The Children of War
by Lila Roldán Vázquez
한국어로 읽기Leer en españolIn Deutsch lesen
Gap
اقرأ بالعربيةLire en françaisЧитать на русском
Abstract
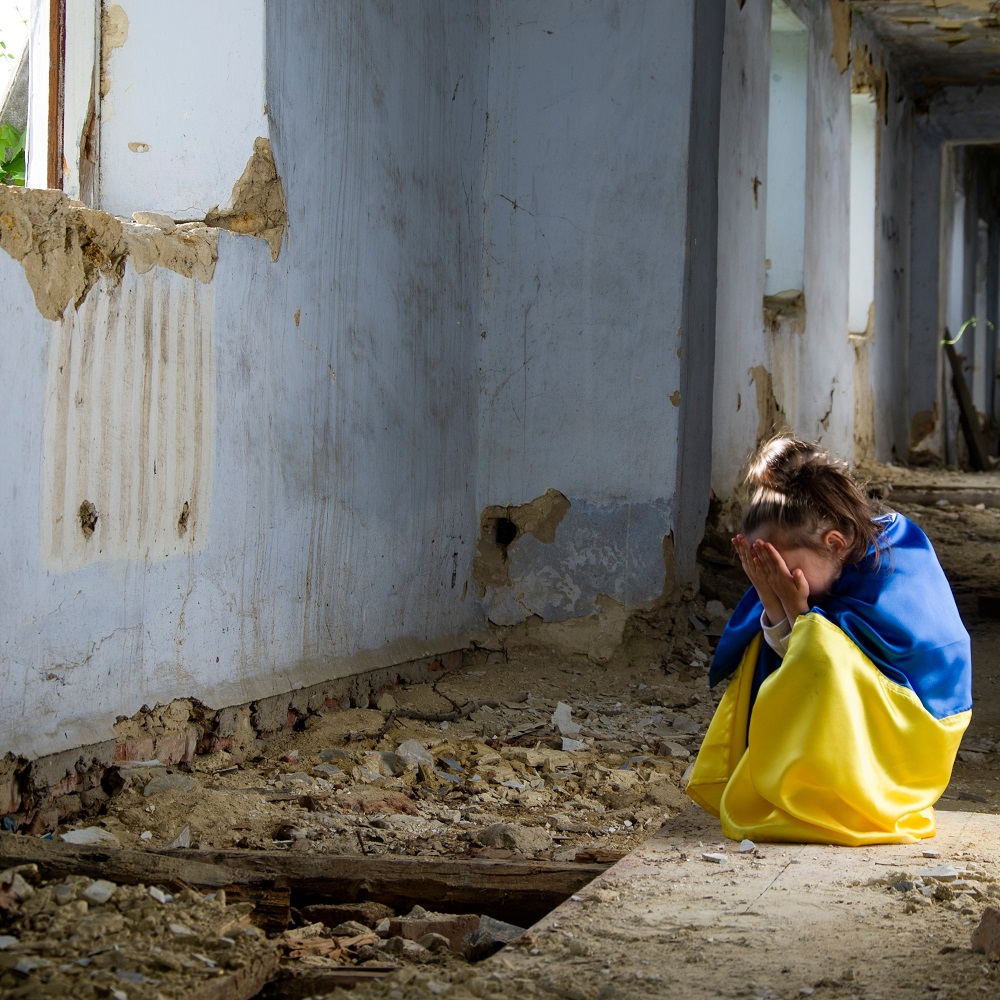
Russia’s full-scale invasion of Ukraine has shaken the world order and has seriously disrupted international peace and security.
The geopolitical impact, the causes of the war and the reasons invoked to justify the armed aggression have been widely discussed. Among the many facets of the war, there is one issue that requires special attention, since it constitutes, without a doubt, one of its most serious consequences: the death of hundreds of children and the abduction of thousands of them, in flagrant violation of humanitarian law.
We aim to analyze the circumstances and consequences of these actions, which may constitute a war crime, and to evaluate their impact in the medium and the long term.
Children as victims of the war
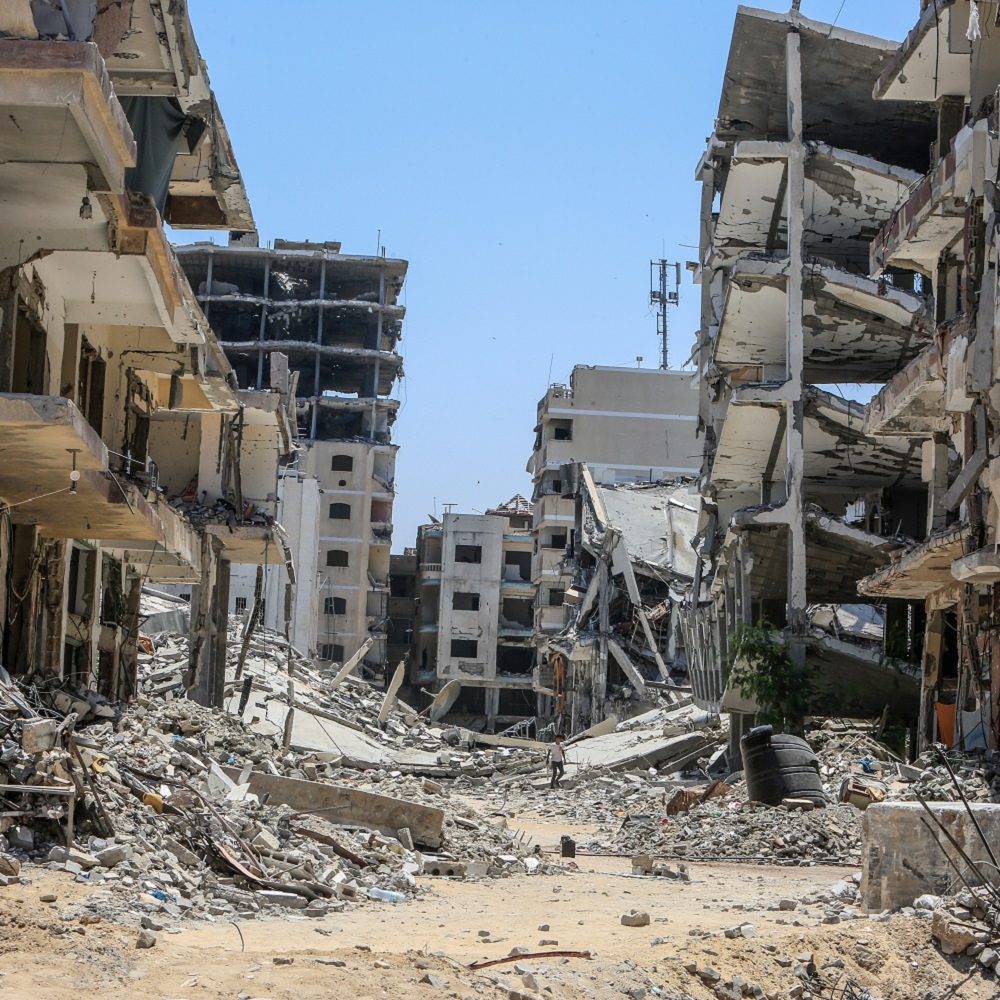
Motyzhyn is a village in the Bucha region, forty-five kilometers west of Kyiv, the capital of Ukraine. It was occupied by Russian forces in the days following the invasion of February 24, 2022, for about a month and a half. Several houses in the town were destroyed and its school partially demolished.
