Defense & Security
The end of Great Illusions and the Revenge of Realism. The Case of the War in Ukraine – Part 2

Image Source : Shutterstock
Subscribe to our weekly newsletters for free
If you want to subscribe to World & New World Newsletter, please enter
your e-mail
Defense & Security

Image Source : Shutterstock
First Published in: Jan.26,2026
Jan.26, 2026
Following the super optimistic narrative and the consequent groupthink, as evidenced in the first part of this paper, the EU has so far imposed no fewer than 19 sanctions packages.[1] The latest package adopted on October 23, 2025, focuses on intensifying pressure on Russia's war economy by targeting key sectors, including energy, finance, military capabilities, transportation, and professional services, while also enhancing anti-circumvention measures. [2]
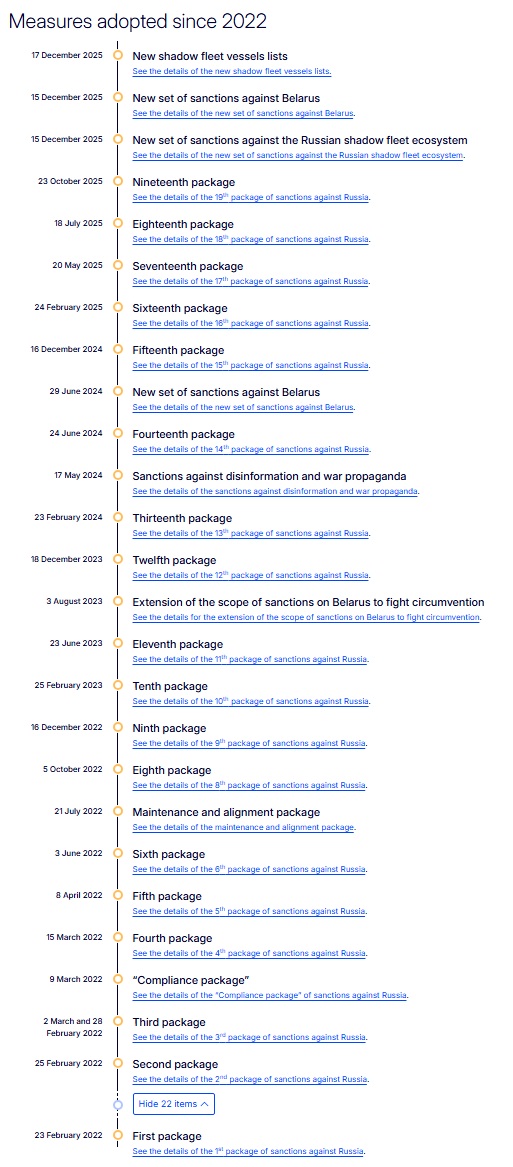
In the meantime, Russia seems to have accepted any adverse consequences of the sanctions and learned to live with them.
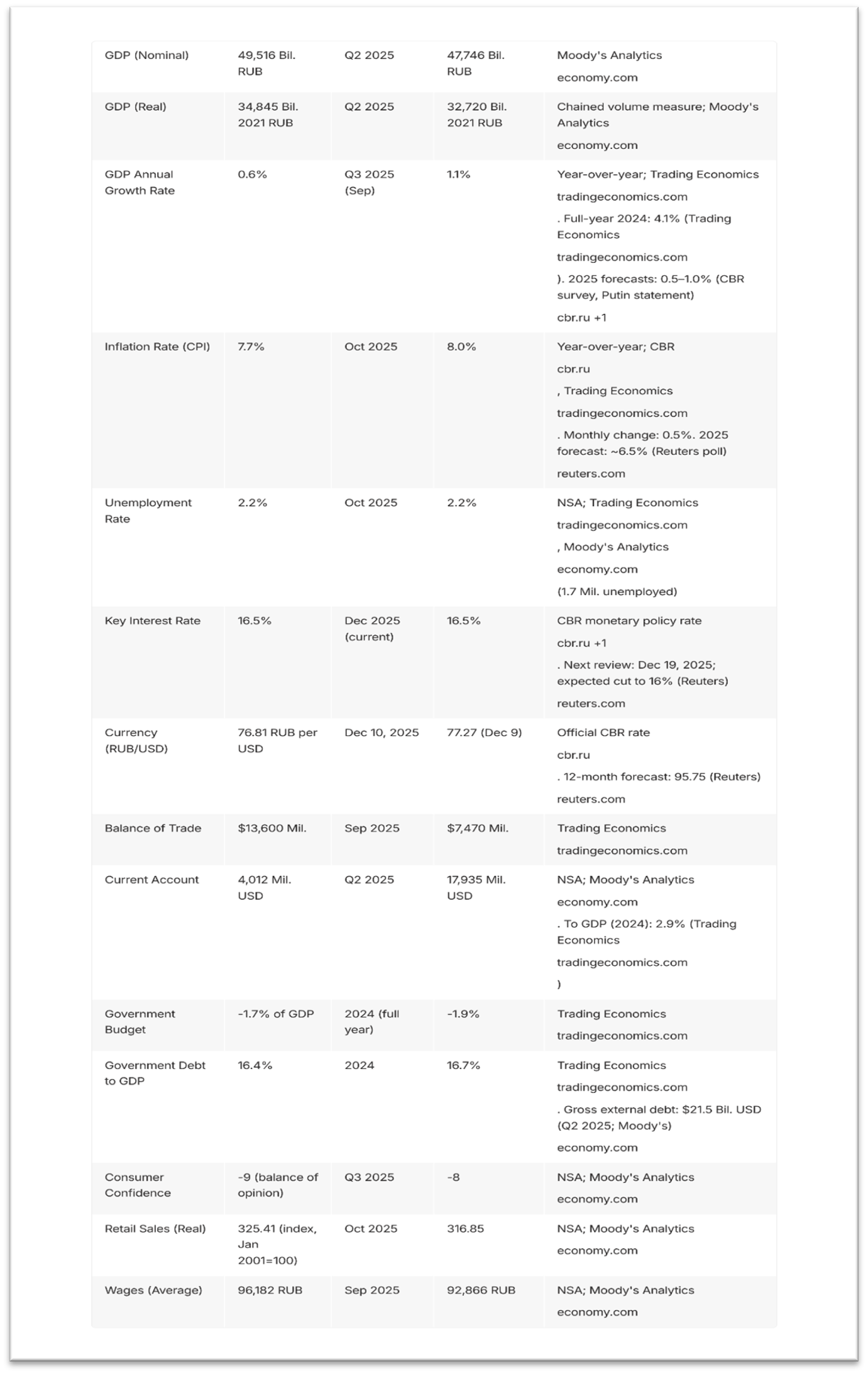
Militarily speaking, though, Russia (which is in fact fighting several NATO countries alongside Ukraine) seems to be not only advancing in the field. As of December 10, 2025, Russian forces have continued offensive operations across multiple fronts in eastern and southern Ukraine. These advances are part of a broader push amid ongoing heavy fighting, with Russian officials claiming momentum along the entire line of contact. Examples include: Pokrovsk Direction (Donetsk Oblast), Kupiansk/Kharkiv Direction, Lyman Direction (Donetsk Oblast), Siversk Direction (Donetsk Oblast), Zaporizhia/Southern Direction. On top of that, the media reports advances on multiple fronts, including Borova, Novopavlivka, and the eastern areas; the liberation of Rovnoye and Petropavlovka; the encirclement and liquidation of Ukrainian forces; and the fall of Dimitrov — widespread strikes on Ukrainian infrastructure.[3]
Importantly, Russian experts and military advisors openly debate the possibility of seizing control of Odessa.[4] Let us make no mistake here. Odessa is strategically important. Economically, Odessa is Ukraine's largest and only deep-water port, handling around 65% of the country's sea-based imports and exports, which account for 70% of Ukraine's total trade.