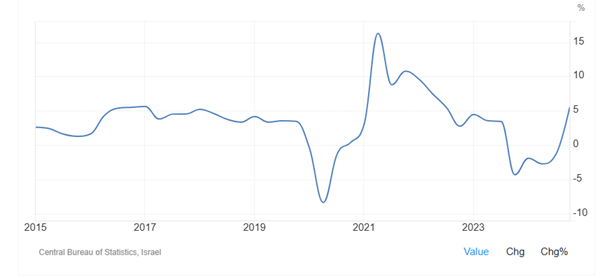
Figure 11-1: Israel's economic growth rate
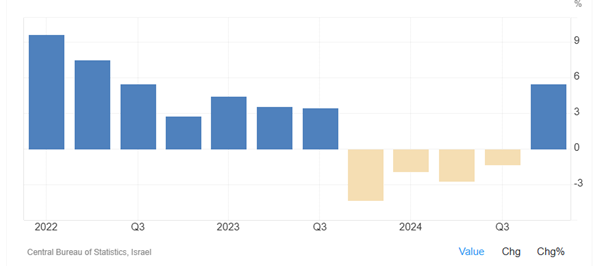
Figure 11-2: Israel's GDP growth (quarterly)
As Figure 12 shows, industrial production in Israel decreased 7.4 percent in December of 2023 and 9.8 percent in March 2024 and then increased 15.9 percent in December 2024. Industrial production in Israel averaged 5.66 percent from 1960 until 2025, reaching an all-time high of 62.70 percent in June of 1968 and a record low of -29.20 percent in June of 1967.
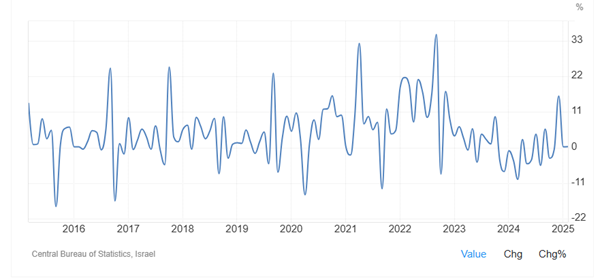
Figure 12: Industrial production in Israel
As Figure 13 shows, unemployment rate in Israel decreased from 4.30 percent in January 2023 to 2.80 percent in November 2023 and 2.60 percent in December 2024. This decline seems to result from the fact that Israeli government called up tens of thousands of reservists to replace conscripts and active-duty soldiers. And then unemployment rate in Israel slightly increased to 2.9% in March 2025. Unemployment rate in Israel averaged 5.89 percent from 1992 until 2025, reaching an all-time high of 11.40 percent in March of 1992 and a record low of 2.60 percent in August & December of 2024.
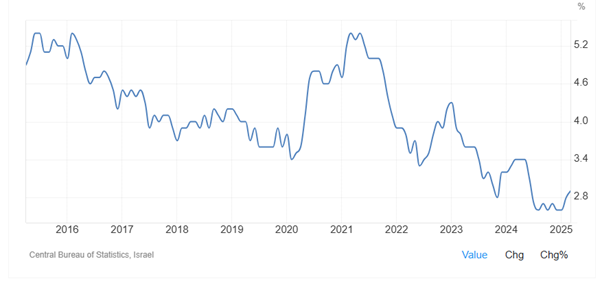
Figure 13: Unemployment Rate in Israel
As Figure 14 shows, the number of unemployed persons in Israel decreased to 119200 in December of 2024 from 184000 in January 2023. Unemployed persons in Israel averaged 192800 from 1991 until 2025, reaching an all-time high of 305400 in September of 2003 and a record low of 119200 in December of 2024.
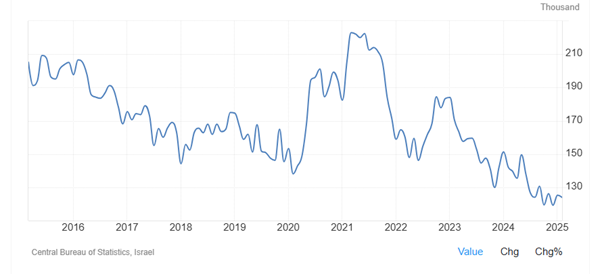
Figure 14: The number of unemployed persons in Israel
As Figure 15 shows, after October 2023, exports in Israel fluctuated between 4470 USD Million in October 2023, 5330 USD Million in March 2024, 4320 USD Million June 2024 and 5250 USD million in December 2024. Exports in Israel averaged 1836.30 USD Million from 1959 until 2025, reaching an all-time high of 6276.70 USD Million in March of 2022 and a record low of 10.80 USD Million in July of 1959.
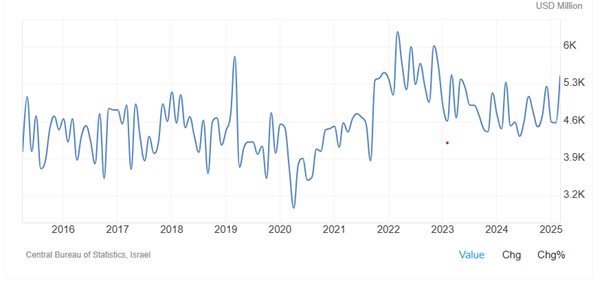
Figure 15: Exports in Israel
As Figure 16 shows, imports in Israel fluctuated between 8090 USD Million in August 2023, 7590 USD Million in December 2023, 7010 USD Million in August 2024, and 8318.70 USD Million in March 2025. Imports in Israel averaged 2500.72 USD Million from 1959 until 2025, reaching an all-time high of 10372.30 USD Million in May of 2022 and a record low of 33.10 USD Million in November of 1959.