When the Russian troops had to withdraw, the bodies of five civilians who had been executed were found, with their hands tied behind their backs. Among them were the village’s mayor, her husband and their son, who had refused to collaborate with the invaders.
Today, the school in Motyzhyn is being rebuilt, but the children and young students who saw their teachers and neighbours die cannot forget the images of war. A group of teenagers trembles as they give their testimony. They express their fear of not being able to have a safe, peaceful life, of not having a future in their land. Their lives are marked forever.
They are not the only ones. The stories of children witness of atrocities number in the hundreds. There are thousands of children separated from their parents, either because they have died, or because the children themselves have been displaced away from the front of the war, or because they have been kidnapped and taken to occupied territories or outside of Ukraine, to Russia or Belarus.
In March 2022, just a month after the full-scale Russian invasion, the United Nations estimated that 78 children had already died and 105 had been injured.' Just over a year later, on June 1, 2023, the UN issued a report according to which the number of children killed in Ukraine since the beginning of the invasion reached 525. The report also stated that there were at least 1047 children injured in 289 cities, towns and villages throughout Ukraine, both in the areas controlled by the Government and in those occupied by Russia, from that same date.2
The UN Human Rights Monitoring Mission in Ukraine, deployed in 2014 in the wake of the occupation of the Crimean peninsula occupation and the armed conflict in the east of the country, stated that until June 2023, the Russian invasion of February 2022 has caused a total of almost 9.000 civilian deaths and more than 15.000 injuries, warning that the real number could be considerably higher, due to the difficulties faced by UN observers in accessing some areas of Ukraine where intense fighting was recorded. In October, the said Observation Mission updated the number of civilian deaths at almost 10.000 people and tens of thousands of wounded.
To the figures detailed in the referenced reports, which are not exhaustive, since no certain data is available on the areas occupied by the Russian Federation, we must naturally add the victims —-dead and injured children that have occurred since the date of evaluations so far. New cases are registered practically every day.
The war in Ukraine has not only caused death and injury to children and adolescents. Forced displacement, abandonment of their homes, disruption of schooling and a normal life, are also indelibly marking their lives. In the first days of the Russian invasion, millions of families were separated, mothers and younger children leaving Ukrainian territory while fathers and older siblings joined the national forces. These massive displacements to, preferably, neighbouring countries -Poland, Romania, Moldova- and from there to other destinations, were carried out under very precarious emergency conditions. Most of the displaced had to remain for long months in refugee camps. According to information collected by the United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF), some children had to escape from Ukrainian territory alone, thereby increasing their exposure to possible abuse, sexual exploitation and human trafficking. During the course of the war, there were also numerous internal displacements from Ukrainian regions where there is greater war activity to regions considered safer, with the consequent unavoidable consequences: housing precariousness, interruption of schooling and special difficulties for institutionalized or disabled children.
The Independent International Commission of Inquiry on Ukraine, established by the Human Rights Council on March 4, 2022, to investigate alleged violations and abuses of human rights, violations of International Humanitarian Law and related crimes in the context of the aggression against Ukraine by the Russian Federation (Resolution 49/1)3, documented sexual crimes and gender violence against civilians, in victims from 4 to 82 years of age. The Commission certified cases of children who were raped, tortured, illegally detained, murdered and injured in indiscriminate attacks with explosive weapons.
On April 4, 2023, the Council, through Resolution 52/32, Situation of Human Rights in Ukraine stemming from the Russian aggression, extended the mandate of the Commission of Inquiry for a new period of one year. This Resolution, approved by 28 votes (Argentina), 2 against (China and Eritrea) and 17 abstentions (Bolivia, Cuba, India and others), in its paragraph 17 “Stresses the importance of respecting, protecting and fulfilling the human rights of children and protecting children from all forms of violence, including sexual and gender -based violence, and emphasizes the importance of investigating and documenting violations and abuses of the rights of the child and violations of international humanitarian law, including forcible transfers and deportation, by relevant mechanisms, including the Commission of Inquiry”.4
In its October 2022 report, the Commission of Inquiry signalled that it had found evidence of the commission of violations of human rights and international humanitarian law corresponding crimes, by the Russian authorities, in areas under their control on Ukrainian territory: “The evidence collected demonstrates that the Russian authorities have committed the war crimes of murder, torture, rape and other sexual violence and the deportation of children to the Russian Federation”.5
Shortly after the full-scale invasion began, the Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe (OSCE) entrusted its Office for Democratic Institutions and Human Rights (ODIHR) with monitoring the situation in Ukraine. In the three reports submitted to date, in July and December 2022 and in July 2023, the ODIHR refers to the children’s situation.
In the first of those reports, the high number of hospitals and schools bombed by the Russian Army is recorded, in “apparent violation of their protected status under International Humanitarian Law”. The report indicates that, according to information from the Ministry of Education and Science of Ukraine, 1899 educational establishments were damaged and 215 were destroyed as of June 30, 2022.6
Also, in the OSCE’s sphere, the Moscow Mechanism adopted in 1991 allows its Member States to request the appointment of an ad hoc mission of independent experts to investigate a particular problem related to the human dimension of the OSCE, either in their own territory or in that of another Member of the Organization.
Ukraine first invoked the application of this Mechanism on March 3, 2022, with the support of 45 Member States. A mission of three experts appointed under this framework was given a broad mandate, which was to establish possible contraventions of OSCE commitments, violations and abuses of international human rights law and international humanitarian law; as well as possible cases of war crimes and crimes against humanity, including due to deliberate and indiscriminate attacks against civilians and civilian infrastructure; and to collect and analyse this information with a view to presenting it to the corresponding accountability mechanisms, as well as to the courts or tribunals with jurisdiction in the matter. The Mission, whose mandate was renewed twice, prepared three reports: in April and December 2022 and in June 2023.
