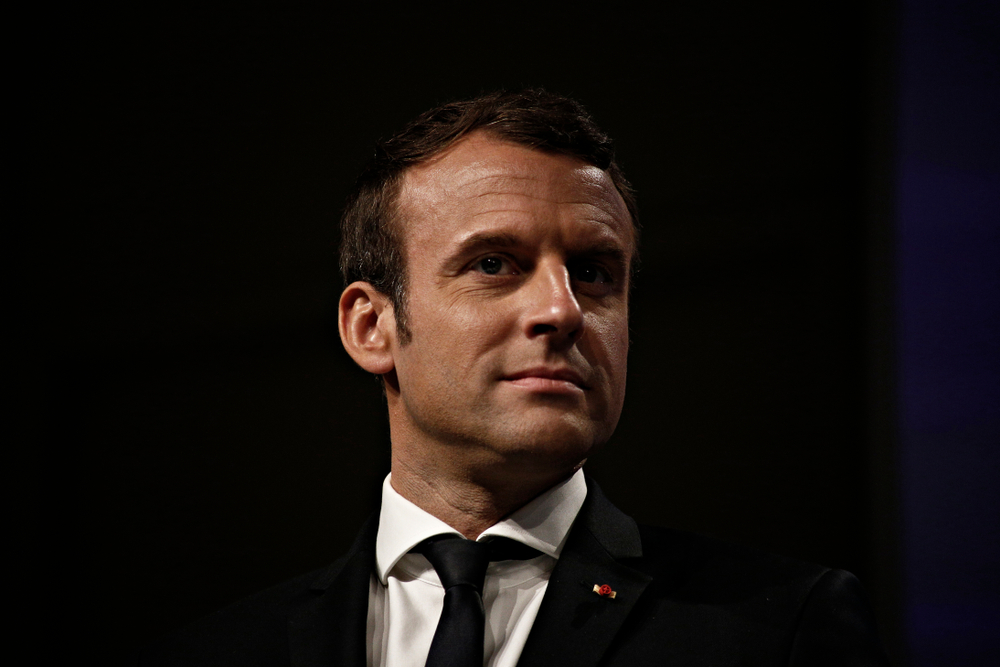
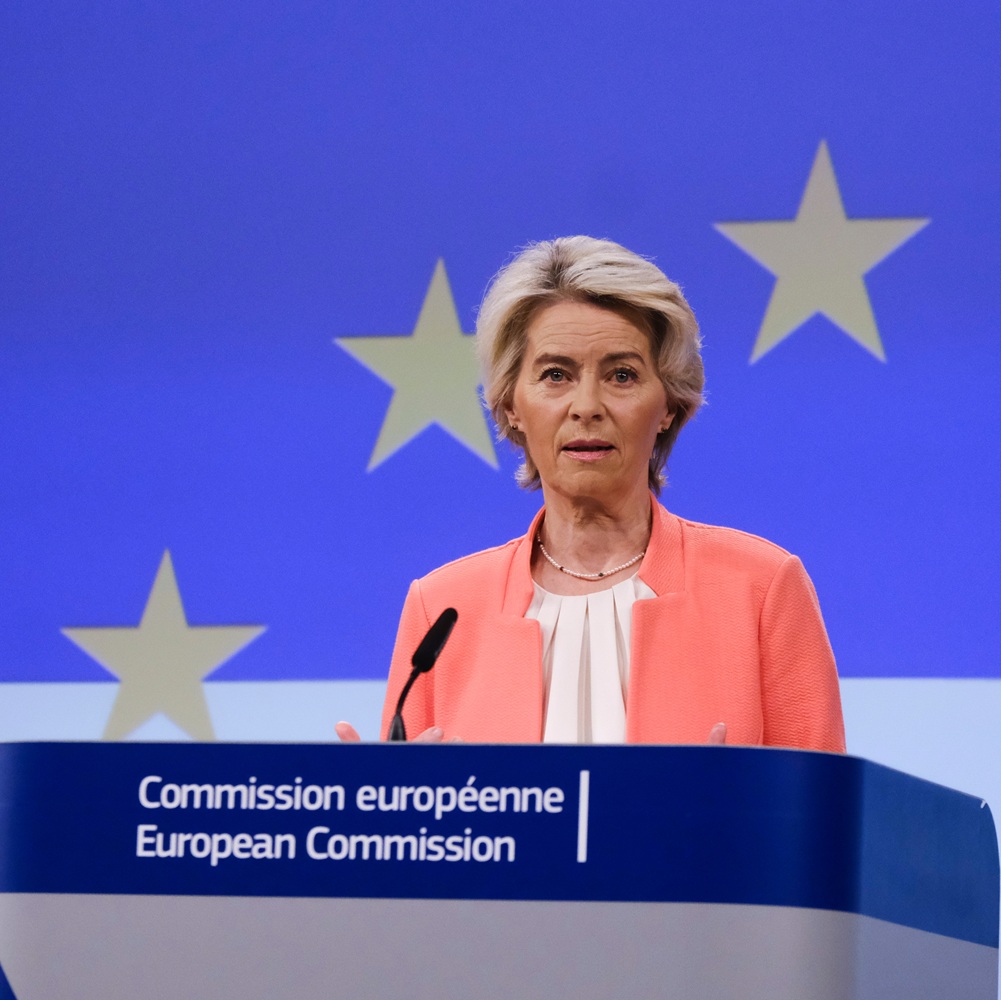
Davos 2025 as a Concentrated Expression of Geopolitical Uncertainty
by Vladislav Belov
한국어로 읽기
Leer en español
In Deutsch lesen
Gap
اقرأ بالعربية
Lire en français
Читать на русском
From January 20 to 24, 2025, the traditional World Economic Forum (WEF) took place in Davos. The organizers registered approximately 2,000 participants from over 130 countries, including around 1,600 executives from major corporations, among them 900 CEOs. The political agenda of the WEF was supported by more than 50 heads of state and government. As part of the official program, about 300 sessions were held, 200 of which were broadcast live. Press accreditation was granted to 76 media companies. For official events, 28,043 square meters of space were allocated, accommodating 117 meeting rooms and 23 lounge areas. Additionally, several participating companies (such as HSBC, EY, and Cognizant) rented additional venues separately for their own events. WEF President Børge Brende, announcing this meeting, emphasized that in 2025, due to geopolitical conflicts, ongoing economic fragmentation, and the acceleration of climate change, the forum would be held under conditions of exceptionally high global uncertainty for the first time in decades. The theme of the Forum was “Cooperation in the Age of Intelligence”. On January, WEF experts presented four reports. The first one, a traditional report and the 20th edition, analyzed the most significant global risks and threats facing the international community. The study is based on a survey of over 900 experts from various fields and covers short-term (2025), medium-term (until 2027), and long-term (until 2035) perspectives. The key risks identified for these periods include the following:- in 2025 the most serious threat for most respondents is interstate armed conflicts, followed by extreme weather events and geoeconomic conflicts, including sanctions and trade measures;- by 2027 key risks include disinformation and fake news, which undermine trust in institutions and intensify social polarization, tension, and instability, as well as an increase in cyberattacks and espionage cases;- by 2035 environmental threats are a major concern, including extreme weather events, biodiversity loss, ecosystem destruction, critical changes in Earth's systems, and natural resource shortages. Additionally, technological risks such as the negative consequences of artificial intelligence and other advanced technologies are highlighted.The authors emphasize the need to strengthen international cooperation and increase resilience to global threats. According to them, rising geopolitical tensions, climate challenges, and other risks require coordinated global action to prevent the escalation of existing issues and the emergence of new crises. The second report presents the perspectives of leading experts on the global economic outlook for 2025. They predict moderate economic slowdown, driven by geoeconomic fragmentation and protectionist measures. The most resilient economic growth is expected in the United States and South Asian countries, while Europe, China, and Latin America may face significant challenges. Inflation is projected to rise in most countries, primarily due to increased government spending and shifts in global supply chains. Most experts consider a further escalation of the U.S.-China trade war likely, along with continued regionalization of global trade, leading to the formation of more isolated economic blocs and reduced global interdependence. While experts acknowledge the high potential of artificial intelligence (AI), they emphasize the need for greater investment in infrastructure and human capital to fully leverage its benefits. The third study provides a comprehensive analysis of employment issues. The main conclusion is that ongoing changes, global trends and new technologies will cause 92 million people to leave the labor market worldwide by 2030, but will also create 170 million new jobs. One of the challenges in this regard is the need to improve skills and train for new specialties. The