Defense & Security
Development of South Korea’s Submarines and Future Prospects

Image Source : Shutterstock
Subscribe to our weekly newsletters for free
If you want to subscribe to World & New World Newsletter, please enter
your e-mail
Defense & Security

Image Source : Shutterstock
First Published in: Dec.29,2025
Dec.19, 2025
In the 21st century, the maritime security environment in Northeast Asia is changing more rapidly than ever, with information superiority and covert operational capabilities at sea emerging as core components of national security. At the heart of this shift lies the submarine force, which possesses both strategic deterrence and surveillance/reconnaissance capabilities. As China, Japan, and North Korea advance their submarine technology, South Korea finds itself in a situation demanding independent maritime strategic assets to counter these developments.
The Republic of Korea Navy (ROKN) submarine force, which initially relied on foreign technology, has now grown into a submarine technology powerhouse capable of indigenous design and construction. The introduction of the KSS-III Dosan Ahn Changho-class submarine, in particular, has equipped South Korea with SLBM operational capability and advanced AIP (Air-Independent Propulsion) and electric propulsion technology, establishing a strategic-level submarine force.
This technological advancement not only strengthens national defense but also elevates the international status of the Korean defense industry, leading to enhanced export competitiveness. Concurrently, amidst the military expansion of surrounding countries, the need for nuclear-powered submarines (SSNs)—which offer far greater strategic survivability and sustained operational capability—is being raised in South Korea. Despite the high cost, the SSN is a strategic asset that provides overwhelming stealth, range, and operational endurance in the long run.
This article will comprehensively examine the importance and technical characteristics of submarines, followed by an analysis of South Korea's submarine force development, its international standing, and comparisons with neighboring countries. Furthermore, it will explore the implications of the nuclear submarine acquisition debate for South Korea's future security strategy.
1. The Importance of Submarines
The submarine is an extremely important weapon system in the defense industry from strategic, technological, and economic perspectives.
1) Strategic Deterrence and Control: Submarines act as a strategic deterrent to covertly check the enemy's maritime activities and protect a nation's sea lines of communication and security. The strategic deterrence of a submarine is based on its 'stealth' and 'lethality'.
- Stealth (Psychological Pressure): A submarine can move and be deployed secretly underwater without being exposed to the enemy, placing psychological pressure on the enemy's maritime operations and strategic weapon deployment during peacetime. Because it is extremely difficult for an attacking enemy to predict or neutralize the submarine's location, the enemy always harbors the fear of a potential strike.
- Lethality (Retaliatory Capability): If the enemy attempts an actual invasion or provocation, the submarine can conduct a sudden and precise strike with high-power weapons like torpedoes or missiles. Specifically, a Strategic Nuclear Submarine (SSBN), equipped with strategic weapons like the SLBM (Submarine-Launched Ballistic Missile), provides a 'second-strike capability' to retaliate against the opponent's core targets at any time.
- Maximizing Deterrence: The mere existence of strategic submarines maximizes the 'psychological deterrent effect', making the enemy's political and military leaders hesitate to initiate an attack. Due to the nature of submarines being covertly deployed anywhere in the ocean, the enemy is constantly exposed to threats, making it difficult to attempt military provocations recklessly. In essence, the core principle of strategic deterrence is the creation of a 'deterrence effect through uncertainty', combining the submarine's covert and unpredictable operational methods, its powerful striking capabilities, and the psychological fear it instills.
2) Enhancing National Defense and Economic Effects: The development of advanced submarines is central to a nation's naval power. It enhances defense self-reliance by securing indigenous design and construction technologies and promises enormous economic benefits through overseas exports. - Asymmetric Warfare Power: With its stealth and lethality, the submarine wields the most potent deterrent force and asymmetric warfare effect among all maritime forces. When surface fleet power is relatively insufficient, an advanced submarine can effectively check large enemy vessels or aircraft carriers and deny access to maritime domains. - Advanced Mission Capabilities: Advanced submarines are deployed for various missions, including long-duration submerged operations, strategic surprise, and special warfare support, utilizing cutting-edge technologies like next-generation guided missiles and sophisticated sonar/navigation systems that make detection and tracking difficult. - Increased Defense Industry Competitiveness: When advanced submarines are developed and operated with indigenous technology, it not only boosts the nation's defense industry capacity and technological self-reliance but also significantly increases related industry development and economic effects. In short, the advanced submarine is the qualitative and strategic linchpin of national naval power, encompassing defense, offense, intelligence deterrence, and the securing of cutting-edge technology. 3) Driving Advancement in Overall Defense Technology: The development of highly sophisticated weapon systems (e.g., SLBMs, advanced sonar, low-noise technology, etc.) also promotes the advancement of overall cutting-edge defense technologies. - SLBM Development: Developing SLBMs is not just missile technology; it complexly requires materials engineering to withstand the extreme pressure of the underwater launch environment, precise guidance systems, and miniaturized propulsion technology. The technology secured during this process naturally transfers to other fields, such as space launch vehicles and precision strike weapons. - Advanced Sonar Technology: The process of increasing the precision of underwater acoustic detection advances capabilities in signal processing, AI-based pattern recognition, and big data analysis. Such technology can also be utilized in civilian sectors, including marine resource exploration, underwater communication, and seismic detection systems. - Low-Noise Technology Development: The ripple effect of low-noise technology development is even greater. Vibration reduction in propulsion systems, special hull coatings, and hydrodynamic optimal design enhance the competitiveness of the shipbuilding industry as a whole. Propeller noise reduction technology, in particular, contributes to improving the fuel efficiency of commercial vessels and protecting the marine ecosystem. Furthermore, the process of developing these advanced technologies fosters high-level research personnel, strengthens industry-academia-research cooperation networks, and promotes the domestic production of materials, components, and equipment. Consequently, the single weapon system of a submarine has the effect of elevating the nation's overall scientific and technological capabilities to the next level. 4) High Competitiveness and International Credibility: The limited number of nations capable of manufacturing submarines ensures high competitiveness and international credibility in the global defense market. Currently, only about 12 countries are capable of independently designing and building submarines: the U.S., Russia, China, the U.K., France, Germany, Sweden, Italy, Spain, India, Japan, and South Korea. This technical rarity offers several strategic advantages. - Favorable Negotiation Power: Due to the high barrier to entry, a limited supplier market is formed, securing favorable negotiation power during exports. - Proof of Overall Defense Technology: Submarine construction capability serves as proof of comprehensive defense technology, raising the credibility of other weapon systems. South Korea, in particular, has demonstrated strengths in technology transfer and localization by successfully achieving domestic production after introducing German technology. This establishes South Korea as an attractive partner for middle-power countries that desire advanced submarines but find self-development difficult. The interest shown by nations like Indonesia and the Philippines in South Korean submarines is within this context. - Sustainable Economic Effects and Strategic Ties: Submarine projects lead to long-term follow-up businesses, including maintenance, upgrades, and crew training, ensuring sustained economic effects and strengthening strategic ties between nations. As such, the submarine is considered a core capability of the defense industry in terms of national security, industrial competitiveness, technological innovation, and economic benefits.
The technical characteristics of submarines can be broadly divided into three key domains: stealth and survivability, propulsion and power systems, and weapons and combat systems.
2.1. Stealth & SurvivabilityThis is the technology area most directly tied to the fundamental purpose of submarines. In underwater environments, radar (radio-wave detection) cannot be used, so detection relies on sonar (sound-wave detection). While radar can detect surface targets from up to 500 km, sonar detection of a quiet, stealthy submarine is typically limited to around 30 km. - Acoustic Quieting Technology is essential for avoiding enemy sonar detection. Submarine noise reduction involves suppressing mechanical noise (machinery vibration), flow noise, structural vibration, and propeller noise through an integrated set of technologies. This is not just a matter of equipment but a comprehensive quieting process that spans the entire lifecycle of a submarine—from design and manufacturing to operation and maintenance. - Non-Acoustic Stealth Technology minimizes physical signatures other than sound—such as magnetic fields, heat/infrared emissions, radar/optical reflections, and surface disturbances—to prevent detection by non-acoustic sensors.