In their First Interim Report of April 2022, the experts confirmed that the conflict has affected children in many different ways: first, they are among the direct victims of the war and, even if they are not directly victims, many of them have lost their parents, which implies a family life interrupted forever.
The report stated that, according to United Nations figures, more than half of the Ukrainian population under 18 years of age -that is, 4.3 million people- had been displaced from February 24, 2022, to that date. More than 1.8 million had left the country, while the remaining 2.5 million were internally displaced. Many of these children and adolescents —among them several thousand who were institutionalized before the conflict- have travelled alone, exposing themselves to numerous risks: dying or being injured during displacement, the risk of human trafficking and exploitation, the risk of child labour, the risk of forced recruitment or the risk of gender violence. Likewise, the Report stated that the conflict has caused the largescale destruction of civil infrastructure and the interruption of vital services, such as food, water and electricity or the provision of health services, all of which also affect children.7
In May 2022, Missing Children Europe also published a report on the children who were reported missing in Ukraine during the first 60 days of war and called on the European Union and its Member States to provide support and protection to all children and families at risk of entering that condition as a result of the conflict.8
Forced displacement and kidnapping of children
In early June 2022, on International Children’s Day, President Zelenskyi noted that as of that date, there were already 200.000 Ukrainian children who had been forced to leave the country and were dispersed in the territory of the Russian Federation. The purpose of those forced transfers of Ukrainian children, according to the president, “is not only to steal them, but to make those who were deported forget about Ukraine and unable to return.9
Ukraine has denounced, and Russia has admitted, the displacement of thousands of children to territories occupied by the Russian Federation or to its territory, although the figures indicated by both states differ.
At the end of September 2023, the official website of the Government of Ukraine that provides updated data and consolidated information on children suffering from the consequences of the armed conflict, registered 19.546 deportees or forcibly displaced minors. According to statements by Ukrainian officials, this figure includes children who have crossed the border with the Russian Federation accompanied by their parents. It would also include those children sent —presumably with paternal consent- to summer camps.
For its part, the Russian Federation maintains that approximately 744.000 Ukrainian children, transferred for reasons of “evacuation”, “medical treatment”, “vacation” or “rehabilitation travel”, now live in Russia or Russian-occupied territories. As of July 2023, the office of the Russian Federation Commissioner for Children’s Rights, Maria Lvova-Belova, reported that of the approximately 4.8 million residents of Ukraine “accepted” in Russia since the beginning of the war, more than 700.000 would be minors, the vast majority of whom would have arrived in that country with their parents or other relatives.10
There was information and statements coming from Russia prior to that date, which would make said figure plausible.11-11bis
The Ukrainian authorities have stated, however, that these figures could be exaggerated: Commissioner for Human Rights, Dmitro Lubinets, suggested that the number of children could reach 150.000.12 Meanwhile, the President’s Commissioner for Children’ Rights, Daria Gerasymchuk, estimates that there could be “between 200 and 300 thousand abducted children”.13
Although all the information available coincides in a very high number of deported minors, the difficulties in establishing accurate figures are evident, given the lack of information shared between the authorities of both countries and the complexity of the regulatory situation, since some Ukrainian territories have been “annexed” by the Russian Federation (without the recognition of the international community) and Putin’s government applies the legislation of that country to them, regarding matters such as nationality, citizenship, adoption and custody of minors.
The difficulties that this creates from the point of view of Private International Law, in cases of parents or legal guardians of minors who require their return, as well as of Public International Law in restitution claims filed by the government of Ukraine, must be the subject of a detailed study.
In its report to the Human Rights Council, the Monitoring Mission in Ukraine points out the lack of information about Ukrainian children, some of them institutionalized and with physical and intellectual disabilities, who have been transferred to localities within the occupied zones or deported to Russia. Cases are mentioned of children who were sent to summer camps in Russia, supposedly with their parents’ consent, but who were then not returned to their homes. The UN Mission warns that the government of the Russian Federation did not identify those children or reunite them with their families.14
The Independent International Commission of Inquiry on Ukraine identified three situations in which Russian authorities have transferred unaccompanied Ukrainian minors from an area controlled by them in Ukrainian territory to another area in the same situation or to the territory of the Russian Federation: i) minors who lost their parents or contact with them during the hostilities; ii) minors who were separated as a result of the arrest of their parents; iii) minors placed in public institutions. According to the Commission, in some of those cases the transfers were made in violation of International Humanitarian Law and qualify as illegal transfers or deportations, which constitutes a war crime.
Another worrying aspect of the deportations is also pointed out, which arises from information provided by Commissioner Lvova -Belova, as well as from interviews with relatives or legal representatives of some children and from press information, and which refers to the placement of minors in foster families in the Russian Federation, with the ostensible goal of having them remain in that country for extended periods of time.15
Indeed, of the 31 minors transferred to the Russian Federation from a public institution in the city of Donetsk in May 2022, one was placed in the custody of Mrs. Maria Lvova- Belova, who in September of that year announced that the minor had been granted a Russian passport and he was now “ours”. This is not a unique case, as other abductions of Ukrainian children by Russian families have already been confirmed.
Regarding the response of the Russian government to the concerns raised by the Commission and by public opinion in general, regarding an eventual mechanism agreed between the two States for the return of transferred children, Foreign Minister Sergey Lavrov declared in September 2023 that “If families are located, we will assist them in reunifying with those children”.16 Mrs. Maria Lvova-Belova in turn pointed out that if a child “has a parent with full parental rights, the family has every possibility of being reunified”.17
However, there are very few cases in which transferred minors have been returned to their parents, in response to private initiatives by the parents, legal guardians or the minors themselves. Occasionally, third States have also intervened to obtain the return of some children. However, these are always specific cases: the majority of transferred minors have not returned to Ukraine or been able to reunite with their parents; on the contrary, they have remained in the Russian Federation for long periods of time, since their abduction.
These actions contravene the legal requirement of International Humanitarian Law, in the sense that evacuations of children must be temporary and can only occur in cases of force majeure for reasons of health or medical treatment. Considering these parameters, the Commission considered that transfers that continue over time are assimilated to illegal deportations, which constitutes a war crime.