fourth report assesses the state of global cooperation across five key areas: trade and capital, innovation and technology, climate and natural capital, health and well-being, and peace and security. After analyzing more than 40 indicators, the authors conclude that due to heightened geopolitical tensions and instability, overall cooperation remains at the same level. However, positive trends are observed in areas such as climate, innovation, technology, and health. Davos as a Symbolic Benchmark of Switzerland Despite existing criticism, the Davos Forum remains a key platform for the annual interaction of leading figures in global politics, business, and the expert community. Without Switzerland's neutral status, the Davos Forum likely would not exist. However, it was Klaus Schwab, who founded the World Economic Forum (WEF) on January 24, 1971, who played a crucial role in transforming this event and its host location into one of Switzerland’s comparative advantages in political and economic terms. Despite his advanced age, Schwab continues to be an active ideologue and architect of Davos, moderating key discussions while fine-tuning his creation and addressing annual criticism. Yet, he has his own limitations—despite Switzerland’s neutrality and his personal reputation for impartiality, Schwab once again refrained from inviting Russian representatives, even at the level of individual entrepreneurs and experts. Such a move, rather than formal attempts to broaden participation and accessibility, could have enhanced the forum’s status. The participation of a Russian delegation would have been particularly relevant in this critical year for global politics, marked by the unpredictable presidency of Donald Trump, which is set to shape most geopolitical and geo-economic processes worldwide. Including Russian representatives could have strengthened the WEF’s competitive standing, but once again, it did not happen. The Swiss leadership highly values the opportunities that the Davos platform provides, particularly in the realm of foreign policy and, most notably, foreign economic relations. In September 2024, both chambers of the Swiss Parliament—the Council of States (the smaller chamber) and the National Council (the larger chamber)—decided to continue state support for the World Economic Forum (WEF) in Davos and allocated budget funding for the period 2025–2027. During the discussions, lawmakers emphasized that the event strengthens Switzerland’s role as a global hub for international dialogue, while also having a positive economic impact on the Graubünden region. As the host country of the forum, Switzerland actively leverages it to advance its own interests. This year, six out of the seven members of the Swiss Federal Council (Cabinet of Ministers) attended the WEF. As part of the European Free Trade Association (EFTA), Swiss Economy Minister Guy Parmelin signed free trade agreements (FTAs) with Kosovo and Thailand, bringing Switzerland’s total number of FTAs to 37. There are also plans to adapt and update the existing FTA with China. One of Bern’s key priorities remains securing an FTA with the MERCOSUR bloc. As a result, a focal point of this year’s WEF was Argentine President Javier Milei, who, during an “exceptionally warm bilateral meeting,” invited Swiss President Karin Keller-Sutter to visit Buenos Aires in 2025. The Trump Factor The opening of the current WEF coincided with the inauguration of Donald Trump, who, in recent months, has made numerous provocative statements and promises, swiftly beginning their implementation upon taking office on January 20. The U.S. president signed nearly 100 executive orders, including the repeal of 78 regulations enacted by his predecessor, Joe Biden. Among these were directives for all federal agencies and departments to address rising living costs and to end government-imposed censorship of free speech. The most significant orders included the U.S. withdrawal from the Paris Climate Agreement and the World Health Organization, as well as the declaration of a state of emergency at the U.S.