Diplomacy
The World is Changing: Who Will Set the Rules?

Image Source : Stutterstock
Subscribe to our weekly newsletters for free
If you want to subscribe to World & New World Newsletter, please enter
your e-mail
Diplomacy

Image Source : Stutterstock
First Published in: Jun.16,2023
Jul.17, 2023
Pivot to Asia - The Global South is on the march in their attempt to reshape the international system. How will this new order impact the old world?
An increasing number of countries from the Global South, especially in Asia, are pushing to redefine the current global order. Three key trends to watch in this attempt to reshape the international system are the (potential) creation of a new economic order, the expansion of the BRICS grouping, and the transformation of China-Russia relationship after the invasion of Ukraine. In this changing international balance, Europe is losing its influence in the Global South, including in Asia. After centuries of global predominance, Europe’s strongest legacy is its role as a major normative power in global affairs. However, this reputation as a rule-setting power is set to change.
1. A (new) economic order. The debate over a “new Washington Consensus” has gained momentum after US national security advisor Jake Sullivan delivered a speech at the Brookings Institution on April 27th. The final communiqué by the G7 countries which met in Hirosahima on May 19-20 is the result of a similar strategic shift within the group, one that implies a move from economic interdependence to economic security. This shift is coupled with a major change in how the G7 intends to deal with emerging economies, such as their rival China and other partners in Asia that might soon become economic competitors in critical technologies. The G7’s sentiment has moved from promoting globalization and open markets to building industrial capacity in critical sectors, while securing existing and creating new strategic supply chains. Europe’s efforts in this context might not be enough: the investments envisaged so far are too little to reverse Europe’s dependency (often on China) in critical sectors. The EU must focus increasingly on diversifying its supply chains through securing access to rising economies in the Indo-Pacific. Here, joining the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP) could represent an opportunity.
2. BRICS+? The BRICS foreign ministers’ summit in June was yet another steppingstone toward enlargement. The countries that expressed a significant interest in joining the grouping are Iran, Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, Cuba, Democratic Republic of Congo, Comoros, Gabon, and Kazakhstan: all these countries sent their representatives to Cape Town. Egypt, Argentina, Bangladesh, Guinea-Bissau and Indonesia participated virtually. While the membership process might be a long one, the group’s upcoming expansion highlights the Global South’s political will to rise its voice, with a plethora of actors eager and able to leverage the new competition between powers which is shaping up after the Ukraine war. In this framework, Asian countries such as China and India are competing with one another to lead the BRICS.
3. China and the Stans. On May 19, Xi Jinping met in Xi’an with the (leaders of) the five Central Asian “Stan”-countries (Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, and Turkmenistan). Russia, the region’s traditional kingmaker, was noticeably absent. The meeting kickstarted – for the first time offline – a summit named C+5 and highlighted Beijing’s belief that it can now make deals within the region without Moscow’s supervision. China’s newfound independence in Central Asia and Moscow’s growing dependence on Beijing after the war in Ukraine provides new insights the on China-Russia relationship: although the two countries are united by their common desire to contest the US-led world order, the Sino-Russian relation seems increasingly tilted in China’s favor. This instable relationship could result in a stronger Chinese presence in Central Asia.
4. Loss of strategic centrality. Europe does not only risk becoming increasingly peripheral in world affairs, but also losing its bargaining power with the emerging Indo-Pacific economies. On the one hand, the EU needs to diversify its supply chains away from China and likely towards the ASEAN; on the other, the Global South – and by default its Asian members – is more aware of the current strategic window of opportunity to redesign the global balance of power.
We are witnessing rapid changes in the international arena. In the coming months there will be increasing requests to review global norms. Therefore, the leading event will be the upcoming BRICS Summit in August: the meeting will probably certify the process to accept new members. Among the countries that are voicing their desire to reset the rules, some are considered by the West (mainly) as rivals, such as China, and as partners, like India. Therefore, Washington and Brussels cannot simply accept or dismiss their requests. Asia is claiming its century: the integration of this claim for a renewed global order into the current world order has just started. Its most important implications will be on the economic side, namely the redistribution of industrial capacity and trade relation in the context of de-risking from China.