The reports of the OSCE-ODIHR, by direct mandate of the Organization or in application of the Moscow Mechanism, also refer to forced transfers of civilians and in particular to forced transfers and deportations of children. Furthermore, the Observation mission carried out by the third ODIHR report on application of the Moscow Mechanism in June 2023, was specifically designated to address that issue and was expressly mandated to “...establish the facts and circumstances involving possible violations of relevant OSCE commitments, violations and abuses of human rights and violations of International Humanitarian Law and Internacional Human Rights Law, as well as possible cases of war crimes and crimes against Humanity, associated with or resulting from the forcible transfer of children within areas of the territory temporary controlled or occupied by Russia and/or their deportation to the Russian Federation...”.18
In their reports, the experts address with great concern the forced transfers and deportations of unaccompanied children, signalling that the policies applied by the Russian Federation in such cases could be contrary to International Law. The last of these reports established that the reasons more commonly invoked to justify the organized displacement of these children are: i) evacuation for security reasons; ii) transfer for adoption or foster care purposes; and iii) temporary stays in the so-called “recreation camps”.
“Evacuation for security reasons” was invoked as legal support for the massive transfers of the civilian population, including children, which were carried out from the Ukrainian regions so called “Donetsk and Luhansk republics”, even from a week prior to the invasion of 24 February 2022.
By the 20th, the authorities of the Rostov region, in the Russian Federation, reported that more than 2.904 children from those regions of Ukraine had entered their territory.
Regardless of the reasons invoked for their transfer or the form of integration: whether by adoption —preferably in cases of children from Crimea— or by virtue of temporary guardianship or custody, Ukrainian children find themselves in an entirely Russian environment, including language, customs and religion and are exposed to information campaigns aimed at re-educating them, as well as giving them military education. The authorities of the Russian Federation do not take any measures to actively promote the return of Ukrainian children to their country, but rather create obstacles for families seeking to recover them.
The experts appointed by the ODIHR reported that, according to statements by officials and the media, the Russian Federation transferred children from occupied territories to “holiday camps”, but once transferred to Crimea or to Russian territory, they are not returned to their families as originally agreed. Cases are cited in Kherson, where in the wake of violent attacks and schools closures, some parents accepted Russia’s offer to take their children to camps in Crimea but were then unable to contact or retrieve them.19
Some Ukrainian minors were even forcibly transferred to Belarus, as it was admitted by the director of the Belarusian Red Cross, Dzmiytryi Shautsou, who pointed out that these transfers had been made for rehabilitation treatments. The authorities of that country recently admitted that more than a thousand children are in Belarus “for health reasons’.
The ODIHR experts assessed that “although certain displacements carried out by the Russian Federation were in line with its obligations under International Humanitarian Law, other practices of non-consensual evacuation, transfers and prolonged displacement of Ukrainian children constitute violations of International Humanitarian Law, and in certain cases involve serious violations of the Geneva Convention IV (GCIV) and war crimes, particularly a violation of the prohibition of forcible transfer or deportation under article 49 of the GCIV”.20
They also considered that altering the nationality of Ukrainian children is a violation of Article 50 of the GCIV.
Imposition of citizenship and illegal adoptions
Just three months after the large-scale invasion of Ukraine began, President Vladimir Putin issued a Decree (330/2022) to facilitate the procedures for attributing Russian citizenship to those Ukrainian children who were not under their parents’ care, which opens the way for subsequent adoption by Russian families.21 This decree also grants directors of orphanages located in occupied territories the possibility of demanding Russian citizenship for minors under fourteen years of age, admitted to the institutions under their charge, without asking for their consent.
In January 2024, Putin issued a new Decree (11/2024) officially aimed at facilitating the process of granting Russian citizenship to foreign nationals and stateless persons. This decree establishes that Ukrainian orphans and children who are not in family care can receive Russian citizenship by Putin’s personal decision alone, without considering all or some of the requirements of federal legislation.22 The naturalization process can be carried out by whoever has legal guardianship of the child or by the head of a Russian organization responsible for the minor. According to the Commissioner for Human Rights of Ukraine, Dmytro Lubinets, the next step after the granting of Russian citizenship is adoption by a Russian family: in this way deported Ukrainian children no longer count de jure as Ukrainians on Russian territory.
The observation missions designated to evaluate possible violations of International Humanitarian Law in the framework of this war, had already expressed their concern about the adoption of the first decree (330/2022), highlighting that International Humanitarian Law prohibits the Russian Federation from changing the status of those children and that the procedures of the Russian Federation do not appear to include measures for the reunification of families or to ensure the principle of respecting the child’s best interest. Applicable international law prescribes that children have the right to retain their identity, name, nationality and family relationships and that children should not be separated from their parents against their will, except when the separation is carried out in accordance with due process of law and if it serves the children’s best interest.
Following the issuance of Decree No. 330 by President Putin, several Russian officials admitted that Ukrainian children from occupied regions of Ukraine had been “adopted” by Russian families. A Russian-appointed Kherson regional administration official, speaking to the Russian news agency RIA Novosti, announced that starting February 24, 2022, children born in that region would automatically acquire Russian nationality. Likewise, orphaned children would also be registered as Russian citizens.23
Shortly after, Ms. Maria Lvova-Belova stated that several Russian families had obtained temporary custody rights over 108 orphans from the Donbass region and, as she noted, “now that the children have received Russian citizenship, temporary custody can be transformed into permanent”.24 In October 2022, Lvova-Belova announced that already 350 orphaned children from Donbass had been placed in foster families in sixteen regions of the Russian Federation. The Commissioner’s Office reported that months earlier, in February 2022, around 2.000 orphaned children or children placed in public institutions without parental control, had been transferred to the Russian Federation and subsequently, those from Donetsk and Luhansk were placed in foster families or in public institutions.
Lvova-Belova declared that she herself had adopted a fifteen-year-old minor transferred to the Russian Federation in a group that came from a public institution in the city of Donetsk. In a bulletin from her Office (2023), it was recorded that the other minors in that group were placed in family centers and later in foster families or under temporary custody of residents of the Moscow region.
One of those minors, 17 years old Bohdan, was effectively “placed” in the care of a Russian family, given Russian documents, and recently received a summons to report to a recruiting office. Which means that he would probably have been forced to fight against his own country’s army. Bohdan, who in March 2023 had already tried to escape and return to Ukraine, was detained at the border. He was finally able to return to his country last November, thanks to the notoriety that his case gained and efforts from the governments of Ukraine and Qatar.25
Children’s relocations to the Russian Federation for the purposes of adoption or custody has been practiced with children from Crimea since the peninsula’s illegal annexation in 2014 and the subsequent application of Russian family laws. In October of that same year, the so-called Ministry of Education, Science and Youth of the occupation administration of the peninsula made public an initiative called the “Train of Hope”, so that “families coming from other regions of the Russian Federation” can contact orphans and children who were not under parental care, with the aim of “placing” them in their families.