[5] For Russia, controlling or disrupting this port serves to cripple Ukraine's economy while bolstering Russia's own position in global markets. First: Ukraine is a major global grain exporter, and Odessa is central to shipping these commodities. Russian attacks on the port, such as those following the withdrawal from the U.N.-backed grain deal in 2023, aim to prevent Ukrainian shipments, allowing Russia to dominate markets in the Middle East, North Africa, and beyond. Russia's Black Sea ports (e.g., Novorossiysk) handle its own $43 billion in annual grain exports, and undermining Odessa helps Russia create global reliance on its foodstuffs amid food insecurity.[6] Second, the port processes petroleum, natural gas, minerals, and even high-purity neon gas for semiconductors. Russia has targeted oil facilities near Odessa to disrupt fuel logistics, and control here would secure routes for Caspian Sea and Middle Eastern energy flows, aligning with Russia's strategy to diversify exports as hydrocarbon revenues decline.[7] Losing Odessa would be a "massive strategic blow" to Ukraine, akin to Britain losing Dover. Militarily, as a major Black Sea hub, Odessa enables Russia to project power and maintain dominance in the region. First, Russia's Black Sea Fleet, based in Crimea, can blockade Ukrainian coasts from Odessa, preventing resupplies and conducting amphibious operations — though these are high-risk due to Ukrainian defenses like mined waters.[8] The fleet supports expeditionary missions (e.g., the 2015 Syrian intervention) and hosts significant missile capabilities, with the capacity to deploy 80 long-range missiles in the area.[9] Second, even without full capture, Russia can harass shipping through mining or interdiction, extending tactics used in the Sea of Azov since 2014. This obstructs Ukrainian trade in the long term, potentially even in ceasefire scenarios, while facilitating Russian oil shipments (22% of which pass through the Black Sea).[10] Geopolitically, Odessa's location amplifies Russia's regional influence. First, capturing Odessa would create a land bridge to Transnistria, a pro-Russian breakaway region in Moldova just 35 miles away, allowing Russia to intimidate Moldova and potentially expand conflict there.[11] This aligns with broader aims to control Ukraine's entire Black Sea coast, threatening neighbours like Romania.