This system is key to determining a submarine's range and submerged operational endurance. It is broadly divided into conventional (non-nuclear) and nuclear propulsion.
1) Conventional Submarines (Diesel-Electric) -Diesel-Electric System: This is the traditional method where a diesel engine powers a generator to charge batteries, and an electric motor provides propulsion. It is favored for its cost-effectiveness and quietness, making it the standard for small and medium-sized submarines. However, because the diesel engine requires oxygen from the atmosphere, the submarine must periodically surface or use a snorkel, which severely limits continuous submerged endurance (to a maximum of about 3 days). Submarines equipped with the latest Lithium-ion batteries can extend this submerged time up to 7 days. - Air-Independent Propulsion (AIP): An innovative technology that produces power underwater without relying on an external oxygen supply. The main types include the Fuel Cell (PEMFC), Stirling Engine, and Closed-Cycle Diesel. AIP is used in conjunction with the diesel-electric system and significantly extends submerged endurance, often up to 3 weeks. Because it is cheaper than nuclear power while offering high strategic value, many nations have adopted it. - Hybrid Propulsion System (Cutting-Edge Technology): The integrated operation of three systems—the diesel generator, Fuel Cell AIP (Air-Independent Propulsion), and Lithium-ion batteries—allows for continuous submerged operation for up to 4 weeks. South Korea's Dosan Ahn Changho-class (KSS-III) utilizes the integrated operation of these three systems: a diesel generator, Fuel Cell AIP, and Lithium-ion batteries. Excluding nuclear power, the current cutting-edge technology is considered to be the Fuel Cell AIP + Lithium-ion battery hybrid system. Each propulsion system is selected based on operational range, mission sustainability, cost-effectiveness, and technological sophistication. South Korea is actively pursuing the development of next-generation submarines that combine both AIP and Lithium-ion battery technologies. However, the maximum continuous submerged endurance (up to 4 weeks) is only achievable when operating at low speeds (5–10 knots, or approx. 9–18 km/h). When operating at maximum speed (around 20 knots, or approx. 37 km/h), the battery consumption is extremely high, causing the submerged time to sharply decrease: - Older Submarines: Can sustain maximum speed for only 1–2 hours. - Li-ion/AIP Submarines: Can sustain maximum speed for 3–6 hours. After high-speed maneuvering, the submarine requires snorkeling for recharging, which significantly increases the risk of detection by the enemy.

Figure 2. Dosan Ahn Chang-ho class (Jangbogo-III) lithium battery system (Source: Hanwha Ocean)

Figure 3. Dosan Ahn Chang-ho class (Jangbogo-III) fuel cell AIP system (Source: Hanwha Ocean)
2) Nuclear-Powered Submarines (SSN/SSBN)
Nuclear-powered submarines use nuclear fission reactors to generate steam, which drives turbines and provides virtually unlimited propulsion. Because they do not require refueling for months, their submerged endurance and operational range are effectively unlimited, enabling them to operate anywhere in the world. Only a small group of states—including the United States, Russia, China, the United Kingdom, France, and India—possess such submarines. Nuclear propulsion is used in both strategic ballistic missile submarines (SSBN: nuclear-powered submarines equipped with ballistic missiles carrying nuclear warheads) and nuclear-powered attack submarines (SSN: fast attack submarines powered by nuclear reactors). However, nuclear submarines are extremely expensive to build and operate, require large hull sizes (especially SSBNs), and demand sophisticated reactor noise-management technologies. Compared to conventional submarines, nuclear submarines can operate at much higher sustained speeds for long periods. Their average top speed is typically 25–30 knots (46–55 km/h), while specialized Soviet/Russian designs such as the Alfa-class have demonstrated speeds exceeding 40 knots in trials. This makes nuclear submarines more than twice as fast as most conventional submarines, with the added advantage of being able to maintain high speeds for extended durations without limitations.
2.3. Weaponry & Combat SystemsThis category encompasses the submarine’s offensive capabilities and intelligence-gathering functions. Submarine weapons and combat platforms can be divided into four major types:
2.3.1. Launch WeaponsLaunch weapons are categorized as follows: - Torpedoes: Underwater weapons fired from a submarine’s horizontal launch tubes, used to attack underwater targets such as other submarines, surface ships, and mines. - Missiles: This includes anti-ship missiles (ASM) and sea-launched cruise missiles (SLCM) designed to strike surface or land targets. Some missiles are launched through Vertical Launch Systems (VLS). - Nuclear Weapons: The primary example is the SLBM (Sea-Launched Ballistic Missile), equipped with a nuclear warhead. These form the core of a nation’s strategic nuclear deterrence capability.
Table 1. Types of Launch Weapons
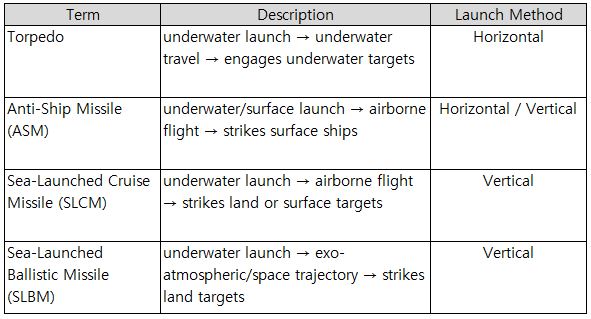
Table 2. Ballistic/Guided Missiles
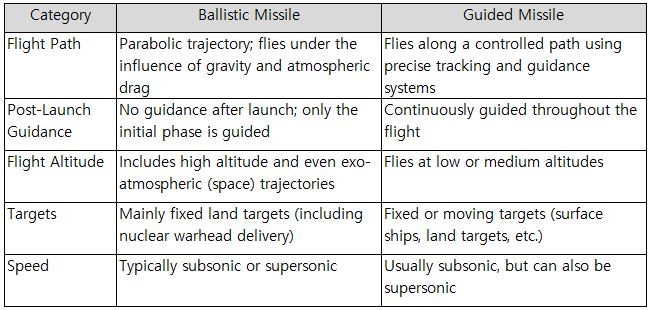
Table 3. Submarine-Launched Weapon Systems
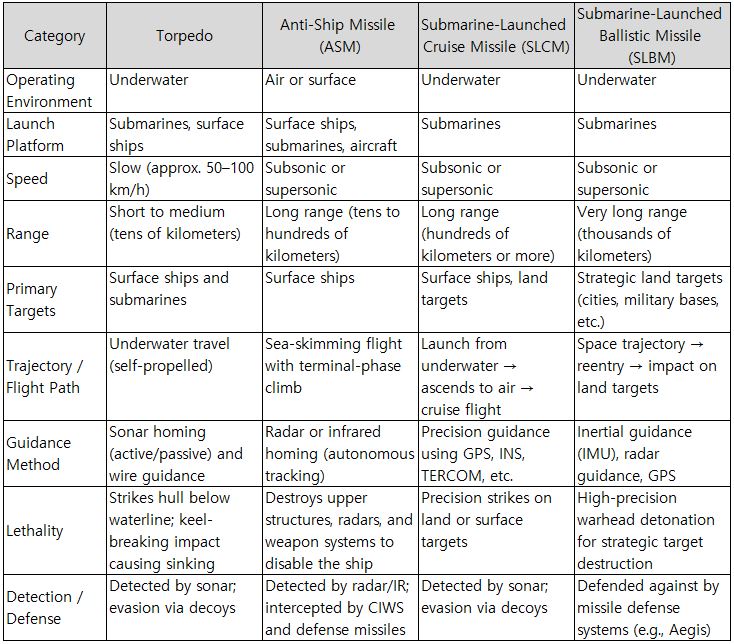

Figure 4. Weapon systems of the Dosan Ahn Chang-ho–class (Jangbogo-III): Torpedoes/Mines (Horizontal Launch) and Missiles (Vertical Launch) (Source: Hanwha Ocean)

Figure 5. Vertical Launch System of the Dosan Ahn Chang-ho–class (Jangbogo-III) (Source: Hanwha Ocean)
2.3.2. Underwater Drones / Unmanned Underwater Vehicles (UUV/AUV)
Unmanned Underwater Vehicles (UUVs) and Autonomous Underwater Vehicles (AUVs) are unmanned underwater platforms deployed from submarines. They can perform missions such as intelligence collection, reconnaissance, mine detection, and even underwater attacks. In the latest technology trends, AUVs serve as important auxiliary assets for submarines, used for tasks such as detecting specific targets, locating and neutralizing naval mines, and tracking enemy submarines.