Spotlight: G7
The G7 Hiroshima Summit has sent some clear messages to the rest of the world. The decision to invite President Zelensky to the gathering was a move meant to reinforce the unity of the members regarding the Ukraine invasion in the face of Russia — and China, too. The West has criticized China’s 12-point position paper on the Ukraine war, since it does not call for Russia to abandon occupied territories. The G7 countries have also announced a strengthening of the sanctions, seeking to curb products that could be used by the Russian military. The other important takeaway of the G7 is the joint statement directed at China, which includes a strong criticism of Beijing’s “economic coercion” and invites the PRC to play according to international rules. The G7 have also reiterated their position on divisive topics such as security in the Indo-Pacific and Taiwan, retreating their commitment to preserve peace and stability in the region. Despite the joint statement and the declarations by the leaders on the challenges posed by China, the G7’s stance on Beijing is still a balancing act. While concerned about being overly vulnerable with China, G7 economies and their industrial base remain strongly interconnected with the Asian country and despite calls for “de-risking”, such as cutting China out from some sectors like raw materials, it is impossible at the time.
The implications of China’s activism among the BRICS countries
The next BRICS Summit will take place at a critical juncture for the Global South. Russia is still at war, Brazil has a new administration eager to flex its muscles globally, and China has reached unprecedented influence across the developing world. Since they are all connected by the same desire of multipolarity away from US and Western hegemony, it is likely that the BRICS will try to offer a roadmap towards a new international order. This roadmap, however, is far from consensual: will Russia embrace the peace dialogues offered by Brazil or African nations – and what role will China play in brokering any such proposal? Will China and the other BRICS be able to cooperate economically to promote development worldwide? Are the BRICS ready for its first enlargement, and who is most likely to join in the coming years? This arrangement will require some mutual concessions and the outcome will help shape the future world order.
Guilherme Casarões, Fundação Getulio Vargas
The push to strengthen and even expand the BRICS, especially by China, should be viewed more broadly through the lens of a pragmatic Chinese foreign policy. It has not only sought to strengthen ties within BRICS but with other regions and countries who are instrumental for its trade and infrastructure connectivity imperatives. This happens against the backdrop of a shift towards a multipolar world order with China as a rising power and rising geo-political tensions. Given that this bloc advocates for issues that are relevant to the Global South (global governance reform, support for a rules-based international order and multilateralism in times when countries retreat to unilateral measures), it is no surprise that other countries in the South wish to join. Regarding this summit, I see no major implications for the bloc, the core business of the BRICS will continue with South Africa advancing its five priority areas. However, we can anticipate a discussion on its formal expansion. Trading with local currency seems to have found new impetus following the sanctions placed on Russia. All this notwithstanding, it is important to note that the ‘de-dollarisation’ in trade debate is not a new concept for BRICS and its less about challenging the dollar but strengthening other currencies against external economic shocks. The real test is for the host country depending on whether President Putin attends the heads of state summit in August, given Pretoria’s obligations under the Rome Statute and domestic law.
Luanda Mpungose, South African Institute of International Affairs (SAIIA)
China’s push for a stronger BRICS on the global stage is advancing along a number of trajectories. Firstly, there is the BRICS expansion as well as the BRICS+ format that are likely to bring the majority of the Global South into BRICS-related platforms of economic cooperation. The implementation of the BRICS+ format may serve as a precursor for liberalizing trade across the Global South and exploiting the potential for boosting South-South trade and investment ties. The expansion in the membership of the Shanghai-based New Development Bank as well as the creation of its regional centers will increase the scope for connectivity projects across the developing world. There is also the greater use of national currencies (most notably the yuan) via de-dollarization as well as the R5 BRICS common currency project that if launched would mark a key transformation of the global financial system.