[12] Second, dominating the northern Black Sea coast from Odessa would weaken Ukraine's security, block NATO reinforcements, and provide Russia with leverage in negotiations. It's seen as more critical to Russia's objectives than other Ukrainian regions, such as Kharkiv. President Putin has indicated in fact that the coastal area "rightfully belongs to Russia" as war spoils.[13] Finally, Odessa was founded in 1794 by Russian Empress Catherine the Great on former Ottoman territory, and it became one of the Russian Empire's largest cities and ports.[14] Arguably, the harbour city has a large Russian-speaking population (Russians are the second-largest ethnic group in Odessa Oblast), and Kremlin officials assert it has "nothing in common with the Kiev regime," viewing it as inherently Russian.[15] More interestingly, it appears that the Russian Military Industrial Complex (MIC) has been using the war, as MICs always do, as a perfect opportunity to modernize its military equipment. Consequently, Russia has advanced missile systems that NATO countries find a real challenge. Examples include: - Intercontinental Ballistic Missiles (ICBMs) RS-28 Sarmat, Russia's newest heavy ICBM, operational since 2023, with a range exceeding 18,000 km (up to 35,000 km in sub-orbital flight), a payload of over 10 tons including up to 16 nuclear warheads or hypersonic glide vehicles, and advanced countermeasures against missile defenses.[16] It's considered the world's longest-range and most powerful ICBM in service. - Hypersonic Systems Avangard Hypersonic Glide Vehicle (HGV), deployed on ICBMs like the Sarmat, can reach speeds up to Mach 27 (about 20,700 mph), perform unpredictable manoeuvres at high altitudes, and generate immense kinetic energy (equivalent to over two megatons of TNT). It's designed to evade all known missile defence systems.[17] Kh-47M2 Kinzhal, an air-launched hypersonic missile with a range of over 2,000 km and speeds up to Mach 10. It can manoeuvre mid-flight, carry nuclear or conventional warheads, and has been used operationally in conflicts like Ukraine.[18] 3M22 Zircon, a scramjet-powered hypersonic cruise missile reaching Mach 9, with a range of about 1,000 km. It's primarily anti-ship, launched from ships or submarines, and has demonstrated hits on maritime targets in exercises like Zapad 2025.