A submarine’s electronic warfare (EW) systems defend against enemy detection through electronic surveillance countermeasures. By transmitting deceptive or disruptive signals, these systems help conceal the submarine’s presence and significantly enhance survivability. Capabilities such as electronic deception, electronic jamming, and counter sonar/radar measures enable the submarine to evade enemy tracking and maintain strategic advantage. In addition, electronic attack (EA) capabilities can inflict direct damage on enemy military assets by disrupting or degrading their electronic systems.
2.3.4. Naval MinesNaval mines are explosive devices used by submarines to block enemy sea routes or hinder the approach of surface vessels. Submarines can deploy underwater mines or launch them from dedicated systems, allowing them to disrupt maritime traffic and defend against the movement of hostile fleets through area denial tactics.
Submarine capabilities are not only crucial for military security but also represent a high-value industry that generates substantial direct and indirect economic effects for the nation.
3.1. Direct Industrial Impact (Manufacturing and Employment)Submarine construction is a highly technology-intensive, large-scale project, creating significant economic effects for the shipbuilding and defense industries: • Development of high-value shipbuilding: Submarines require extremely high precision and complex construction within much tighter spaces than commercial ships. The construction process itself represents the pinnacle of shipbuilding technology, directly enhancing the competitiveness and qualitative growth of the shipbuilding industry. • Job creation: Building a single submarine involves thousands of workers over several years, from design and component production to final assembly and sea trials, creating a large number of highly skilled technical jobs. • Activation of component and partner industries: Submarines consist of numerous precision components (sonar systems, propulsion units, special alloys, batteries, etc.), which stimulates supply chains largely composed of small and medium-sized defense companies and elevates technological capabilities across the sector.
3.2. Indirect Economic Impact (Security and Exports)The existence of a submarine fleet generates invisible economic benefits and opportunities: • Reduction of national security costs: Submarines are one of the most effective tools of asymmetric deterrence — a military strategy where a country at a disadvantage in conventional forces or numbers neutralizes an adversary’s attack intentions and deters war through unique and unpredictable means. Maintaining submarine capabilities helps prevent potential economic damages in crises (trade disruptions, destruction of industrial facilities) and raises the cost of potential aggression, effectively reducing national security expenditures. • Protection of sea lines of communication (SLOCs): As a highly trade-dependent nation, Korea relies critically on maritime routes. Submarines deter hostile naval forces threatening these routes during crises and protect major trade arteries, ensuring the continuity of economic activity. • Opportunities for defense exports (K-Defense): o Demonstrating Korea’s ability to independently design, build, and operate submarines (Dosan Ahn Changho-class / Jangbogo-III KSS-III) establishes technological credibility in global markets. o This capability generates high-value defense export opportunities, not only for the submarines themselves but also for related components, maintenance, and training systems (Korea has already exported submarines to Southeast Asia). In conclusion, submarine capabilities serve as a form of national security insurance while fostering domestic advanced technology industries and opening export markets, providing significant economic value as a future growth engine.
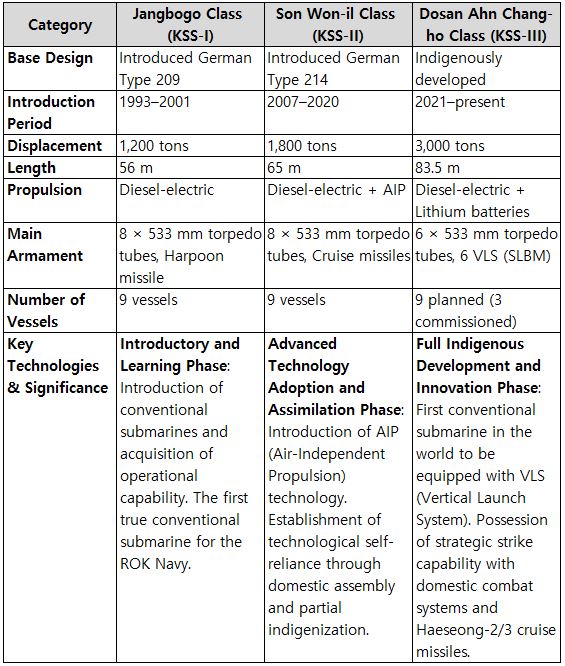
Although the history of the Republic of Korea Navy’s submarines is relatively short, it has made significant leaps in both independent technological development and force enhancement. The following outlines the chronological development and progress of Korea’s submarine forces.

Starting in 1975, the ROK Navy acquired seven small Italian-made Cosmos-class submarines (70-ton class) for intelligence missions and special operations, laying the foundation for Korea’s underwater capabilities. These submarines were primarily used for special operations, such as special forces infiltration, mine-laying, and intelligence gathering, rather than as conventional warships. Crew members of the Cosmos-class submarines later became key personnel in the development of the Dolphin-class indigenous submarines in the early 1980s.
4.2. Formative Stage (1983–1991): The Dolphin-class Small Submarine EraIn the beginning in 1977, the Agency for Defense Development (ADD) started developing a submarine modeled after Italy’s Cosmos-class. Construction took place at Tacoma Korea’s Masan Shipyard, and a total of three submarines were commissioned starting in 1983. This marked Korea’s first domestically built submarines, and the experience gained became the foundation for developing South Korea’s own underwater weapons. Based on operational results from the first submarine delivered in 1984, the second and third units were designed and built, being commissioned in 1990 and 1991, with reinforced pressure hulls and improved armament: SSM-051 1985 commissioned, 2003 decommissioned, SSM-052 1990 commissioned, 2016 decommissioned, SSM-053 1991 commissioned, 2016 decommissioned. The experience with the Dolphin-class played a critical role in advancing domestic submarine construction technology, serving as the stepping stone for the introduction and deployment of medium- to large-sized submarines.
Table 4. Specifications of the Dolphin-class Submarines (Source: Namuwiki)
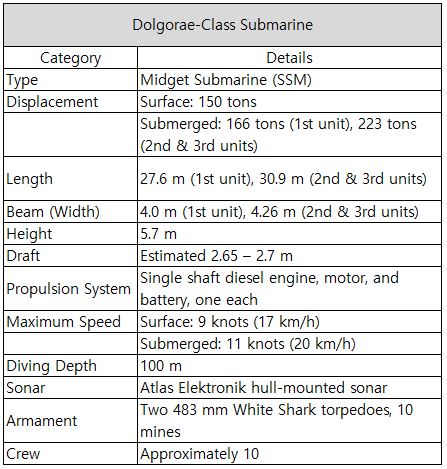
4.3. Development Stage (1992–2006): Introduction and Localization of the Jangbogo-class (Jangbogo-I)
In 1987, the ROK Navy signed a contract with the German company HDW for three Type 209 submarines (license for design acquisition), officially launching the Jangbogo-class (KSS-I) 1,200-ton program. Among these, one submarine was delivered as a complete unit from Germany in 1992, while the other two were assembled and constructed at Daewoo Shipbuilding & Marine Engineering’s Okpo shipyard using imported German parts, delivered in 1994 and 1995 respectively. Subsequently, six additional submarines were built, bringing the total to nine in service by 2001. This program was not merely an import project; the core goal was to transfer German technology and secure domestic assembly and construction capabilities. It laid the foundation for Korea’s submarine technology independence and advanced development. Leveraging the experience gained from constructing the Jangbogo-class, Daewoo Shipbuilding & Marine Engineering (DSME) signed a contract in 2011 to build three 1,400-ton submarines for Indonesia. Known as the DSME1400, these submarines are named the Nagapasa-class in the Indonesian Navy, marking Korea’s advancement in export capabilities.