Yaroslav Lissovolik, BRICS+ Analytics
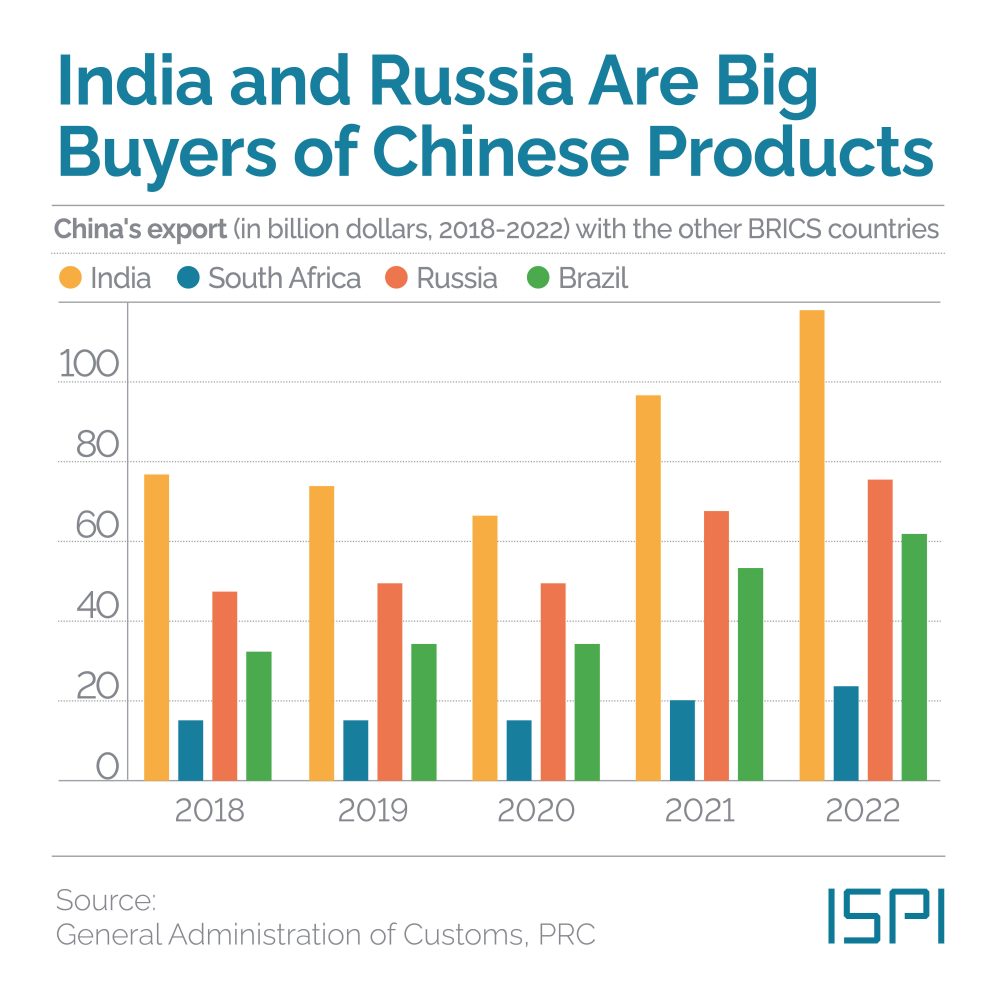
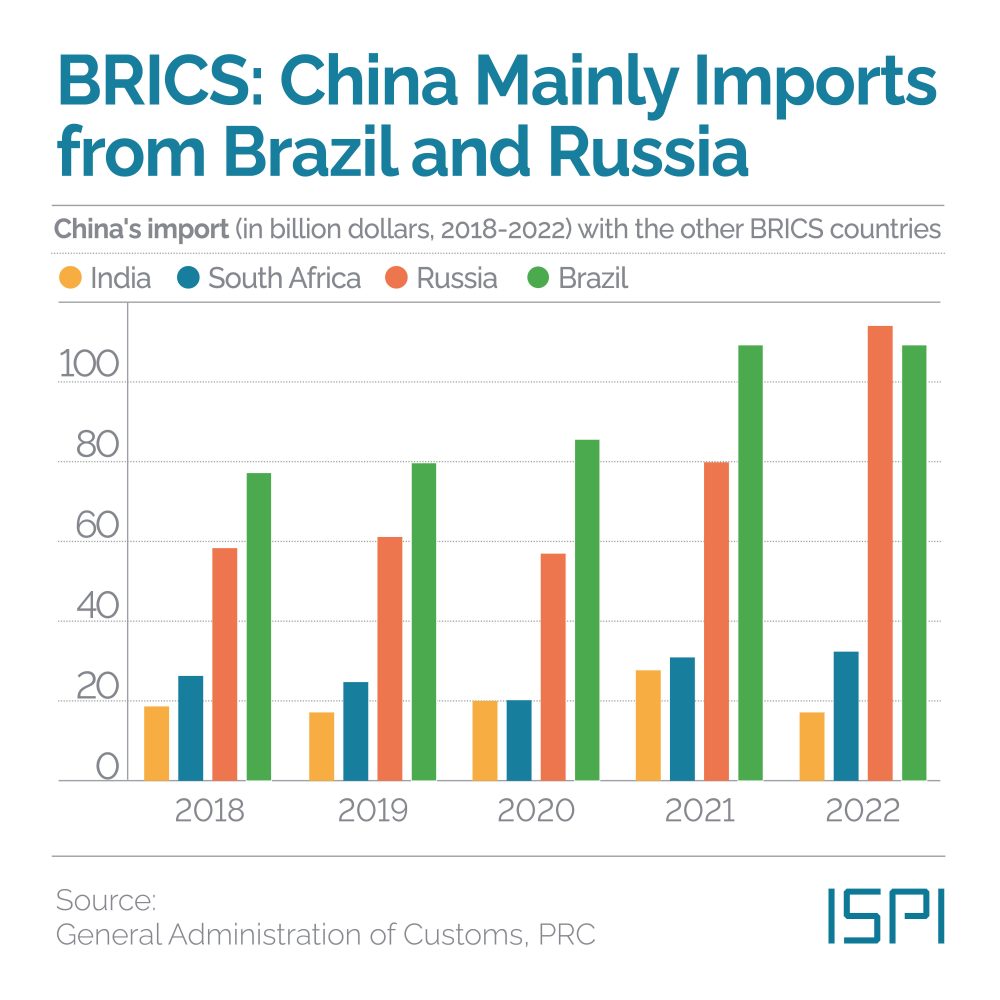
Thailand is ready to Move Forward
The May elections in Thailand resulted in a clear victory for the opposition parties. Led by Pita Limjaroenrat, Move Forward has won 152 seats, becoming the most voted party in the elections. This party is the heir to Future Forward, which was dissolved by the military government in February 2020, and was born out of the 2020-2021 protests against the army and the monarchy. The second party in the country is the historic Thai opposition party led by the Shinawatra family, the Pheu Thai. However, while the population has expressed its preference, there is no guarantee yet that Move Forward, and the opposition, will govern. Indeed, to be elected Prime Minister, and form a government, Pita will need to win the majority in the bicameral parliament made up of the elected 500 seats in House of Representatives and the 250 seats of the Senate – whose members are handpicked by the military. The Move Forward coalition with Pheu Thai and the other opposition parties so far can count on little more than 310 votes, a long shot from the majority needed to govern. The opposition must garner support among the senators – which generally have little interest in going against the military that put them in power – or among the parties that have yet to declare their allegiance.
Cambodia: Hun Sen is getting rid of the competition ahead of July elections
On the 14 of May, Cambodia’s opposition party – the Candlelight Party – has been disqualified from running in the upcoming July elections by the country’s election commission. The party has allegedly failed to submit the necessary documentation to participate in the electoral race. With the exclusion of the Candlelight Party from the coming elections, the only possible competitor to the ruling Cambodian People’s party (CPP) of PM Hun Sen – who has been in power for 38 years – has been eliminated. This is not the first time that the main opposition party has been cut out of the electoral race. For instance, in the 2017 the Cambodian court, which is heavily colluded with the CPP, dissolved the Cambodian National Rescue Party (CNRP) before the 2018 general elections – a party that was given new life when its members created the Candlelight Party. However, the members of the opposition continue to be persecuted by Hun Sen’s forces with many political exponents arrested on charges of treason, assaulted, or forced to leave the country. With the opposition forces largely depleted and the main party banned from running for elections, Hun Sen is likely guaranteed another term.