-Mexico border to enforce strict immigration controls. In one way or another, the presence of the “new-old” president was felt across nearly all discussion platforms at the forum. On January 23, Donald Trump addressed the participants of the Davos Forum via video conference, outlining the following agenda:- NATO defense spending: Member states should increase their defense budgets from 2% to 5% of GDP to ensure a more equitable distribution of financial burdens within the alliance.- Trade tensions with the EU: The EU and its member states treat economic relations with the U.S. unfairly. European business regulations, including tax policies, disadvantage American companies, particularly in the tech sector, prompting Trump’s call for tariffs on European imports.- Criticism of the EU’s Green Deal: Labeling it as a “new green scam”, Trump emphasized that the U.S. would ramp up oil and gas production and expand power plant construction to become the “capital of artificial intelligence and cryptography”.- Oil prices and the Ukraine conflict: Trump suggested that lower oil prices from Saudi Arabia could help resolve the Ukraine conflict and urged Saudi leadership to take necessary steps, emphasizing their responsibility in the matter.- Tariffs on companies outsourcing production: Countries whose companies manufacture outside the U.S. will face tariffs to incentivize production relocation to American soil.- China's role in Ukraine: Trump called on China to support ending the Ukraine conflict, while stating his own efforts to mediate a peace deal between Russia and Ukraine.- U.S. domestic policy shift: A large-scale deregulation program is underway in the U.S., including tax cuts and potential elimination of diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) initiatives, which Trump views as discriminatory.Trump’s speech elicited mixed reactions among forum participants. His focus on protectionist policies and sharp criticism of international partners raised concerns about potential consequences for the global economy, particularly among European attendees. Additionally, his stance signaled an escalation in the strategic rivalry between Washington and Beijing, which is expected to play out through potential trade conflicts, tensions in the South and East China Seas, continued arms sales to Taiwan, and other geopolitical developments. The Europe Factor At Davos, Europe is traditionally represented by the European Union, with the United States as its primary political and economic partner. Ursula von der Leyen, re-elected as President of the European Commission and beginning her new term on December 1, 2024, addressed the forum on January 21. Her speech largely responded to challenges outlined by Donald Trump before the WEF began, setting out the EU’s key priorities for the coming years: overcoming economic stagnation, enhancing competitiveness, and further integrating the single market across all 27 member states. A central theme of her address was the “Competitiveness Compass” initiative, first introduced in late 2024. This strategy, shaped by recommendations from Mario Draghi’s influential report, aims to drive economic reform and growth within the EU. The European Commission planned to unveil the full document by the end of January. At Davos, Ursula von der Leyen effectively introduced the concept of “Europe United” as a counterbalance to “America First” and cautioned the U.S. against igniting a trade war with the European Union. She emphasized the importance of early engagement and dialogue on shared interests, stating: “Our priority will be to initiate discussions as early as possible, focusing on common interests and readiness for negotiations. We will be pragmatic, but we will always adhere to our principles. Protecting our interests and defending our values is the European way”. At the same time, the European Commission president highlighted the high level of interdependence between the European and American economic models. She underscored that the era of global cooperation has given way to intense geostrategic competition, stating: “The world's largest economies are competing for access to raw materials, new technologies, and global trade routes—from artificial