Table 5. Specifications of the Jangbogo-class Submarine (Source: Namuwiki). Note: A batch refers to a group of submarines of the same model built in series, with incremental performance improvements applied in each production run.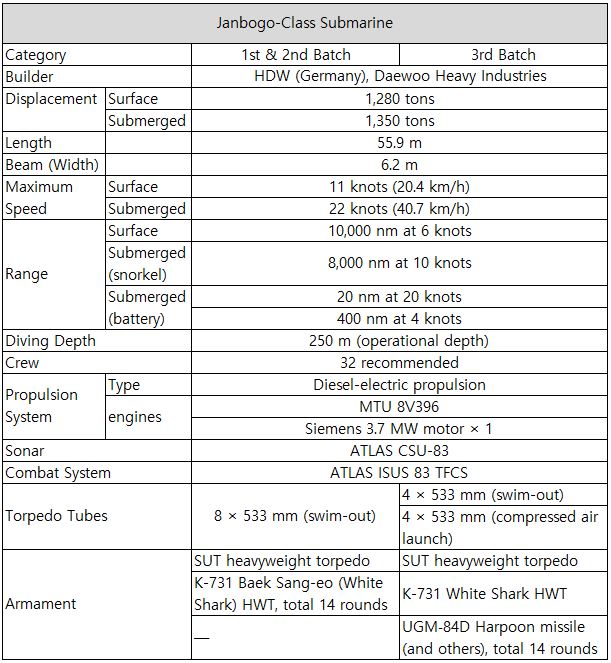
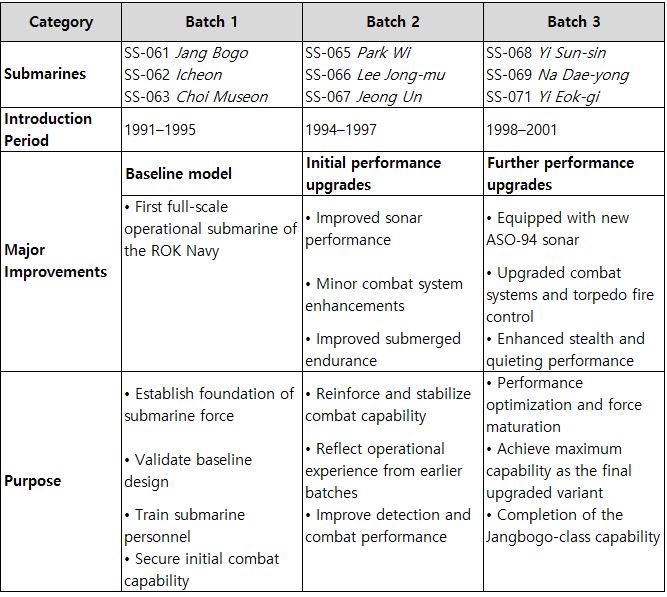
In 2000, the Republic of Korea Navy signed a contract with Germany’s HDW to acquire three Type-214 submarines under a design-license arrangement, launching a full-scale 1,800-ton Son Won-il–class program with Hyundai Heavy Industries. The first submarine, Son Won-il, was delivered in 2007, and an additional six submarines were subsequently built by Hyundai Heavy Industries and Daewoo Shipbuilding & Marine Engineering (DSME). The key feature of the Son Won-il class is its AIP (Air Independent Propulsion) system, which uses fuel cells to allow submerged operations for 2–3 weeks without surfacing. Construction was divided between Hanwha Ocean (formerly DSME) and HD Hyundai Heavy Industries. The vessels are named Son Won-il, Jeong Ji, An Jung-geun, Kim Dae-geon, Hong Beom-do, Yu Gwan-sun, Yun Bong-gil, Ahn Chang-ho, and Baekdusan.
Table 7. Specifications of the Son Won-il Class Submarines (Source: Namuwiki)
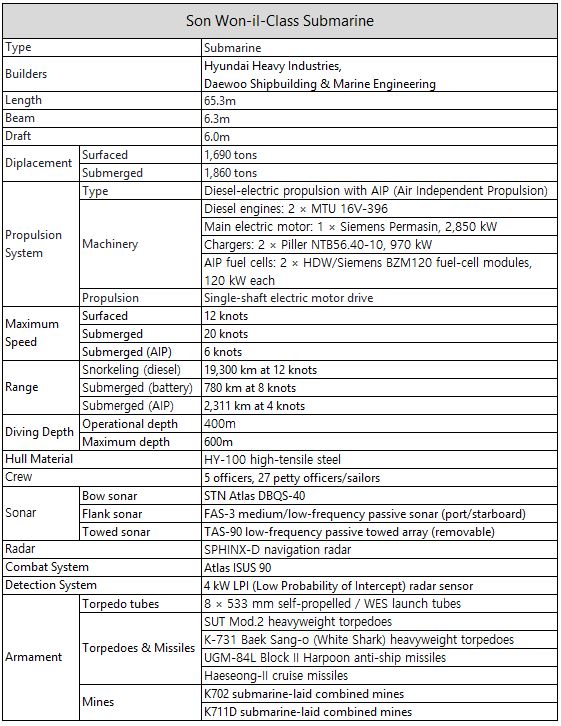
Table 8. Development Stages of the Son Won-il-Class Submarine
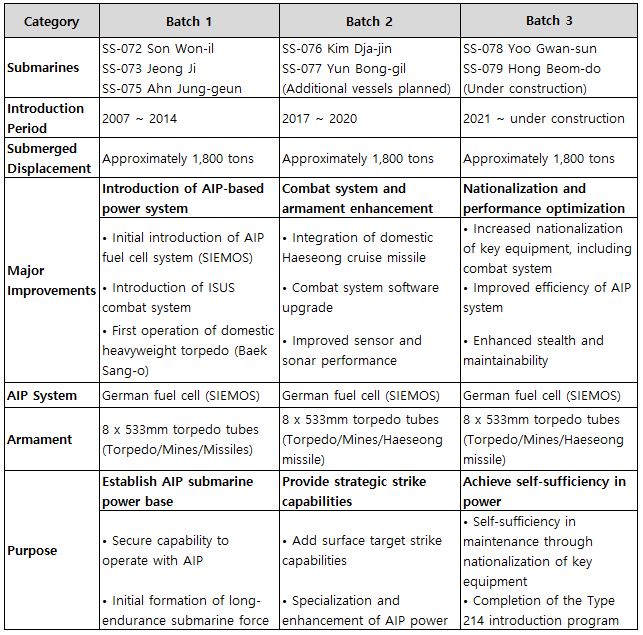
Over time, the armament and electronic systems have progressively advanced. Below is a simplified cross-sectional diagram of the HDW Type 214, which was used as a reference for the construction of the Son Won-il class submarines. The diagram helps to easily understand the complex internal structure by showing the main components. Here, the Fuel Cell Plant represents the AIP (Air Independent Propulsion) technology.