[19] - Air and Missile Defence Systems S-500 Prometheus, an advanced surface-to-air missile system capable of intercepting targets at 600 km, tracking up to 300 simultaneously, and engaging hypersonic weapons, ICBMs, and stealth aircraft. It's integrated with multiple radars for resilience against jamming.[20] - Emerging or Experimental Systems 9M370 Burevestnik (SSC-X-09 Skyfall), a nuclear-powered cruise missile with theoretically unlimited range due to its onboard reactor. It underwent a successful test flight in October 2025 but remains in development, with concerns about safety and reliability.[21] Poseidon (Status-6), an unmanned, nuclear-powered underwater drone (torpedo-like) capable of carrying megaton-class warheads over intercontinental distances. It's designed for coastal targets and was tested alongside Burevestnik in 2025, though full operational status is unclear.[22] Oreshnik, a new intermediate-range ballistic missile (IRBM) with hypersonic capabilities, is evading Western defences. Russia plans deployments in Belarus by late 2025, enhancing strike options in Europe.[23] Last but not least, the media reports on a new, potentially game-changing technology: the TOS-1A Solntsepyok, a heavy multiple launch rocket system (MLRS) designed primarily to deliver thermobaric (fuel-air explosive) and incendiary munitions. It is mounted on a modified T-72 tank chassis for mobility and protection in combat zones, and it serves as a short-range area-denial weapon, often used to target fortified positions, infantry, and light armoured vehicles by creating massive blast waves and high temperatures.[24]
As of early 2026, Russia continues to make territorial gains (capturing over 5,600 square kilometers, mainly in Donetsk Oblast). According to the Institute for the Study of War (ISW) (a non-partisan, non-profit American think tank), German intelligence sources claim that “Germany expects Russia to target German energy and defence infrastructure early, given Germany’s role as a NATO hub for moving and sustaining forces and forecasts that Russia will see Germany as a priority target for long range missile strikes, armed drones, and special forces after an open armed attack on NATO’s eastern flank”[25] Consequently, according to ISW, Russia would likely be able to pose a significant threat to NATO earlier than many Western estimates, particularly in the event of a future ceasefire in Ukraine that would free up Russian forces and allow Russia to rearm and reconstitute.