intelligence to clean technologies, from quantum computing to space, from the Arctic to the South China Sea. The race is on”. Christine Lagarde, President of the European Central Bank (ECB) emphasized that Brussels must be prepared for U.S. trade tariffs which are expected to be more “selective and targeted”, especially given the “existential crisis” facing the EU economy. She also noted that the ECB is not overly concerned about the impact of inflation from other countries, including the U.S., on the eurozone. The UK was also represented at Davos, with its delegation led by Chancellor of the Exchequer Rachel Reeves. She used the trip primarily to promote Britain’s economic landscape, focusing on the country’s political and economic stability, its business-friendly environment, and recent government efforts to reduce regulatory barriers—all under the central message: “Now is the time to invest in Britain”. However, the extent to which this narrative aligns with reality remained beyond the scope of the Forum. The true assessment was left to the executives of major corporations with whom Reeves held meetings, including JPMorgan and Goldman Sachs, discussing investment opportunities in the UK's infrastructure and green projects. Additionally, the UK delegation engaged in negotiations aimed at restoring and strengthening ties with sovereign wealth funds and private investors from the U.S. and the Gulf states. The Ukraine Factor Due to the ongoing Ukraine conflict, Davos once again served as a prelude to the Munich Security Conference, which traditionally takes place in early February in Bavaria. While the war and Donald Trump’s influence shaped many discussions, Ukraine was not the central focus of the forum, resulting in a somewhat reduced emphasis compared to previous years. Ukraine’s interests at the World Economic Forum (WEF) were primarily represented by V.Zelensky, who took it upon himself to “educate” European politicians and “interpret” the signals previously sent by Donald Trump. His focus was on defense spending, emphasizing that a significant portion should go toward supporting the Kyiv regime, the presence of foreign troops on Ukrainian territory, and the need for “real security guarantees”. In the first days after taking office, the U.S. president made several key clarifications regarding his previously stated 24-hour timeline for resolving the Ukraine conflict — this period has now been significantly extended. The reason lies in the fact that, regardless of the revocation of Zelensky’s well-known decree, Ukraine must have a head of state authorized to negotiate and officially confirm any agreements or their outcomes. As of late January, no such figure was present in Kyiv, and Washington is aware of this reality. Switzerland, while emphasizing its neutral status (despite being designated by Russia as an “unfriendly state”), consistently maintains that it provides Ukraine only humanitarian aid and diplomatic support at Kyiv’s request. At the 2024 WEF, the well-known Bürgenstock Conference was announced, which later took place in the summer. However, in 2025, no similarly large-scale initiatives were introduced. Nevertheless, discussions at the Forum once again touched on the possibility of granting Switzerland the right to represent Kyiv’s interests on the international stage. Additionally, it was reported that a Swiss-Ukrainian memorandum was signed, with Ukrainian Economy Minister Yulia Svyrydenko representing Kyiv. The agreement focuses on the participation of Swiss private businesses in Ukraine’s reconstruction efforts. V.Zelensky used Davos as an opportunity to meet with world leaders, including German Chancellor Olaf Scholz, who had recently blocked additional aid to Ukraine. However, his main competitor in Germany’s upcoming snap Bundestag elections, Friedrich Merz, was more open to the idea of support, and Zelensky also held a discussion with him. Both meetings were held behind closed doors, and no details were disclosed. Meanwhile, German Green Party leader Robert Habeck managed to avoid an impromptu conversation with Zelensky, who had attempted to engage with him on the