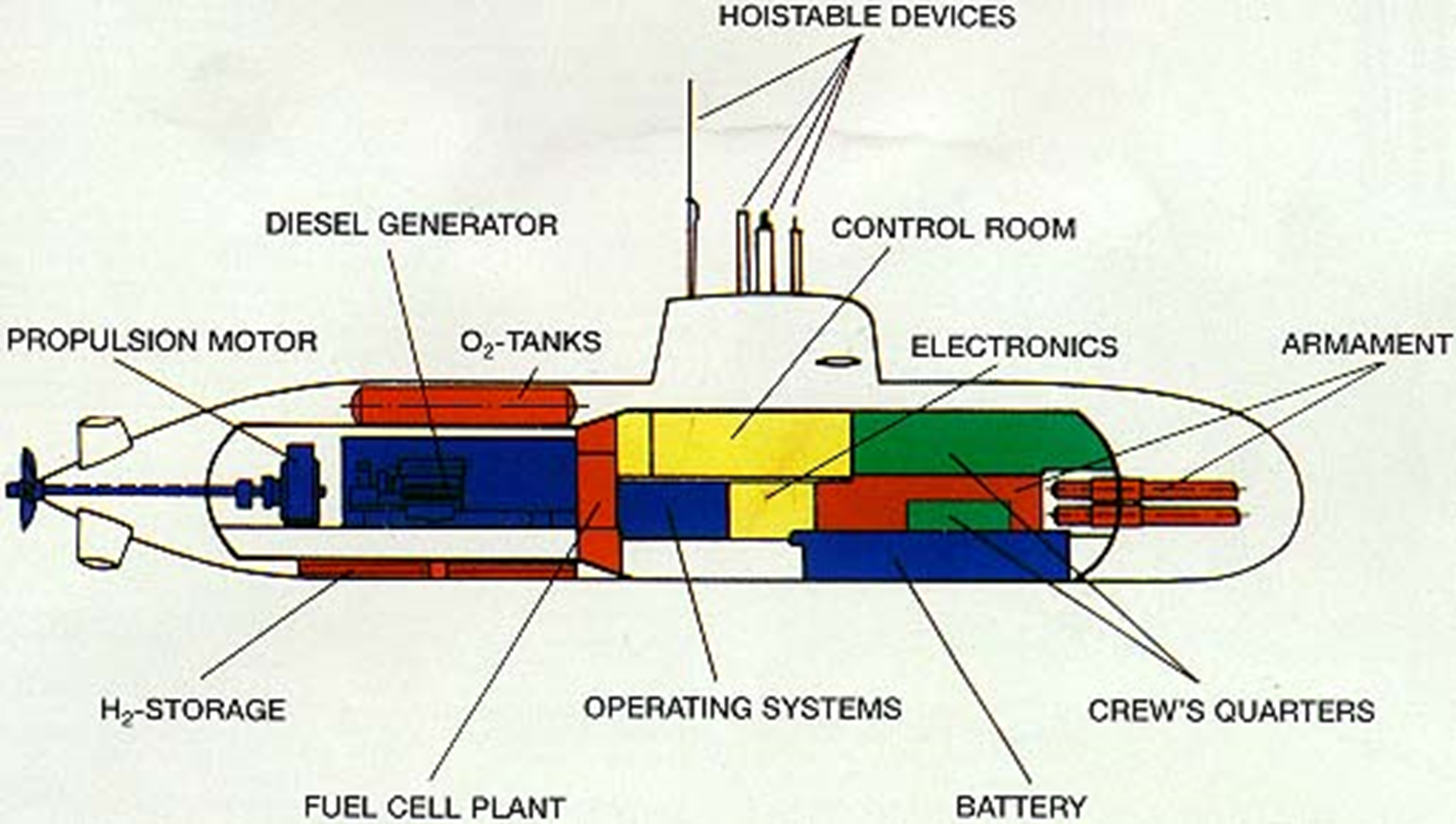
Figure 8. Simplified cross-section of the Type 214 Submarine (Source: TKMS)
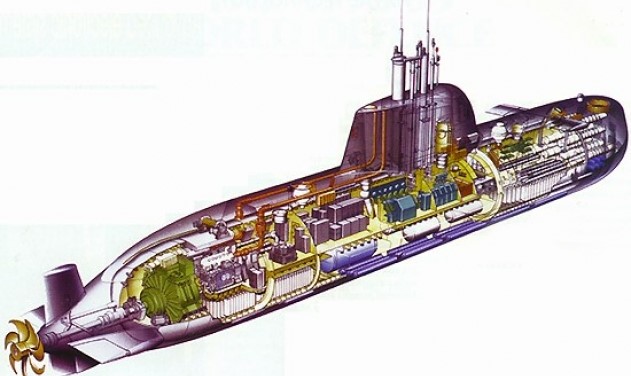
Figure 9. Cross-section of the Son Won-il-class Submarine (Source: Defense Mirror)
4.5. Independent Period (2021–Present): Dosan Ahn Chang-ho Class (Jangbogo-III) Indigenous Design
Achievements of Complete Domestic Design
In December 2012, the Defense Acquisition Program Administration (DAPA) signed a contract with Daewoo Shipbuilding & Marine Engineering (DSME) for the construction of two Dosan Ahn Chang-ho class submarines. The contract amount for the two submarines was approximately 1.675 trillion KRW (1.14 billion USD). The project was based on the construction experience of the Jangbogo-class and Son Won-il-class submarines, as well as the technology transferred from HDW and the experience in developing the DSME-1400 submarine (Nagapasa-class submarine) based on the Type 209 design. Dosan Ahn Chang-ho (launched in August 2021) is the first submarine fully designed, built, and equipped with its own weapon systems by South Korea. It has a displacement of 3,000 tons, making it a large submarine. It is the first in the world to be equipped with lithium-ion batteries, enabling long-term submerged operations without the need for an AIP system.
Strategic Weapon Deployment CapabilityThe most notable feature of the Dosan Ahn Chang-ho class is the vertical launch system (VLS) with 6 launchers (Batch-II will have 10 launchers), which allows the operation of the Hyunmoo-4-4 submarine-launched ballistic missile (SLBM). This capability is considered the most powerful strategic strike capability among non-nuclear nations. Currently, the Dosan Ahn Chang-ho, Kim Jong-seo, and Yun Bong-gil have been commissioned, with a total of 9 submarines planned: 3 from Batch-I, 3 from Batch-II, and 3 from Batch-III.
Table 9. Specifications of the Dosan Ahn Chang-ho Class Submarine (Source: Namuwiki)
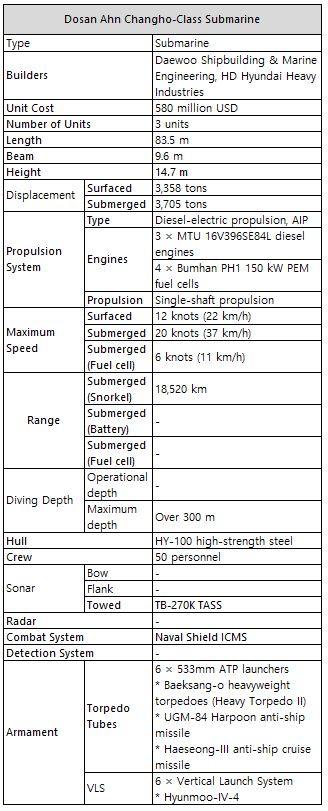
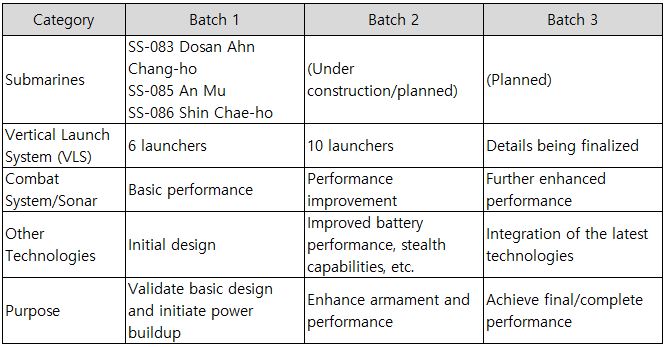
The following is information on the improvement projects for Batch 2 and Batch 3.
Table 10. Development Stages of the Dosan Ahn Chang-ho Class Submarine
Over time, the missile payload and electronic systems continue to evolve. Below is a cross-sectional diagram of the Dosan Ahn Chang-ho-class submarine, including a comparison of its size with the North Korean Romeo-class and the German Type 214 submarines. It also includes the proposed diagram by Daewoo Shipbuilding & Marine Engineering (now Hanwha Ocean) for the BrahMos missile-equipped version, which was part of their bid for the Indian next-generation submarine construction project.