Within the framework of the investigations conducted by designated international experts, the Representative of the President of Ukraine in the Autonomous Republic of Crimea reported that more than 1.000 children from the peninsula could have been deported to various parts of the Russian Federation through this initiative.
The new legislation on the adoption of Ukrainian minors ordered by President Putin has even benefited a renowned Russian congressman, Sergey Mironov, president of the Only Russia political party -of the opposition authorized by the Russian State- who would have adopted with his wife, Inna Varlamova, a little two-year-old girl, Margarita, transferred to Moscow along with 47 other minors from a center for infants in Kherson. According to statements from the centre’s employees, it was Russian soldiers and officials who took Margarita —who had already been previously visited by Mrs. Varlamova, and shortly after returned to “evacuate” the rest of the children.26
Children forcefully transferred to Russia must attend schools with local curricula and books —-even some that have been edited or adapted since the beginning of the war to give a biased vision of History-, they are not allowed to speak Ukrainian and must express pro-Russian feelings, singing for example the national anthem of the Russian Federation, as part of a re-education campaign which includes “patriotic” and military instruction.
The Moscow-appointed governor of the Zaporizhia region -which, although illegally annexed by Russia, is not fully occupied by its army- reported that the Russian Ministry of Culture had transferred more than 300 children from that region to Moscow and Saint Petersburg, in order to educate them in Russian culture, within the framework of a program that foresees the participation of more than 2.500 schoolchildren.
From the Russian Federation, the governor of the Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous District, announced the launch of a three-year program in which more than 500 Ukrainian children from the Volnovaya region, in the occupied zone of Donetsk, will participate and will visit cultural heritage sites in Moscow, Saint Petersburg and Nizhny Novgorod.
The forced reintegration and re-education of a large number of Ukrainian children can have serious ethnic and sociological consequences, causing a severe impact on the future projection of Ukrainians as a national group, by constituting a factor of disruption in its continuity.
Psychological Impact
The row of seven or eight children standing in front of a group of academics and foreign visitors, in the classroom of a school in which others are still completely destroyed, is a devastating image. They are teenagers, perhaps between twelve and sixteen years old, and some of them are holding hands to support each other. Only two or three of them speak, sometimes through tears; the others nod with eyes still full of terror. They have seen death and destruction and when they speak, they tell how hard the experience of the Russian occupation has been, but they also talk about their future. They are convinced that it will be very hard, that they will have a very different life than the one they had or dreamed of eighteen months ago, although they are also sure that they want to fight for that future. They don’t want to leave Ukraine, they say, they just want to be left alone to recover, study and rebuild their country.
In its report on the psychological impact of the war on Ukrainian children and adolescents, “A Heavy Toll”, the nongovernmental organization Save the Children estimated that “the boys and girls in Ukraine have been forced to hide underground for an average of 920 hours in the last year (2022) - which is equivalent to 38,3 days, or more than a month- since the reactivation of the conflict on February 24 of last year’. They have been “constantly faced with danger” with “the psychological distress of having witnessed violence, separation from family and friends, displacement or lack of access to education”.
The fighting has forced the closure of schools in many parts of the country and in those cases only the possibility of online education remains, but less than 30 percent of Ukrainian children have access to an individual computer and frequent power outages make access difficult for those who do have them. Many of them have lost years of education due to the duration of the conflict in the east since 2014, the quarantine due to the COVID-19 pandemic and the ongoing hostilities in the country.27
As mentioned above, the United Nations Independent International Commission of Inquiry on Ukraine has documented cases in which minors have been raped, tortured, illegally confined, killed or injured in indiscriminate attacks with explosive weapons. This exposure to permanent explosions, crimes, forced displacement and separation from family members profoundly affects the well-being and mental health of children and adolescents. 75 % of parents report that their children have symptoms of psychological trauma and that 1 in 6 children report memory problems, attention deficits and a decrease in their learning ability. The hostilities have had a significant impact on children’s right to education due to damage or destruction of hundreds of schools and daycare centers.28
Minors in recreational or educational fields. The ZMINA Center for Human Rights, a Ukrainian non-governmental organization, has verified the existence of at least 43 “camps” in the occupied areas of Ukraine, where the occupation authorities intern minors. Likewise, according to statements by Russian officials, a distribution of children from the occupied areas was organized in different centers for minors in Russian territory, assigning correspondence between districts or regions of Ukraine and regions of the Russian Federation.
In cases of parents in a vulnerable situation, or who, due to the violence of the fighting in the area or the lack of housing or food, wish to protect their children, the occupation authorities offer them to sign a “consent for the transfer” document for a certain period of time, which does not specify the person who will take care of the minor. At the same time, the child’s documents and birth certificate are confiscated. The children are not returned at the end of the “recreation stay”: in some cases, the “stay” is extended, in others the children are transferred to another camp without their parents’ knowledge, and sometimes Russian regional leaders declare that the children will not return.
One of the main objectives of internment in these camps would be the re-education of minors: according to the ZMINA report, at least 32 of the 43 camps are “actively and systematically involved in providing education and cultural development” of the Ukrainian children according to the Russian system. The program includes narratives about the nature of the large-scale invasion and the history of Russian-Ukrainian relations. Minors receive lessons on “main or important topics”, such as the peace-keeping operations of the Russian army in Nagorno-Karabakh, South Ossetia or Kazakhstan, the defeat of terrorists in Syria, the protection of Russian nationals and the “liberation” of the Donbass. And they must speak exclusively in the Russian language.
The ZMINA'’s report recalls that according to the Convention on the Rights of the Child, States are obliged for respect the right of the child to preserve his or her identity, including nationality, name and family relations as recognized by law without unlawful interference. ... Due regard shall be paid to the desirability of continuity in a child’s upbringing and to the child’s ethnic, religious, cultural and linguistic background. The education of children under 15 years old, orphaned or separated from their families as a result of the war, should be entrusted to people with the same cultural traditions and, as far as possible, of the same nationality, language and religion.29
The Ukrainian government has established in Kyiv a center for the care of minors affected by the war, whether they are attacks’ survivors, recovered from deportations or who have remained in a filtration center: the Center for the Protection of Children’s Rights, Minors are received there to give them support; they usually have an initial conversation with those responsible for the Center and are provided assistance with a multifunctional team of doctors, psychologists and other professionals.