spot. At a January 23 briefing, Russian Foreign Ministry spokesperson Maria Zakharova commented on V.Zelensky’s speeches at Davos 2025, describing them, among other things, as “narcotic madness”. The Germany Factor Germany, still holding its position as the political and economic leader of the European Union, was represented at Davos by key political heavyweights: Chancellor Olaf Scholz, Economy and Climate Protection Minister (and Vice-Chancellor) Robert Habeck, and CDU/CSU Chairman Friedrich Merz. All three have been selected by their respective parties as key candidates for chancellor in Germany’s snap Bundestag elections scheduled for February 23, 2025. Given this, it was no surprise that they used the Swiss platform as part of their election campaigns. The current head of the German government had an objective advantage: he delivered a keynote speech on behalf of Germany, in which he focused on the presence of traditional standard factors (the largest economy in the EU; efficient small, medium and large businesses; government support for investments; low level of government debt), which should help to overcome the crisis. Regarding the United States, he declared his interest in maintaining close relations with the new administration, but “without false fawning and servility”. D. Trump and his team, according to him, will keep the whole world on edge in the coming years, but the German leadership will be able to cope with this. O. Scholz's main message is that constructive European-American interaction “is of decisive importance for security throughout the world and is the engine of successful economic development”. It is noteworthy that there were many empty seats in the hall and after the Chancellor's speech there were no questions for him for a long time, which greatly surprised the moderator of the session, K. Schwab. O. Scholz's closest associate, Finance Minister J.Kukis, who was appointed to this position to replace K. Lindner, who was dismissed in early November 2024, was participating in the Forum. He was unable to provide any special pre-election support to his boss during the Forum, and did not distinguish himself in any special way. Incidentally, K. Lindner himself preferred to remain in Germany and continue to fight there for the votes of voters, which are extremely necessary for the liberals to overcome the five percent barrier and get into the Bundestag. F.Merz, who is very likely the future head of the German Cabinet, and his possible future deputy R. Habeck also sought to prove their chances of winning the elections during their speeches. O. Scholz and F.Merz organized meetings with leading representatives of German business, trying to show which of them understood their problems better and was ready to solve them constructively. Despite all their differences, they were united on one issue - the need to soften the provision on the “debt brake” enshrined in the Basic Law (Constitution) and increase support for entrepreneurs. External observers considered that F.Merz was more convincing, including regarding the transatlantic economic vector. R.Habeck unexpectedly engaged in self-criticism during the podium discussion, stating that he initially believed that the difficult economic situation in the country was due to a short-term cyclical crisis, but it turned out that this was a consequence of a long-term structural crisis. Such “self-education” of the minister cost Germany dearly. During the Forum (January 22) in the Bavarian town of Aschaffenburg, an Afghan refugee subject to deportation committed a crime, killing a child and an adult who was protecting him. This event pushed the issue of migration regulation to the top of the election campaign agenda. Unexpectedly, F.Merz found himself in a sticky situation, when his parliamentary request as the leading representative of the opposition in the current Bundestag for stricter controls at the external borders of the FRG could only count on success with the support of the unpopular Alternative for Germany and the center-left Sahra Wagenknecht Union. From Davos, Olaf Scholz traveled to Paris for a meeting with Emmanuel Macron. The