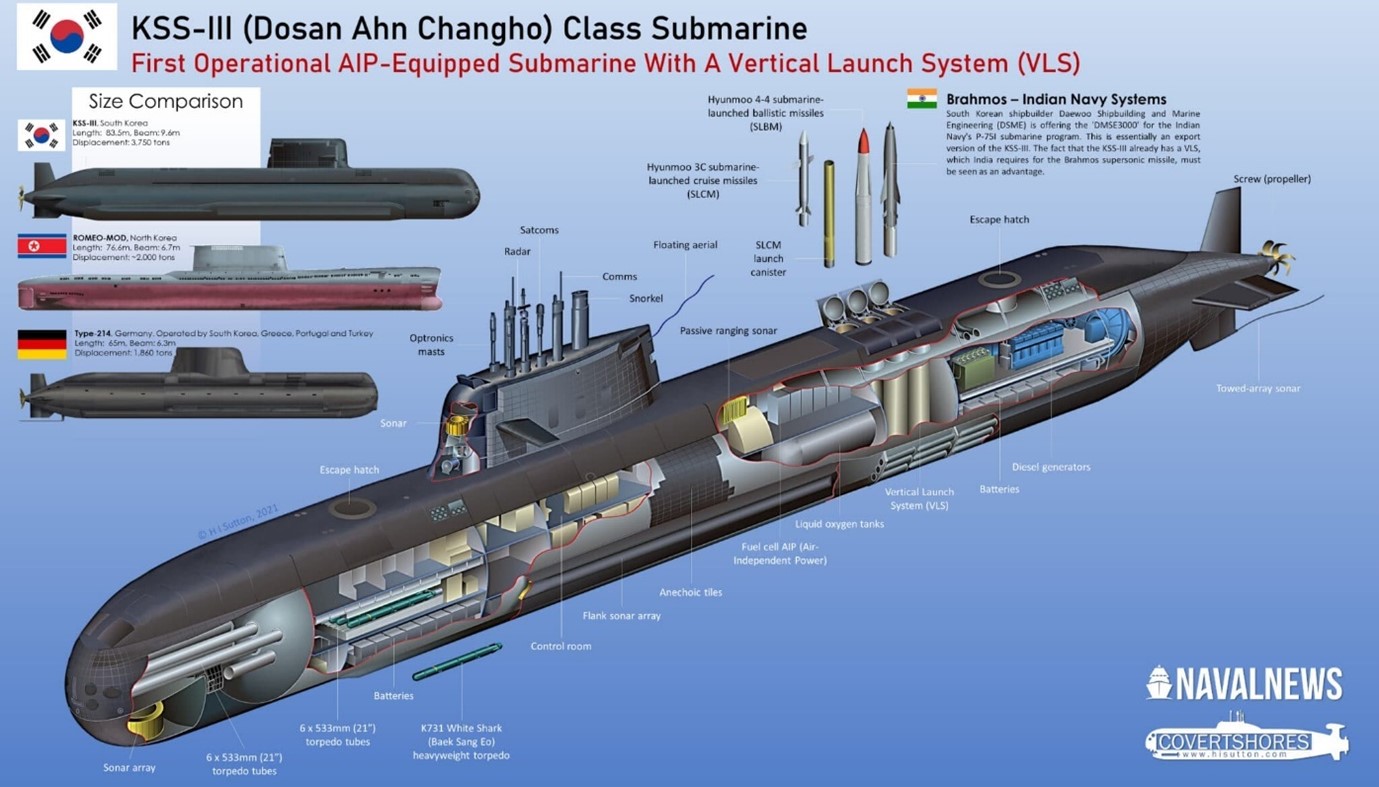
The history of South Korean submarines follows a trajectory of introduction, indigenization, technological accumulation, advancement, and international expansion. In 2011, South Korea became the first Asian country to export submarines by selling three Jangbogo-class derivative Nagapasa-class submarines to Indonesia for 1.1 billion USD. Currently, South Korea owns 18 submarines, making it the 8th largest submarine-owning country in the world. When it comes to conventional (diesel-electric) submarines, South Korea is regarded as one of the top global powers, along with Germany and Japan.
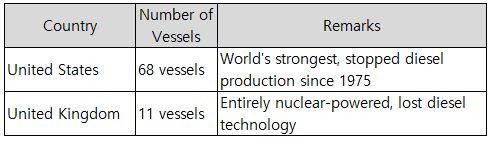
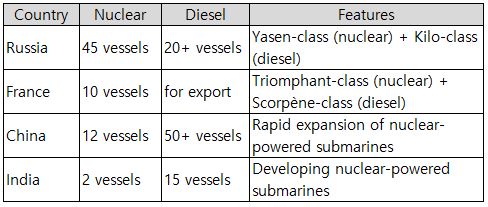
Current Submarine Power Rankings1. United States (68 nuclear submarines) - Overwhelming leader 2. Russia (45 nuclear submarines + 20+ diesel submarines) 3. China (12 nuclear submarines + 50+ diesel submarines) 4. United Kingdom (11 nuclear submarines) - Entirely nuclear-powered submarines 5. France (10 nuclear submarines + diesel) 6. India (2 nuclear submarines + 15 diesel submarines) 7. Japan (22 diesel submarines) 8. South Korea (18 diesel submarines) 9. Germany (6 diesel submarines, export power) 10. Sweden (5 diesel submarines, technological powerhouse)
Detailed Classification by Country
A. Nuclear Submarine Exclusives
B. Nuclear + Conventional Submarine
C. Conventional Submarine
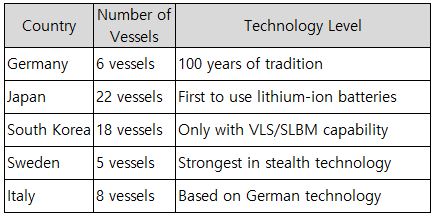
The following are the rankings of the leading countries in conventional submarine exports: 1. Germany - 100 years of tradition, top exporter 2. Japan - Highest technological capabilities 3. South Korea - Only country with VLS/SLBM capability 4. Sweden - Specializes in stealth technology 5. France - Combines nuclear and diesel capabilities The following compares the key features of export submarines from each country.
Table 12. South Korean KSS-III Competitor Submarines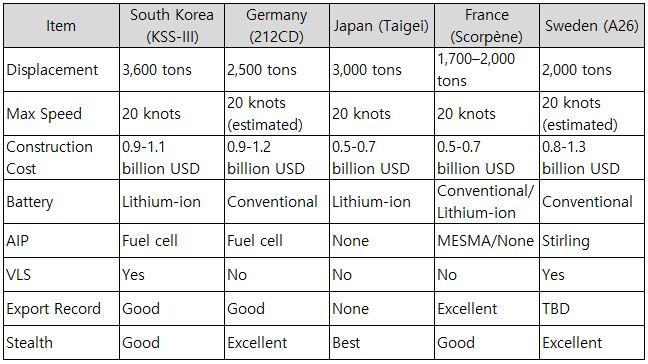
Top Exporting Countries 1. Germany - Type 209/214 series, more than 100 units exported 2. France - Scorpène, 16+ units (additional orders in progress) 3. South Korea - 3 units exported, actively competing in various tenders Latest Trends • Lithium-ion Batteries: South Korea (Jang Yeong-sil class), Japan (Taigei class), France (Scorpène Evolved) • VLS (Vertical Launch System): South Korea (SLBM), Sweden (Cruise Missiles) • Stealth Technology: Germany (Diamond hull), Sweden (Ghost), Japan (Low noise) Hanwha Ocean, the builder of the Dosan Ahn Chang-ho-class KSS-III submarines, and the South Korean government are actively engaging with the following countries for submarine exports: • Canada: The Canadian Navy's Submarine Replacement Program (CSCP) is a major project worth up to 40 billion USD (with an acquisition cost of about 14 billion USD and operation and maintenance costs of around 27 billion USD). Canada plans to introduce 12 new submarines. The KSS-III, at 4,000 tons, is considered a strong candidate due to its suitability for Canada’s operational environment (including the Arctic). South Korean defense companies are offering technical cooperation and local construction options in an effort to secure the deal. • Poland: Poland is pursuing the Orka project to modernize its navy, aiming to acquire 3 new submarines project worth about 14 billion USD. The KSS-III is consistently mentioned as one of the main contenders by the Polish government. • Philippines and other Southeast Asian countries: The Philippines is focused on strengthening its naval power to counter China. Other Southeast Asian nations are also looking to enhance maritime security through submarine acquisitions. South Korea, having previously exported submarines (e.g., the Nagapasa-class to Indonesia), is actively pursuing KSS-III sales in the region.
This section examines the key features of the latest submarine technologies of South Korea, North Korea, China, and Japan.