Margarita, 6 years old and her sister Xenia, 12, both of them born in Mariupol, recently passed through that Center. They had been deported to Russia and once recovered, were able to reunite with their mother. Their father is still a prisoner in the Russian Federation.
And there now is Oleg, 12 years old, who gives a heartbreaking testimony: coming from a small town near Mariupol, he remembers the night when he heard 22 “Grads” explosions and shortly after the town was occupied. Oleg and his family spent two months in a basement, without bread or running water. One day when his mother and aunt went to another town in search of food, explosions were heard near the shelter. Oleg went out and found bodies of his neighbours lying on the street. Russian soldiers detained him, and he spent two months in a “filtration camp” until his family was able to rescue him. Today, Oleg suffers from eating disorders, psychological disorders and aggressiveness.
Minors in “filtration camps”. Particular attention should be given to cases of minors who, by themselves or with their parents or relatives, have been detained by the Russian military or authorities appointed by the Russian government, for prolonged periods of time, in order to determine their status and loyalty to Ukraine. The “filtration” consists of a process of interrogating civilians from territories occupied by Russia in its military campaign, to find out their political opinions. It also includes the collection of biometric data and the requisition of their personal effects, including their cell phones. This process can last several hours or be extended for more than a month. If the parents of a minor fail to “approve” the filtration and are detained or forcibly disappeared, the minor will be deported to the Russian Federation.
In September 2022, United Nations Under- Secretary General for Political Affairs and Peace -Building, Rosemary DiCarlo and Under- Secretary General for Human Rights and Head of UN Haigh Commissioner for Human Rights Office (OHCHR) in New York, Ilze Brands Kehris, presented reports to the Security Council, in which they addressed the “filtration” system practiced by Russia in the occupied Ukrainian territories. Rosemary DiCarlo, while mentioning the very high number of refugees and internal displaced people provoked by the war, emphasized that the persistent reports of forced displacements, deportations and the so called “filtration camps” are extremely worrying and demanded that such information be investigated with due diligence and with the cooperation of competent authorities. She added that the International Committee of the Red Cross and the UN Human Rights Monitoring Mission in Ukraine must have free access to all the individuals detained in connection with the war.
llze Brands Kehris informed the Council that the OHCHR has verified that the Russian armed forces and armed groups related to them have subjected Ukrainian citizens to the practice of “filtering”, a system of security checks and collection of personal data during which they practice detailed searches and interrogations, and women and girls are at risk of sexual abuse.
The Permanent Representative of the Russian Federation to the United Nations responded to these presentations that the term “filtration” does not have a clear definition in International Humanitarian Law and that the identification of Ukrainian citizens who want to emigrate to the Russian Federation is a normal practice for any army. Recalling that his country is the largest recipient of Ukrainian refugees, he underlined that this is a registration process, not “filtration.”30
International reaction
The Convention on the Rights of the Child, to which the Russian Federation is a party, prescribes in its Article 6 that “States Parties recognize that every child has the inherent right to life” and that the Parties “shall ensure to the maximum extent possible the survival and development of the child”.31
Given the increasingly critical conditions for minors in war zones, the UN General Assembly created in 1997 the office of the Special Representative of the Secretary General for Children in Armed Conflicts, with the mandate of evaluating the progress, the measures adopted, and the difficulties detected in the protection of children in situations of armed conflicts. In a 2004 report, the Special Representation detected the six mayor violations against children committed in that context, one of which is the abduction of children. In 2015, following a new report that -particularly evaluating the situation of children in armed conflicts in African countries— highlights this crime, the Security Council adopted Resolution 2225 (2015) on the subject in which, among other recommendations, the resolution called for the “immediate, safe and unconditional” release of children kidnapped during the conflict.32
In July 2022, once a pattern of violations against children in the framework of conflict had been proved, Ukraine was included as a “situation of concern” in the UN Secretary General’s Annual Report on Children and Armed Conflicts. From this inclusion, the Organization has the responsibility of controlling and reporting on serious violations against children, which has been accomplished through the UN Human Rights Observation Mission (created previously, in 2014, following the invasion of Crimea) and from 2022, also through the Independent International Commission of Inquiry on Ukraine, whose reports we have commented on.
In an almost unprecedented decision -with the only exception of Libya in 2011-, on April 7, 2022, the United Nations General Assembly decided the suspension of the Russian Federation from the Human Rights Council, by 93 votes in Favor, 24 against and 58 abstentions (Argentina voted in Favor). In the text of the Resolution, the General Assembly expresses “grave concern at the ongoing human rights and humanitarian crisis in Ukraine, in particular at the reports of violations and abuses of human rights and violations of international humanitarian law by the Russian Federation, including gross and systematic violations and abuses of human rights...”.
In its decision, the General Assembly considered the expressions of concern by the High Commissioner for Human Rights, Michelle Bachelet, as well as the latest update on the human rights situation in Ukraine by the human rights monitoring mission in Ukraine, of 26 March 2022.33
At the Latin-American regional level, the Organization of American States (OAS) approved a Communiqué34 and a Resolution35 condemning the Russian Federation for the invasion of Ukraine, and finally decided to suspend it as an Observer Member of the Organization.36
The European Parliament also adopted a decision on this issue. In July 2023, the European body issued a Joint Motion for a statement on the detention of two Ukrainian minors by Russian authorities and the denunciation of their actions against minors, citing numerous reports on the oppression of Ukrainian children, “the victims most vulnerable of the Russian war of aggression”. Parliament mentions figures of deceased and injured minors and those deported to Russia (around 19.500), as well as those missing (3.924) and condemns the deliberate Russian targeting of minors through measures that include forced transfer within the territories of Ukraine temporarily occupied by Russia, illegal deportations to Belarus and Russia, illegal adoptions and attempts to impose re-education on them.37
The Parliamentary Assembly of the Council of Europe (PACE) adopted a Resolution in April 2023, in which it stated that the forcible transfer and Russification of Ukrainian children by the Russian Federation “indicates an intention to destroy Ukraine and Ukrainian identity, as well as the cultural and linguistic characteristics of its people” and highlighted that “the forced transfer of children from one group to another with the intention of destroying, totally or in part a national, ethnic, racial or religious group is considered a crime of genocide” according to the Convention against Genocide, in the first pronouncement of an international organization in that regard.38
In November of that same year, PACE approved the creation of a Special Committee for Ukrainian Children’s Affairs and in January 2024 it adopted Resolution 2529 (2024) in which “the Parliamentary Assembly firmly reiterates its condemnation of the full-scale war of aggression being waged by the Russian Federation against Ukraine and the massive violations of the rights of Ukrainian children, who are particularly vulnerable victims of this war. Children should never be used as means of exerting pressure, or as war trophies”. Through the Resolution, “The Assembly calls upon member States’ parliaments to enhance their political support towards meeting the objectives of the humanitarian response plan for Ukraine, with a specific emphasis on the needs of internally displaced children and their families”.39
The kidnapping and transfer of Ukrainian children was the crime -a potential war crime for which, unlike the economic sanctions applied to institutions and individuals of the Russian Federation, international justice held President Vladimir Putin directly responsible. In late February 2022, International Criminal Court prosecutor Karim Kahn opened an investigation for war crimes and crimes against Humanity. Slightly more than a year after, on March 17, 2023, the Pre-Trial Chamber of the International Criminal Court (ICC), with the support of the UN, issued an arrest warrant against Russian President Vladimir Putin, in connection with alleged war crimes related to the deportation and “illegal transfer” of Ukrainian children. The international arrest warrant is extensive to the Russian Government’s Commissioner for Children, Maria Lvova-Belova.