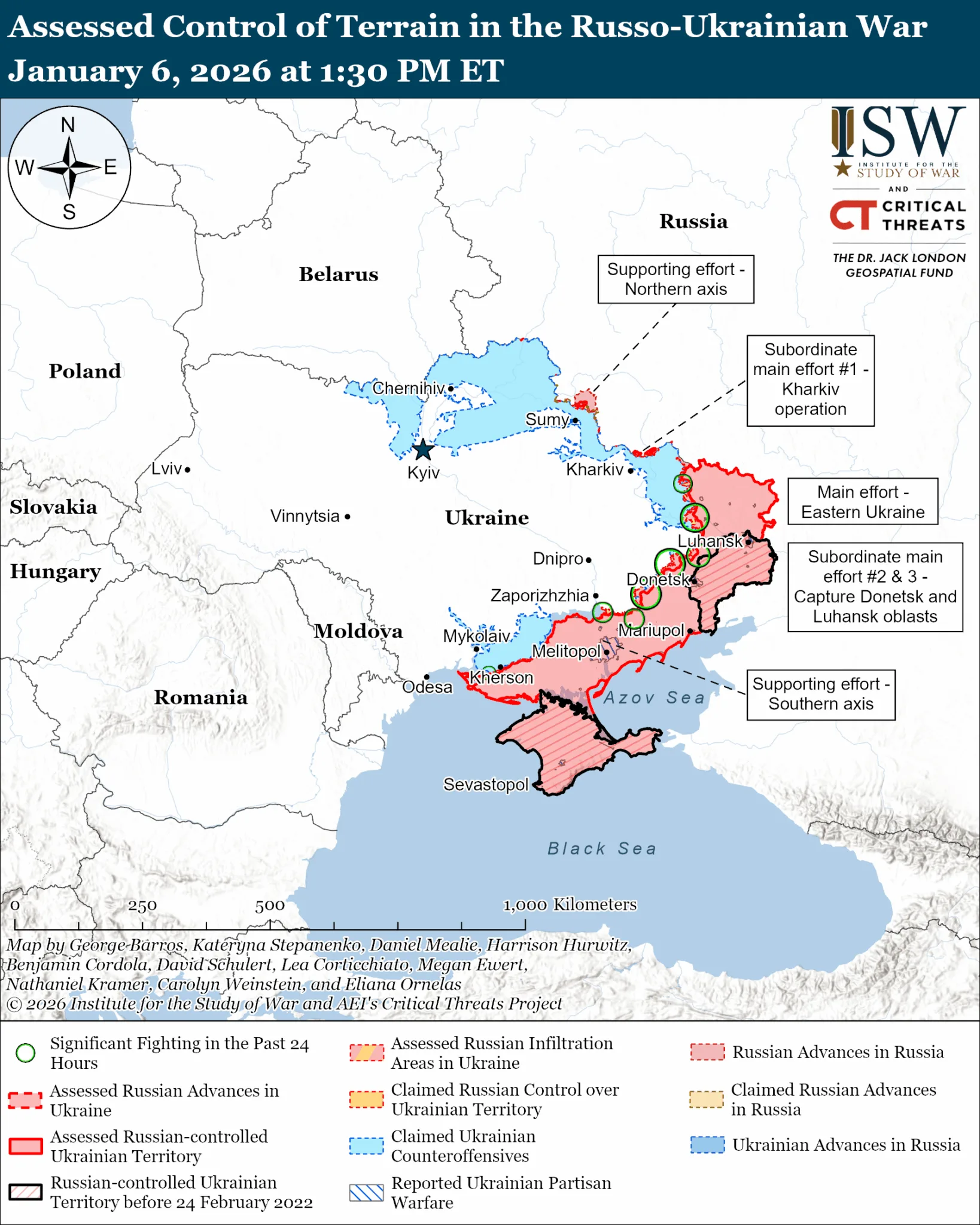
Against this backdrop, any post-war territorial options generally involve compromises due to military realities, though complete restoration of Ukraine's 2014 borders is seen as improbable without major shifts. These options are shaped by Ukraine's constitution (which prohibits ceding territory without a nationwide referendum or amendments), international law against forced border changes, and Russia's demands for recognition of annexed areas such as Crimea, the Donbas (Donetsk and Luhansk), Kherson, and Zaporizhzhia.[26] Russia's battlefield advantages and confidence reduce incentives for concessions, while Ukraine seeks security guarantees (e.g., EU integration or European military presence) in exchange for any deals.[27] Below, the reader will find a summary of some of the options discussed by diplomats:
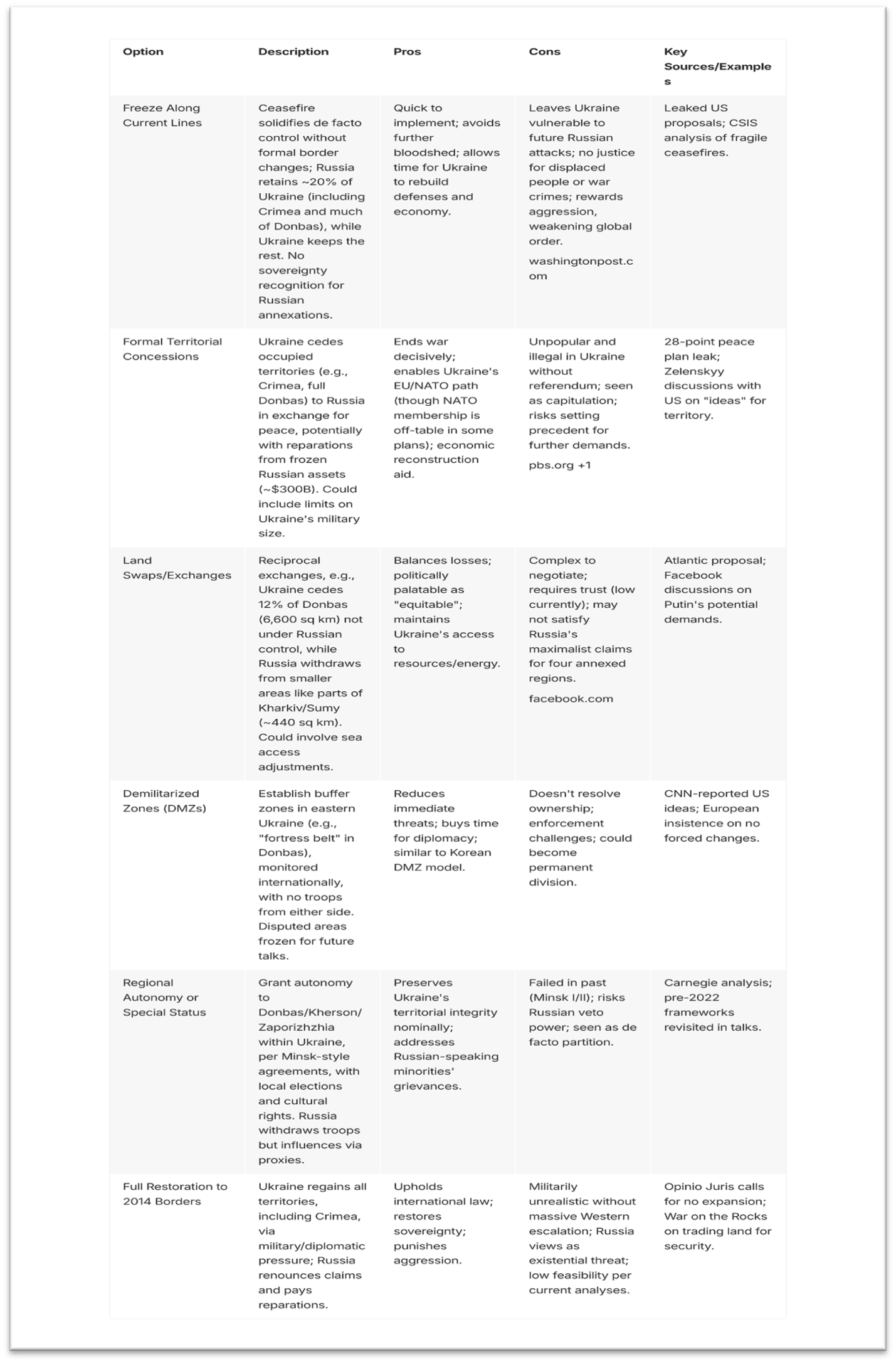
In addition to territorial change options, any deal will most likely include non-territorial elements such as Ukraine's neutrality (no NATO), demilitarisation caps, the return of abducted children, and economic reintegration of Russia (e.g., sanctions relief). Experts warn that rushed agreements could lead to renewed conflict, emphasising sustainable security for Ukraine (e.g., European troops or arms build-up).[28] Outcomes in 2026 hinge on battlefield shifts, US pressure, and European unity, with diplomacy intensifying but no breakthroughs yet.
On 11 December, NATO Secretary General Mark Rutte warned in a speech in Germany that Russia is escalating its war campaign against Europe, not just Ukraine. “We must be prepared for the scale of war our grandparents or great-grandparents endured,” he said.[29] On the very same day, the EU made the bold move of indefinitely immobilising frozen Russian assets worth €210 billion; €185 billion held at Belgium’s Euroclear, and €25 billion held in banks across other member states. European Commission President Ursula von der Leyen hailed the move that day, sending a strong signal to Russia that "as long as this brutal war of aggression continues, Russia's costs will continue to rise. […] This is a powerful message to Ukraine: We want to make sure that our brave neighbour becomes even stronger on the battlefield