Table 13. Comparison of the latest submarines of South Korea and neighboring countries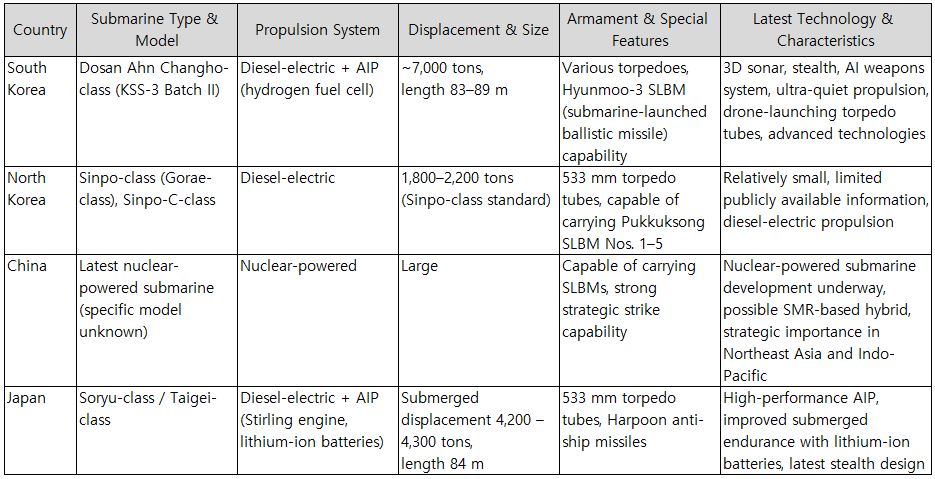
Military Ranking: Evaluated as top-tier in Asia in the order of China > Japan > South Korea > North Korea. • Advanced Technology: Japan, South Korea, and China are rapidly advancing in technological innovation, while North Korea focuses on strategic threat capabilities. • Operational Capability: Japan and South Korea excel in maritime route defense and blockade capabilities, whereas China’s strength lies in ocean-going and strategic power projection. Asian military experts particularly regard South Korea’s KSS-III, Japan’s Soryu-class/Taigei-class, and China’s latest submarines as the pinnacle of their respective national defense technologies. North Korea, while still relatively underdeveloped, raises the threat level through the public display of its strategic nuclear-powered capabilities.
South Korea is considering the development of next-generation submarines over 4,000 tons in the 2030s, with nuclear-powered submarines being a key option under discussion. In the past, in 2003, the basic design for a 4,000-ton reactor was completed, but at that time, cooperation with the United States was essential due to restrictions such as the Korea–U.S. nuclear agreement (“123 Agreement”). Recently, with the revitalization of Korea–U.S. shipbuilding cooperation through Hanwha Ocean and Philly shipyards, the possibility of acquiring nuclear submarine technology has increased. In particular, following the official U.S. approval of South Korea’s nuclear-powered submarine construction at the 2025 APEC Summit, technical, fuel, and policy cooperation with the U.S. is expected to move forward in earnest for South Korea’s project. 1. Scope of Future Cooperation • The U.S. has agreed to share key technologies for South Korea to build nuclear-powered submarines. • Cooperation will also include securing nuclear fuel for propulsion (highly enriched uranium or HALEU – high-assay low-enriched uranium) and the design and fabrication of small reactors for submarine use. • Both countries have agreed to expand mutual investment and technical collaboration in shipbuilding, marine plants, and submarine construction industries. 2. Technology Transfer and Conditions • South Korea has requested U.S. approval and supply for submarine propulsion nuclear fuel, and the U.S. is reported to have approved the use of nuclear fuel for South Korea’s submarine construction. • However, based on currently available information, this does not automatically include the full transfer of submarine reactor design or propulsion systems; the scope and method of technology transfer (joint development vs. full transfer) are still under discussion. • If South Korea transitions to third-country technology transfer or domestic development under U.S. cooperation, there could be restrictions linked to the Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT) and the 123 Agreement. 3. Potential Timeline • According to the fact sheet released at the APEC Summit, this cooperation is linked to investment in the shipbuilding industry, and South Korea is reported to have pledged around US$150 billion to U.S. shipbuilding. • South Korean government reports indicate the goal is to secure four or more medium-sized (approximately 5,000-ton or larger) nuclear-powered submarines by the mid-2030s. • However, specific milestones such as design completion, project start, construction, and delivery dates have not been officially finalized, and Korean officials have stated that detailed schedules are still under coordination.
Nuclear submarines can be broadly divided into two types based on their primary missions: 1) Strategic Nuclear Submarine (SSBN: Ship Submersible Ballistic missile Nuclear) • Primary Mission: Equipped with ballistic missiles (SLBMs) carrying nuclear warheads, SSBNs patrol covertly for extended periods to maintain nuclear deterrence. This means deterring adversaries from using nuclear or major conventional attacks by maintaining the capability to retaliate with nuclear weapons, thereby preventing war. • Characteristics: Large in size, prioritizes extreme stealth and long-range operational capability. 2) Torpedo-Attack Nuclear Submarine (SSN: Ship Submersible Nuclear) • Primary Mission: Engage enemy submarines (Sub Hunter) or surface ships (Ship Killer), conduct intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR), support special operations forces, or carry out land-attack missions using cruise missiles. • Characteristics: Smaller and faster than SSBNs, emphasizes agility and maneuverability. Summary: • SSBN: Strategic missions with nuclear missiles. • SSN: Tactical attack missions with torpedoes and cruise missiles.
8.1. Nuclear-Powered Submarines vs. Conventional (Diesel-Electric) Submarines – Propulsion ComparisonThe most fundamental difference is in the power source: • Nuclear propulsion: Uses a reactor; heat from nuclear fission boils water to produce steam, which drives turbines to generate propulsion and electricity. • Diesel-electric submarines: Operate differently on the surface/snorkeling versus submerged. o Surface / Snorkeling: Diesel engines are run to propel the submarine or charge the batteries. The submarine must surface or use a snorkel to intake air and expel exhaust gases, reducing stealth. o Submerged: Diesel engines are turned off; the submarine runs solely on large charged batteries powering electric motors. This allows for very quiet, stealthy operation, but operational endurance is limited. Once the batteries are depleted, the submarine must surface to run diesel engines and recharge.
Table 14. Comparison of Nuclear Submarine and Conventional Submarine Specifications
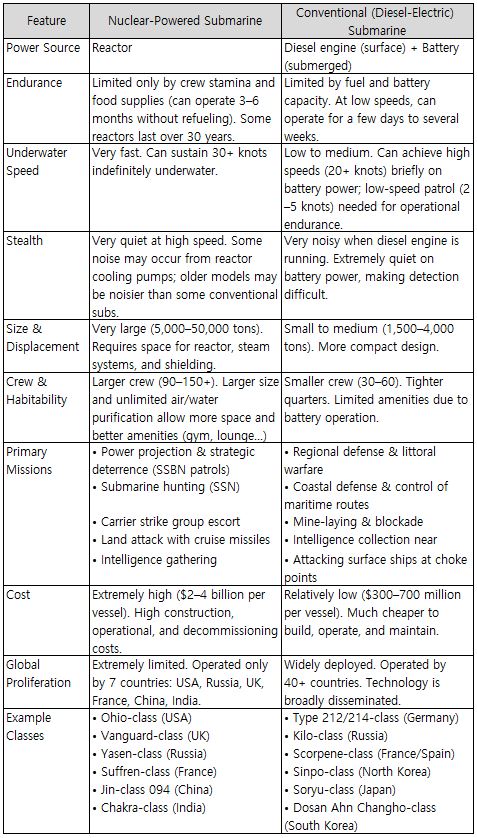
Key Points
•
A nuclear-powered submarine is similar to an aircraft carrier: it provides long-range, high-endurance capability and serves as a powerful tool for global power projection. It is designed to dominate the open ocean. • A conventional submarine is comparable to a coastal patrol craft or a hunter-killer submarine: a stealthy and cost-effective weapon optimized for controlling regional waters and coastlines. Its greatest advantage is extremely low noise during battery-powered operation, making it a deadly threat in shallow waters—like “a hole in the water.” • Choosing a submarine type is not about absolute superiority, but about selecting the model best suited to a country’s strategic goals, budgetary limits, and geographic operational environment.