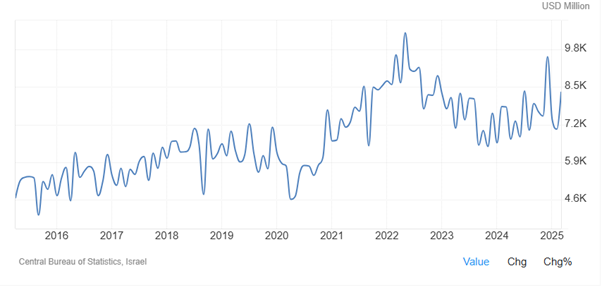
Figure 16: Imports in Israel
As Figure 17 shows, inflation rate in Israel decreased from 5.40 percent in January 2023 to 3.70 percent in October 2023 and 2.50 percent in February 2024. It then increased to 3.60 percent in August 2024 and 3.80 percent in January 2025. Inflation rate in Israel averaged 26.75 percent from 1952 until 2025, reaching an all-time high of 486.20 percent in November of 1984 and a record low of -2.70 percent in March of 2004.
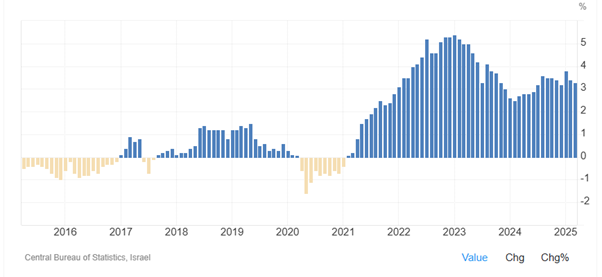
Figure 17: Inflation rate in Israel
As Figure 18 shows, despite on-going warfare in Gaza, gasoline price in Israel did not rise significantly. It increased from 1.82 USD/Liter in September 2023 to 1.98 and 2.14 USD/Liter in January and May 2024, respectively and then dropped to 2.06 and 2.04 USD/Liter in August 2024 and February 2025, respectively. Gasoline prices in Israel averaged 1.78 USD/Liter from 1995 until 2025, reaching an all-time high of 2.30 USD/Liter in June of 2022 and a record low of 0.73 USD/Liter in December of 1995.
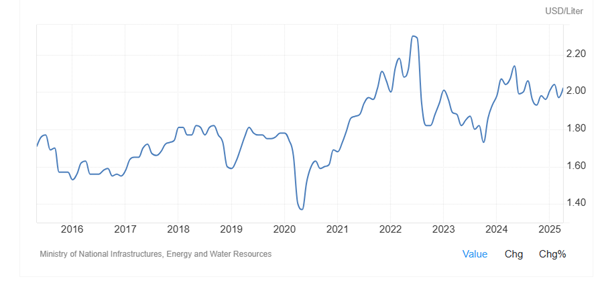
Figure 18: Gasoline price in Israel
IV. Conclusion
The Gaza war has had negative impacts on both Palestine and Israel, but the negative effects were much bigger in Palestine than in Israel. The number of casualties was much higher in Palestine. Especially the war brought down Palestine economy, lowering economic growth, reducing industrial productions, and increasing inflation & unemployment in Palestine. The Israeli economy has also slowed down, and budget deficit increased. However, unemployment went down, and inflation has been stable between 2 and 5 percent. Trade has maintained a pre-war level, although there have been some difficulties.
References
Bilmes, Linda, and Joseph E. Stiglitz. 2006. The Economic Costs of the Iraq War: An Appraisal Three Years After the Beginning of the Conflict. Cambridge, MA: National Bureau of Economic Research.
Chan, Steve. 1985. “The Impact of Defense Spending on Economic Performance: A Survey of Evidence and Problems.” Orbis 29 (2): 403–434.CIA Factbook. 2024. “Ukraine.”
Gilpin, Robert. 1981. War and Change in World Politics. New York: Cambridge University Press.
Glick, Rouven and Alan Taylor. 2010. “Collateral Damage: Trade Disruption and the Economic Impact of War.” The Review of Economics and Statistics 92(1): 102-127.
Iklé, Fred C. 1991. Every War Must End. New York: Columbia University Press.
Kešeljević, Aleksandar, and Rok Spruk. 2023. Estimating the Effects of Syrian Civil War. Empirical Economics.
Koumi, Valley. 2005. “War and Economic Performance.” Journal of Peace Research 42 (1): 67-82.
Liadze, Iana, Corrado Macchiarelli, Paul Mortimer-Lee, and Patricia Sanchez Juanino. 2023. “Economic Costs of the Russia-Ukraine War.” The World Economy 46: 874–886.
Organski, A. F. K., and Jacek Kugler. 1980. The War Ledger. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Russett, Bruce. 1970. What Price Vigilance? The Burdens of National Defense. New Haven: Yale University Press.
First published in :
World & New World Journal

Unlock articles by signing up or logging in.
Become a member for unrestricted reading!