In his statement on the decision, Prosecutor Kahn indicated that, based on the evidence collected, there are sufficient indications to believe that Putin and Lvova-Belova bear criminal responsibility for the illegal deportation and transfer or Ukrainian children from occupied areas of Ukraine to the Russian Federation. He added that many of these children have been put for adoption in that country and that, by decree, President Putin had modified the applicable law in order to facilitate the granting of Russian citizenship to these children and, consequently, expedite their adoption by Russian families. Prosecutor Kahn also pointed out that these actions, among others, demonstrate the intention to permanently separate these children from their country of origin.40
The recovery of minors abducted by the Russian Federation is extremely difficult, given the particular conditions in which deportations take place and the subsequent distribution of children in territories occupied by Russia or in its own extensive territory, to which is added the change of identity through the granting of Russian nationality and adoptions. And as Belgian diplomat Mariam Lambert, who works with a non-governmental organization in the recovery of Ukrainian children, says: “they must be brought back quickly, because the more time passes, the more difficult it will be to track them and it will be much more traumatic for the children, after a new transfer, a new change in their lives, with the consequent psychological impact”.
Many States and non-governmental Human Rights organizations constantly demand that Russia cease these kidnapping and deportation actions and return the minors currently in its possession. Recently, efforts carried out by Qatar have managed to return several minors between two and seventeen years old to Ukraine and their families, four the first time in October 2023 and six more in the first days of December the same year. Qatar also mediated for the return of Bohdan, a Ukrainian teenager who had been placed with a foster family in Moscow province and then summoned to military service, as we mentioned above. 41-41bis
In December 2023, the Ukrainian Government convened the first meeting of the International Coalition of Countries for the Return of Ukrainian Children, which was attended by seventy-two high-level representatives from several countries - Canada, Qatar, the United Kingdom, the United States, Norway, the Netherlands, Estonia, among others- and international organizations such as the United Nations Observation and Monitoring Mission, UNICEF, the OSCE and the Council of Europe, among others. The objective of this international coalition is to support Ukraine in the return of forcibly transferred minors, as well as their rehabilitation and reintegration.
Unfortunately, between the noise of war cannons and the geopolitical confusion on the international scene, the tragedy of the Ukrainian children is not adequately addressed by the international media nor, consequently, sufficiently known. It is, however, one of the most worrying aspects of this war, in which Putin seeks precisely the extinction of the Ukrainian identity and the people of Ukraine as an independent nation.
The world, Western or not, must open its eyes to this true tragedy and demand in every stance the restitution of the children of Ukraine and the interruption of a practice that defies all moral parameters and international coexistence.
References:
1
United Nations. “One month after the war, note that half of Ukraine’s children have been displaced”. 15 March 2022. https://news.un.org/es/story/2022/03/1506172
2
United Nations. “More than 1500 children dead or injured in Ukraine’s war”. 1 June 2023. https://news.un.org/es/story/2023/06/1521552
3
Resolution 49/1 adopted by the Human Rights Council, March 4, 2022. Situation of Human Rights in Ucrania following the Russian invasion.
4
Resolution 52/32 adopted by the Human Rights Council,, April 4, 2023. Situation of Human Rights in Ucrania following the Russian invasion.
5
International Independent Investigative Commission Report to the UN General Assembly. October 18, 2022
6
OSCE - Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe - Office for Democratic Institutions and Human Rights Interim Report on reported violations of international humanitarian law and international human rights law in Ukraine.
7
OSCE - Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe - Office for Democratic Institutions and Human Rights 132/2022 - ODIHR.GAL/26/22/Rev.1 - Report of the OSCE Moscow Mechanism’s mission of experts entitled ‘Report On Violations Of International Humanitarian And Human Rights Law, War Crimes And Crimes Against Humanity Committed In Ukraine Since 24 February 2022'.
8
War on Ukraine responsible for surge in missing children cases, Missing Children in Europe, 25 May 2022. https://missingchildreneurope.eu/press-releaseimed-2022/
9
President Zelenskyi: 243 Ukrainian children have died, 446 have been injured and 39 remain disappeared, warning that these numbers could be even bigger, since there is no reliable information on the zones occupied by Russia. The Associated Press, “Volodymyr Zelenskyy Says 200,000 Children among Ukrainians Forcefully Taken to Russia,” First post, 2 June 2022, https://www.firstpost.com/world/volodymyr-zelenskyv-says-200000-children-among-ukrainians-forcefully-taken-to-russia-10747981.html
10
https://www.currenttime.tv/a/v-rossiyuvyvezli-bolee-700-tysyach-ukrainskihdetey/32527102.html
11
In May 2022, Russian news agency TASS published declarations from an official of the Russian Federations’ Ministry of Defense, Mikhail Mizintsev, on the transfer of a million people from Ukraine to Russia, including approximately 200.000 children, in the previous two months. The official added that this figure included more than 1.800 children who had been “evacuated to the Russian Federation” the day before from dangerous zones in Donetsk, Luhansk and other Ukrainian regions, “without the participation of the Ukrainian authorities”. 2 In July 2022, the same TASS agency reported that more than 2.8 million Ukrainians had entered the Russian Federation from Ukraine, including 448.000 children, in a dispatch collected by Human Rights Watch (09/2022) and by the OSDE’s Office for Democratic Institutions and Human Rights (12/2022). “We had no choice’: ‘Filtration’ and the Crime of Forcibly Transferring Ukrainian Civilians to Russia”, Human Rights Watch, 1 September 2022, https://www.hrw.org/report/2022/09/01/we-had-no-choice/filtration-and-crime-forciblytransferring-ukrainiancivilians#fin107.