French president was unable to attend the Forum due to domestic political circumstances and the need to manage the situation on the ground. The two leaders discussed the prospects for cooperation between their countries in strengthening their economic and political frameworks, as well as the European Union as a whole. None of the three key chancellor candidates managed to present a clear vision for Germany’s economic and political future, one that would be based on creativity, radical progress, technological breakthroughs, and prosperity—transforming the country into an innovation powerhouse not only for Europe but for the collective West as a whole. This means that Germany risks falling behind, failing to establish itself as an economic model capable of competing on equal terms with Donald Trump’s transforming North American economic space.Under Friedrich Merz, Olaf Scholz, and Robert Habeck, Germany faces the danger of remaining trapped in the past, relying too heavily on its post-war economic miracle—Made in Germany—which was achieved through the brilliance of ordoliberal economists and engineers. Davos 2025 made it clear that leaning solely on past achievements is no longer enough to drive a radical leap toward the future. If the German political elite, represented by the “handshake” established parties, remains in such reactionary positions in relation to the need for qualitative changes in economic policy, then the German standard will have no chance to take a leading place among the world's innovation locations. Here we will briefly indicate that, according to the estimates of the authors of the global risks report, the main ones for Germany are (in descending order): a shortage of highly qualified labor, recession / stagnation of the economy, illegal migration, disinformation, and a shortage of energy resources. They are the ones that largely determine the content of the current election campaign for the German parliament. The China Factor Among the political heavyweights representing the countries of the Global South at Davos 2025, the participation of the Chinese delegation, led by Vice Premier of the State Council of the People's Republic of China Ding Xuexiang, stands out. In his keynote speech, he emphasized Beijing's commitment to economic globalization, which is “not a zero-sum game, but a process of mutual benefit and common progress” and declared that protectionism does not lead to success, and trade wars have no winners. Among the key messages were that China is economically attractive, does not seek a trade surplus, is ready to import more competitive and high-quality goods and services to achieve balanced trade, is open to investment from foreign companies, and is ready to solve problems faced by both domestic and foreign firms. While condemning protectionism, he emphasized the importance of multilateralism and the role of the UN. While mildly critical of the “new-old” US president, he never mentioned him by name. Ding repeatedly referred to Xi Jinping, including his initiatives on global development and security. As part of the Forum, Ding Xuexiang hosted a private luncheon with top global financiers and business leaders, including the CEOs of BlackRock, Bridgewater Associates, JPMorgan, Blackstone, and Visa. Discussions centered on China’s ongoing economic reforms, efforts to stabilize the real estate market, stimulate domestic demand, and attract foreign investment. Experts noted that global business leaders responded positively to Ding Xuexiang’s statements, signaling growing confidence in China’s economic direction. In general, he fulfilled the standard mission assigned to him: to increase the international community's confidence in China's economic policy and confirm its role as a key player in the global economy. At the same time, the Forum participants remained concerned about a slowdown in China's economic growth, especially in the context of a possible increase in tariffs by the United States. The Artificial Intelligence Factor One of the leitmotifs of the forum, along with rethinking economic growth, industrial development prospects, climate and restoring trust, were