and at the negotiating table,” von der Leyen added. There is one problem that most EU leaders overlook. Namely, European societies are deeply divided, with large sections unwilling to go to war with Russia. Numerous polls evidence this. A recent ECFP Poll (June) was conducted by YouGov, Datapraxis, and Norstat across 12 countries (Denmark, Estonia, France, Germany, Hungary, Italy, Poland, Portugal, Romania, Spain, Switzerland, UK). It focused on readiness for potential war, including amid Russia's invasion of Ukraine and U.S. policy shifts. Key findings suggest: 50% overall support increasing defence spending (highest in Poland and Denmark at 70%); majorities in France (62%), Germany (53%), and Poland (51%) favour reintroducing mandatory military service; 59% support continuing military aid to Ukraine even without U.S. involvement; 54% back a European nuclear deterrent independent of the U.S. All of this seems to reflect acceptance of preparation for conflict, though not direct personal willingness to fight.[30] According to John Mearsheimer, a leading realist scholar, Russia's decision to invade Ukraine was primarily a rational response to the changing material realities of the international system, particularly the eastward expansion of NATO and the European Union (EU), which Russia perceived as a direct threat to its core strategic interests and great power status. Mearsheimer contends that the anarchic international system compels states, especially great powers, to maximise their power to ensure survival. Thus, Russia acted to prevent Ukraine from becoming a Western stronghold on its border, viewing the West's policies as provocative and threatening to its security. This perspective emphasises the structural pressures and incentives created by anarchy and power competition, suggesting that the imperative drove Russia's actions to survive and maintain regional dominance amid Western encroachment.[31] Admittedly, Mearsheimer’s views are much criticised by Western scholars and media experts. And yet, with the recent actions of the United States against Venezuela (the kinetic attack against the state and the kidnapping of its president and his wife – all against the most sacred principles of international law), one wonders why the cold-blooded, objective analysis has been forgone in favour of wishful thinking.