8.2. Maintenance Comparison Between Nuclear-Powered and Conventional SubmarinesWhich force should a nation prioritize: Nuclear submarines, the backbone of strategic deterrence thanks to their unlimited underwater endurance, or conventional submarines, which offer excellent cost-effectiveness and are easier to field in larger numbers? One of the core factors in this decision is operational cost-efficiency. Beyond construction cost, the long-term burden of decades of maintenance, training, reactor refueling, and life-cycle logistics must be considered. The comparison below outlines these sustainment requirements.
Table 15. Maintenance Comparison: Nuclear vs. Conventional Submarines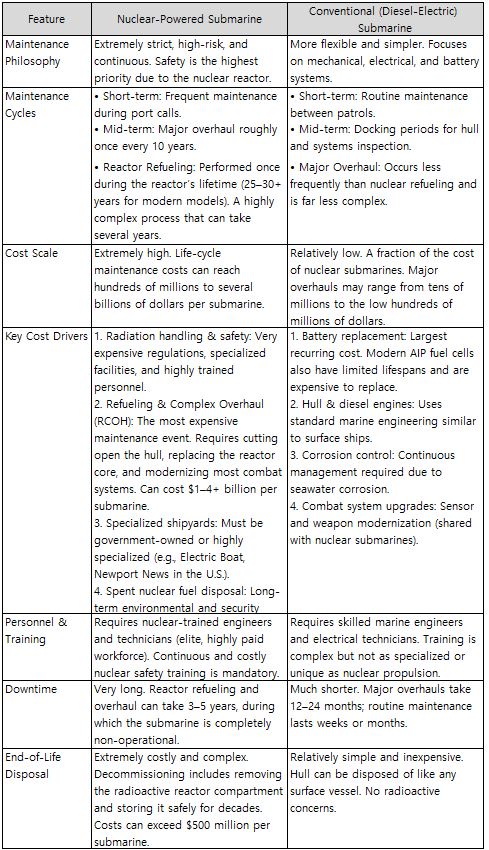
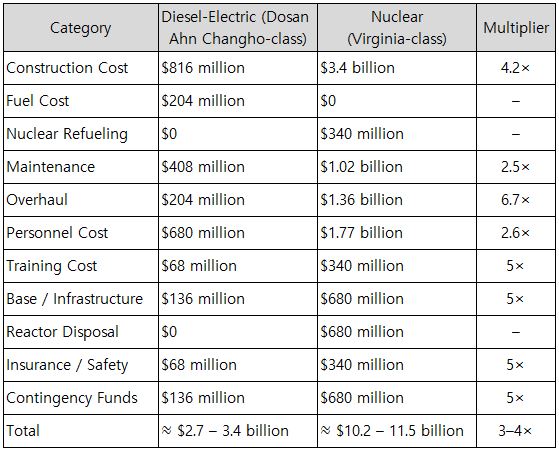
Let us compare two submarines of similar class size as examples: • Dosan Ahn Changho–class (KSS-III, South Korea) — conventional (diesel-electric + AIP) • Virginia-class (SSN, United States) — nuclear-powered Between these two types, the Total Lifetime Cost is 3 to 4 times higher for the nuclear-powered submarine. Below, we analyze the causes of this massive cost difference using concrete figures.
Table 16. Total Life-Cycle Cost Comparison: Nuclear Submarine vs. Conventional Submarine
8.4. Importance of Nuclear-Powered Submarines for the Republic of Korea Navy
Despite the enormous cost gap shown earlier, the South Korean government has strong reasons for wanting to acquire nuclear-powered submarines. These reasons are rooted in national security, strategic autonomy, and enhanced maritime defense capability. Key strategic motivations include: 1) Responding to North Korea’s SLBM Threat North Korea: Developing the Sinpo-class SSBN (armed with SLBMs). If a North Korean SLBM submarine hides in the deep waters of the East Sea, it becomes impossible to track with conventional submarines. Only nuclear-powered submarines can conduct continuous 24-hour tracking due to their unlimited underwater endurance 2) Monitoring Chinese Submarine Activity: China has ~12 nuclear submarines + ~50 diesel-electric submarines and is increasing activity in the East China Sea and Western Pacific. To monitor Chinese submarines operating in the open ocean, nuclear-powered submarines are essential 3) Strengthening Strategic Deterrence: Current South Korean SLBM range: ~500 km, requiring operations near the Korean Peninsula. A nuclear submarine can launch from anywhere in the Pacific, drastically expanding deterrence. Provides a “survivable second-strike capability”—a retaliatory force that cannot be located or neutralized 4) National Prestige: Nations that operate nuclear submarines are considered major military powers. Only six countries currently possess them. Strengthens technological sovereignty and diplomatic leverage South Korea’s desire to operate nuclear-powered submarines is driven by strategic and security needs that far outweigh cost considerations. For over 30 years, South Korea has pursued nuclear submarine capabilities as part of a long-term defense strategy, aiming to achieve: enhanced nuclear deterrence, increased strategic autonomy, breakthroughs in defense technology, effective countermeasures against the expanding submarine forces of North Korea and China. Nuclear-powered submarines are seen as essential platforms capable of long-duration, high-speed, and highly covert operations—capabilities that are crucial in Korea’s security environment.
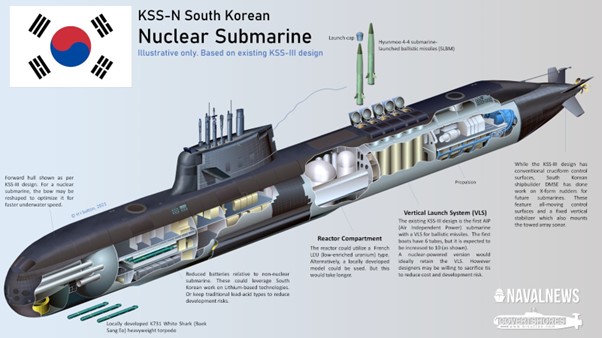
The Republic of Korea began with the small Dolgorae-class submarines in 1983, and in 42 years has risen to become the world’s 8th-largest submarine operator and one of the “Big Three” diesel-electric submarine powers (Germany, Japan, Korea). The Dosan Ahn Chang-ho class (KSS-III), in particular, is the world’s only diesel-electric submarine equipped with 10 VLS cells for SLBMs, and with its combination of AIP and lithium-ion batteries, it possesses some of the strongest underwater endurance and operational capability in the world. It has proven its real-world combat performance by eluding detection from a U.S. aircraft carrier during the RIMPAC exercises, and has demonstrated strong export competitiveness—Korea has already secured a 1.1 billion USD contract with Indonesia, and is competing for additional tenders in Canada, Poland, and the Philippines. Despite the overwhelming cost burden of nuclear-powered submarines, they remain essential for South Korea to counter North Korea’s SLBM-equipped SSBNs, and China’s expanding submarine fleet. Only nuclear-powered submarines can perform unlimited submerged operations and maintain high-speed, long-duration tracking of North Korean SSBNs 24/7. They also allow South Korea to exercise strategic deterrence across the entire Pacific, not just near the Korean Peninsula. While challenges remain—such as restrictions from the U.S.–Korea 123 Nuclear Agreement and various technological barriers—ongoing Korea–U.S. naval cooperation through Hanwha Ocean’s Philadelphia Shipyard significantly increases the likelihood of acquiring nuclear-submarine technology. Securing 4 to 6 nuclear-powered submarines would mark a transformational leap for the ROK Navy and a historic turning point in Korea’s rise as a true maritime power. South Korea’s submarine industry is not just a weapons program—it is an advanced technology sector and a driver of economic growth. It represents a core capability for self-reliant defense and national security. Based on its world-class diesel-electric submarine expertise, if Korea succeeds in acquiring nuclear-powered submarines as well, it will firmly establish itself as one of the world’s top five submarine powers. As history teaches that “those who command the seas command the future”, the continued advancement of South Korea’s submarine capabilities will serve as the foundation for peace and stability on the Korean Peninsula and in Northeast Asia in the 21st century.
First published in :
World & New World Journal

Unlock articles by signing up or logging in.
Become a member for unrestricted reading!