11 bis
За год с Украины и из Донбасса на территорию РФ прибыло 5,3 млн беженцев, ТАСС, 20 февраля 2023.
12
Кількість незаконно вивезених у росію українських дітей може сягати 150 тисяч, Укрінформ, 17. 2. 2023.
13
У Офісі Президента заявили, що у росії створили понад 70 таборів для "перевиховання" депортованих дітей з України, Рубрика, 23 квітня 2023
14
Head of UN Human Rights Monitoring Mission in Ukraine presents the latest human rights report 06 October 2023. https://ukraine.un.org/en/248423-head-unhuman-rights-monitoring-mission-ukraine-presents-latest-human-rights-report.
15
UNGA - A/78/540 Promotion and protection of human rights: human rights situations and reports of special rapporteurs and representatives. Independent International Commission of Inquiry on Ukraine.
16
See United Nations Web TV, “Press conference: H.E. Mr. Sergey Lavrov, Minister of Foreign Affairs of the Russian Federation”, September 23, 2023.
17
See Maria Lvova-Belova, “Activities of the Russian Federation Presidential
Commissioner for Children’s Rights Maria Lvova-Belova to protect children during a special military operation”, The Bulletin, no. 1, 4 April 2023 (2023).
18
ODIHR.GAL/37/23/Rev.1/Corr.1 4 May 2023. Report on violations and abuses of International Humanitarian and Human Rights Law, War crimes and Crimes against Humanity, related to the forcible transfer and/or deportation of Ukrainian children to the Russian Federation.
19
Ibid.
20
ODIHR.GAL/37/23/Rev.1/Corr.1 4 May 2023. Report on violations and abuses of International Humanitarian and Human Rights Law, War crimes and Crimes against Humanity, related to the forcible transfer and/or deportation of Ukrainian children to the Russian Federation.
21
Decree of the President of the Russian Federation of 30.05.2022 No. 330, Russian Federation official internet portal of legal information, 30 May 2022, http://publication.pravo.gov.ru/Document/View/0001202205300008.
22
President of the Russian Federation’s Decree 11/2024, January 4th, 2024. http://static.kremlin.ru/media/events/files/ru/sXZxkRw7u0DOOSE2Snp3416FcAPNuPRL.pdf
23
“Moscow says babies born in occupied Kherson will automatically get Russian citizenship”, New York Times, 16 June 2022. https://www.nytimes.com/2022/06/16/world/europe/ukraine-kherson-babies-russian-citizenship.htm.
24
Lvova-Belova: Families from six regions of the Russian Federation will take custody over 108 orphans from Donbas, RGRU, 15 July 2022.
25
Ukrainian teen who received call-up to Russian army. BBC, https://www.bbc.com/news/world-europe-67368313, 10/11/2023.
26
“Missing Ukrainian child traced to Putin ally” BBC, https://www.bbc.com/news/world-europe-67488646. 23/11/2023
27
Save the Children, A Heavy Toll – Full Report, 02/12/23. Boys and girls in Ukraine have spent 900 hours in bunkers, more than a month of their lives. https://www.savethechildren.es/sites/default/files/2023-02/
28
A/77/5332/2322-23590 Report of the Independiente International Commission of Inquiry on Ukraine - https://documents-dds-ny.un.org/doc/UNDOC/GEN/N22/637/77/PDF/N2263777.pdf? Open Element
29
Forcible Transfer and Deportation of Children from the Temporary Occupied Territories of Ukraine to the Russian Federation. Analytical Report by the Human Rights Center ZMINA, April 2023.
30
UN Security Council, “Reports of Russian Federation Forces Putting Ukrainian Civilians in ‘Filtration’ Camps Must Be Investigated” SC/15023, 7 September 2022, https://press.un.org/en/2022/sc15023.doc.html
31
Convention on the Rights of the Child. https://www.ohchr.org/en/instrumentsmechanisms/instruments/conventionrights-child
32
United Nations Security Council: Resolution 2225 (2015) adopted by the Security Council in its 7466a session, on June 18, 2015. https://www.acnur.org/fileadmin/Documentos/BDL/2015/10114.pdf, Dr. Virginia Gamba, of Argentine nationality, has occupied the position of Secretary General Special Representative for Children in Armed Conflicts since April 2017.
33
UNGA, Eleventh extraordinary period of emergency sessions. Resolution adopted by the General Assembly on April 7, 2022, ES-11/3 Suspension of the Russian Federation’s right to integrate the Human Rights Council.
34 Organization of American States General Secretariat Communiqué Comunicado C-008/22. Source: OAS.
35
Organization of American States Permanent Council Resolution “The crisis in Ukraine” (CP/RES. 1192 (2371/22), 3/25/2022. Source: OAS.
36
Organization of American States Permanent Council Resolution CP/RES. 1195 (2374/22), 4/24/2022. Source: OAS.
37
European Parliament “Joint Motion”. European Parliament Resolution of 15 June 2023 on the torture and criminal prosecution of Ukrainian minors Tihran Ohannisian and Mykyta Khanhanov by the Russian Federation (2023/2735(RSP))
38
Parliamentary Assembly of the Council of Europe. https://pace.coe.int/en/news/9075/the-forcible-transfer-and-russification-ofukrainian-children-shows-evidence-ofgenocide-says-pace, Resolution 2495 (2023) https://pace.coe.int/en/files/31776/html, 4/27/23.
39
Parliamentary Assembly of the Council of Europe Resolution 2529 (2024) Situation of the children of Ukraine, 25 January 2024. https://pace.coe.int/en/files/33348/html
40
ICC, Statement by Prosecutor Karim A. Khan KC on the Issuance of Arrest Warrants against President Vladimir Putin and Ms Maria Lvova-Belova, 17 March 2023, https://www.icc-cpi.int/news/statement-prosecutor-karim-khan-kc-issuance-arrest-warrants-againstpresident-vladimir-putin
41
Russia returns four Ukrainian children in Qatari deal. BBC News: https://www.bbc.com/news/world-europe-67121574, 10/16/2022
41 bis
Qatar announces return of 6 Ukrainian children from Russia. The Kyiv Independent. https://kyivindependent.com/gatar-announces-release-of-6-ukrainian-children/. 12/16/2023.