[1] Sanctions adopted following Russia’s military aggression against Ukraine. (2025, October 29). European Commission. https://finance.ec.europa.eu/eu-and-world/sanctions-restrictive-measures/sanctions-adopted-following-russias-military-aggression-against-ukraine_en [2] Fisch, E. J., Junck, R. D., Sève, M., Albrecht vom Kolke, M., Benson, J., Lainé, W., Mueller, P., Seidner, G., & Vianesi, G. (2025, November 12). EU Adopts 19th Russia Sanctions Package Alongside New Sanctions Being Imposed by US and UK. Skadden. https://www.skadden.com/insights/publications/2025/11/eu-adopts-19th-sanctions-package [3] Grok: What are the latest advances of Russian troops in Ukraine? [4] Каминский, А. (2025, October 2). «СВО закончится взятием Одессы». НАТО готовит румын и французов. Что в планах у Минобороны России? RuNews24. https://runews24.ru/articles/02/10/2025/svo-zakonchitsya-vzyatiem-odessyi-nato-gotovit-rumyin-i-franczuzov-chto-v-planax-u-minoboronyi-rossii also Крылова, А. (2025, December 3). Названы сроки, в которые Российская армия сможет дойти до Одессы. Абзац. https://absatz.media/news/143321-nazvany-sroki-v-kotorye-rossijskaya-armiya-smozhet-dojti-do-odessy or Елистратов, А. (2025, November 20). Эксперт: русским нет смысла соглашаться на план Трампа, они и так дойдут до Одессы. Репортёр. https://topcor.ru/66186-jekspert-russkim-net-smysla-soglashatsja-na-plan-trampa-oni-i-tak-dojdut-do-odessy.html [5] Costea, C. A. (2022, March 25). The strategic importance of the port of Odessa. Romanian Centre for Russian Studies. https://russianstudiesromania.eu/2022/03/25/the-strategic-importance-of-the-port-of-odessa/ [6] Black, E., & Kaushal, S. (2025, April 14). Black Sea Significance to European Security. Romanian Centre for Russian Studies. https://www.rusi.org/explore-our-research/publications/commentary/black-sea-significance-european-security [7] Ozberk, T. (2022, April 5). Why is Odessa important for Russia? Defence Procurement International. https://www.defenceprocurementinternational.com/features/sea/why-is-odessa-important-for-russia [8] Ibidem. [9] Black, E., & Kaushal, S. (2025, April 14). Black Sea Significance to European Security. Romanian Centre for Russian Studies. https://www.rusi.org/explore-our-research/publications/commentary/black-sea-significance-european-security [10] Mathers, J. (2025, September 8). Russia has provided fresh evidence of its territorial ambitions in Ukraine. The Conversation. https://theconversation.com/russia-has-provided-fresh-evidence-of-its-territorial-ambitions-in-ukraine-264592 [11] Akage, A. (2022, May 20). Is Odessa Next? Putin Sees A Gateway To Moldova — And Chance For Revenge. Worldcrunch. https://worldcrunch.com/world-affairs/why-odessa-is-important/ [12] Boyse, M. (2024, March 21). Operation Odesa: Russia Wants the Entire Ukrainian Black Sea Coast. Hudson Institute. https://www.hudson.org/defense-strategy/operation-odesa-russia-wants-entire-ukrainian-black-sea-coast-matthew-boyse [13] Mathers, J. (2025, September 8). Russia has provided fresh evidence of its territorial ambitions in Ukraine. The Conversation. https://theconversation.com/russia-has-provided-fresh-evidence-of-its-territorial-ambitions-in-ukraine-264592 [14] Santora, M. (2023, July 