The United States seeks to expand influence in the Indo-Pacific
Washington took advantage of two key international events to strengthen its strategic position in the region. During the Quad Leaders’ Summit, which took place on the sidelines of the G7 in Hiroshima, President Biden, Australia’s PM Albanese, PM Kishida of Japan and PM Modi of India stressed their unity and stated their plans to invest in digital infrastructure in the region. Throughout the meeting they did not mention China directly in their statements, but their references to the country were clear. The Quad expressed concern over the militarization of the region and the use of both economic and military coercion to alter the status quo – a clear reference to Chinese activity in the South China Sea. Another important step for the US to consolidate its position in the region is the announcement of the Supply Chain Agreement under the framework of the Indo-Pacific Economic Framework for Prosperity (IPEF). The agreement includes the 14 IPEF partner countries, namely Australia, Brunei, Fiji, India, Indonesia, Japan, Malaysia, New Zealand, the Philippines, Singapore, South Korea, Thailand, the US, and Vietnam. A year following the launch of the IPEF, this agreement is the first practical measure undertaken by the group. The group did not announce any official trade commitments, there is expectation among partners for increased cooperation and monitoring of supply chains fragility. The concrete development is still unclear, but the agreement signals the need for Indo-Pacific countries to avoid supply chain disruption and to minimize their dependence on the region’s main economic player, China.
Semiconductors: China fires back
China has gone on the offensive in competition over the semiconductor sector. The Cyberspace Administration of China (CAC) has stated that products by Micron, the US largest memory chip maker, are a “security risk for the information infrastructure supply chain” barring infrastructure operators from buying them. While additional information has yet to be revealed, some negative impacts are expected for Micron even if China and Hong Kong accounted for only 16% of the revenue of the company in 2022. The measure is a retaliation to America’s effort to cut China out from the semiconductor sector and slow the development of its industrial base. Since October 2022, the Biden Administration has imposed strict controls over chips export, followed by the Netherlands and Japan, preventing China from accessing and producing more advanced semiconductors. China’s declaration comes also after the leaders of the G7 grouping released a statement criticizing the country’s economic coercion tactic. After the move from Beijing, Micron fears that their products will be replaced by South Korean competitors, Samsung and SK Hynix, on the Chinese market. In the rising technological row between the US and China, there is also fear that Beijing might choose to put some export controls over other sensitive technologies, such as solar panels – where China dominates the whole supply chain.