discussions on the rapid development of AI, its impact on the labor market, prospects and challenges associated with the integration of this technology into various sectors of the economy. Experts identified a few trends that will emerge by 2030. AI and automation will increase the demand of enterprises for specialists in the field of AI, big data analysis, digital marketing, and cybersecurity. About half of the current skills of such employees in these areas may become obsolete, which suggests the need for timely adaptation of secondary and higher education to such a challenge. Employees whose professions will become unclaimed due to automation, especially in traditional sectors, will have to undergo advanced training programs. Special attention in the expert sessions was given to the ethical aspects of AI application and the related problems of developing the necessary standards. Issues of international cooperation took an important place, including in the context of ensuring a fair distribution of the benefits of AI application, as well as minimizing the potential risks it generates for society (for example, possible discrimination and bias in algorithms, as well as the protection of users' personal data). In terms of geopolitical rivalry in the field of AI, the global race for leadership in this area, which has already begun between the United States, China and several EU countries, was discussed. Experts pointed out the concerns of the leaders of the latter regarding the need to strengthen the positions of European companies in this area. Strategies for government stimulation of innovation and support for businesses developing AI were discussed. In addition, the participants in the discussions considered the possibilities of using artificial intelligence technologies to achieve sustainable development goals, including combating climate change, improving healthcare and increasing resource efficiency. Examples of using AI to monitor the environment, optimize energy consumption, develop new methods of treating diseases, and improve various aspects of life were of interest. *** The World Economic Forum 2025 in Davos was predictably held under the sign of global challenges, the Ukraine conflict, and increased economic competition, set against the backdrop of geopolitical and geoeconomic changes. Børge Brende, summarizing the event, accurately noted that the current time is “a moment of serious consequences and uncertainties”. This is largely linked to the return of Donald Trump to the White House. At the Forum, the United States’ priorities in strengthening national interests were outlined, including the goal of reducing import flows. This move drew criticism from the European Union and other participants, who expressed growing concerns about the escalation of trade conflicts and the fragmentation of the global economy. The President of the European Commission highlighted the prospects for strengthening the EU’s competitiveness and increasing its independence, considering the intensifying rivalry between the American and Chinese economic spheres. In this regard, representatives of China advocated for reducing trade tensions and strengthening regional alliances, while Germany emphasized the current risks facing its economic standard, outlining the difficulties of finding ways to minimize them. The Ukrainian conflict once again became one of the central topics, but with the formal support of the leaders of the collective West, delegations from the global South showed a restrained reaction to V.Zelensky's speech and messages. Discussions about AI became quite meaningful. Overall, Davos 2025 and its participants confirmed the important role of the WEF as a platform for discussing global challenges and finding constructive answers to them. The need for collective efforts to solve the most pressing issues was noted. One of B. Borge's final messages: the only way to achieve progress in solving global problems is to work together and “find solutions that will make the world a better place”. It is evident that Russia could have significantly contributed to enhancing the effectiveness of this approach.