19). Why Odesa Is So Important to Ukraine in the War With Russia. The New York Times. https://www.nytimes.com/2023/07/19/world/europe/odesa-ukraine-war-russia.html [15] Ozberk, T. (2022, April 5). Why is Odessa important for Russia? Defence Procurement International. https://www.defenceprocurementinternational.com/features/sea/why-is-odessa-important-for-russia [16] Ali, I. A. (2025, December 2). From Sarmat to Avangard: 10 most technologically advanced Russian weapon systems. WION. https://www.wionews.com/photos/from-sarmat-to-avangard-10-most-technologically-advanced-russian-weapon-systems-1764678135158/1764678135159 [17] Ibidem. [18] See more at: https://missilethreat.csis.org/country_tax/russia/ [19] Charpentreau, C. (2025, September 15). Russia uses Zapad 2025 for ‘hypersonic posturing’ with Zircon, Kinzhal drills. AeroTime. https://www.aerotime.aero/articles/zapad-2025-russia-hypersonic-posture-zircon-kinzhal [20] Ali, I. A. (2025, December 2). From Sarmat to Avangard: 10 most technologically advanced Russian weapon systems. WION. https://www.wionews.com/photos/from-sarmat-to-avangard-10-most-technologically-advanced-russian-weapon-systems-1764678135158/1764678135159 [21] Gwadera, Z. (2025, November 20). Russia’s Burevestnik and Poseidon tests. IISS. https://www.iiss.org/online-analysis/missile-dialogue-initiative/2025/11/russias-burevestnik-and-poseidon-tests/ [22] Ibidem. [23] See more at: https://youtu.be/D22JNoLzj9E?si=BtZ3NMCs7KoUk7ue [24] See more at: https://www.globalsecurity.org/military/world/russia/tos-1a.htm [25] Young, J., Harward, C., Simanovskyy, M., Mappes, G., Nasreddine, D., & Barros, G. (2026, January 6). Russian Offensive Campaign Assessment, January 6, 2026. Institute for the Study of War. https://understandingwar.org/research/russia-ukraine/russian-offensive-campaign-assessment-january-6-2026/ [26] Yurchuk, V. (2025, August 12). Ceding land to Russia not only unpopular in Ukraine, but also illegal. PBS NEWS. https://www.pbs.org/newshour/world/ceding-land-to-russia-not-only-unpopular-in-ukraine-but-also-illegal [27] Harding, E. (2025, November 24). What Is the Strategy in the Ukraine-Russia Peace Negotiations? Centre for Strategic & International Studies. https://www.csis.org/analysis/what-strategy-ukraine-russia-peace-negotiations [28] Wright, T. (2025, August 18). The Only Plausible Path to End the War in Ukraine. The Atlantic. https://www.theatlantic.com/ideas/archive/2025/08/trump-ukraine-russia-peace/683907/ [29] Kiorri, E., & Cabanas, L. B. (2025, December 30). Would you fight for the EU’s borders? Take our poll. Euronews. https://www.euronews.com/my-europe/2025/12/30/would-you-fight-for-the-eus-borders-take-our-poll?fbclid=IwT01FWAPFTrZleHRuA2FlbQIxMABzcnRjBmFwcF9pZAwzNTA2ODU1MzE3MjgAAR4KLt3FfIaCbSxjUO8ldmbDys6WPnLeZaNIpZuhAApKVUs073MB4vZj8DKbOA_aem_lLTRWqCcGPL3F9z5-SX65g [30] https://www.eureporter.co/world/2025/06/26/most-eu-citizens-are-ready-for-war-new-poll/ [31] Smith, N. R., & Dawson, G. (2022). Mearsheimer, realism, and the Ukraine war. Analyse & Kritik, 44(2), 175–200. https://doi.org/10.1515/auk-2022-2023
First published in :
World & New World Journal

Unlock articles by signing up or logging in.
Become a member for unrestricted reading!