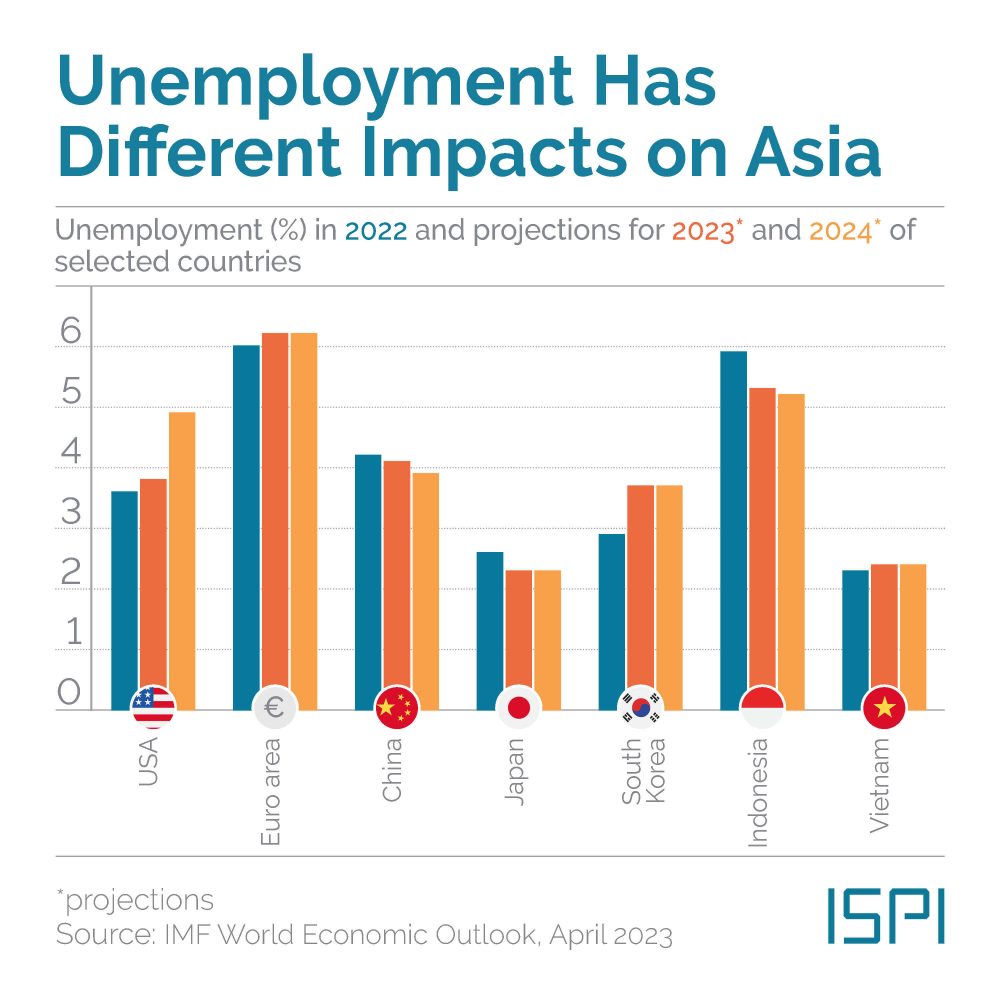
TREND: Despite rate hikes, Asian unemployment is faring well (but not for everyone)
In the current context of high inflation and high rates, unemployment has turned out to be one of the main socio-political issues of Asia. With skyrocketing prices hurting businesses and consumers, many central banks in the West have adopted more hawkish monetary policies during the last year. Yet, the soaring cost of money has forced many businesses into a tight spot with concerning consequences on the employment level. Some countries though – like Japan, China, and Indonesia – have made the unorthodox choice to not significantly raise rates during the last year, while others – like South Korea and India – have adopted similar policies to those of the FED and the ECB. However, the results vary. In Japan the unemployment rate has been quite steady at around 2.6% for some time now, but in China the range (5.2-5.7%) was wider, especially due to the uneven nature of the post-Covid economic recovery. Yet, as the economy is slowly returning to normal, Beijing’s unemployment rate is gradually decreasing. Meanwhile Korea has consolidated a positive trend, with the last available figure at 2.5%, but the reforms of the labor market proposed by President Yoon Suk-yeol may cause some issues. The critical indicator though will be youth unemployment. Employment in aging societies, like those of East Asia, will increasingly become a core issue to maintain the viability of existing social welfare programs. So far China has a staggering 20.8% unemployment rate in the 16-24 years old age group which is particularly concerning, as it is the 7.2% recorded in South Korea. Japan is faring quite well but unemployment in the 25-34 years old age bracket has risen since the beginning of the year from 3% to 4%.
First published in :

Before joining ISPI Filippo Fasulo served as the Director of the Italy-China Foundation’s Centre on Business Research (CeSIF). In 2014, he earned a Ph.D. in Politics and Istitutions from the Catholic University of Milan with a dissertation on the concept of power in China’s politics that was awarded the Cesare Bonacossa Prize by the University of Pavia. In 2012, he received a MSc in China in Comparative Perspectives at the London School of Economics and Political Science. Since 2011, he has been lecturing on China-related topics at the Catholic University of Milan. He is also Academic Secretary for the course in Far Eastern Studies at the Accademia Ambrosiana in Milan. From 2014 to 2016, he has been a board member of the Institute for Public Administration Science (ISAP – Istituto per la scienza dell’amministrazione pubblica).
His research focus is on Asia with particular interest in China at both the domestic and international levels.
Unlock articles by signing up or logging in.
Become a member for unrestricted reading!