The Developments in the Middle East: a Reflection of the World’s Bigger Picture
by Andrey Kortunov, Russian International Affair
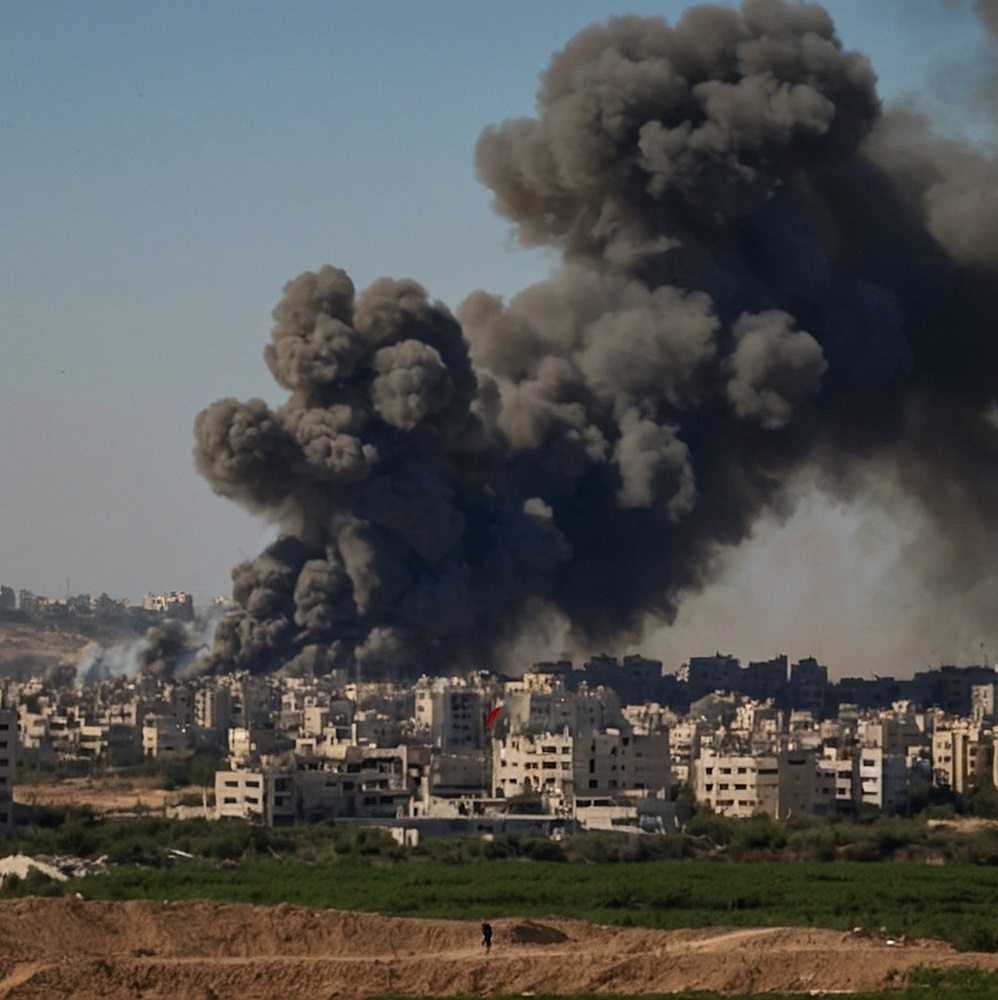
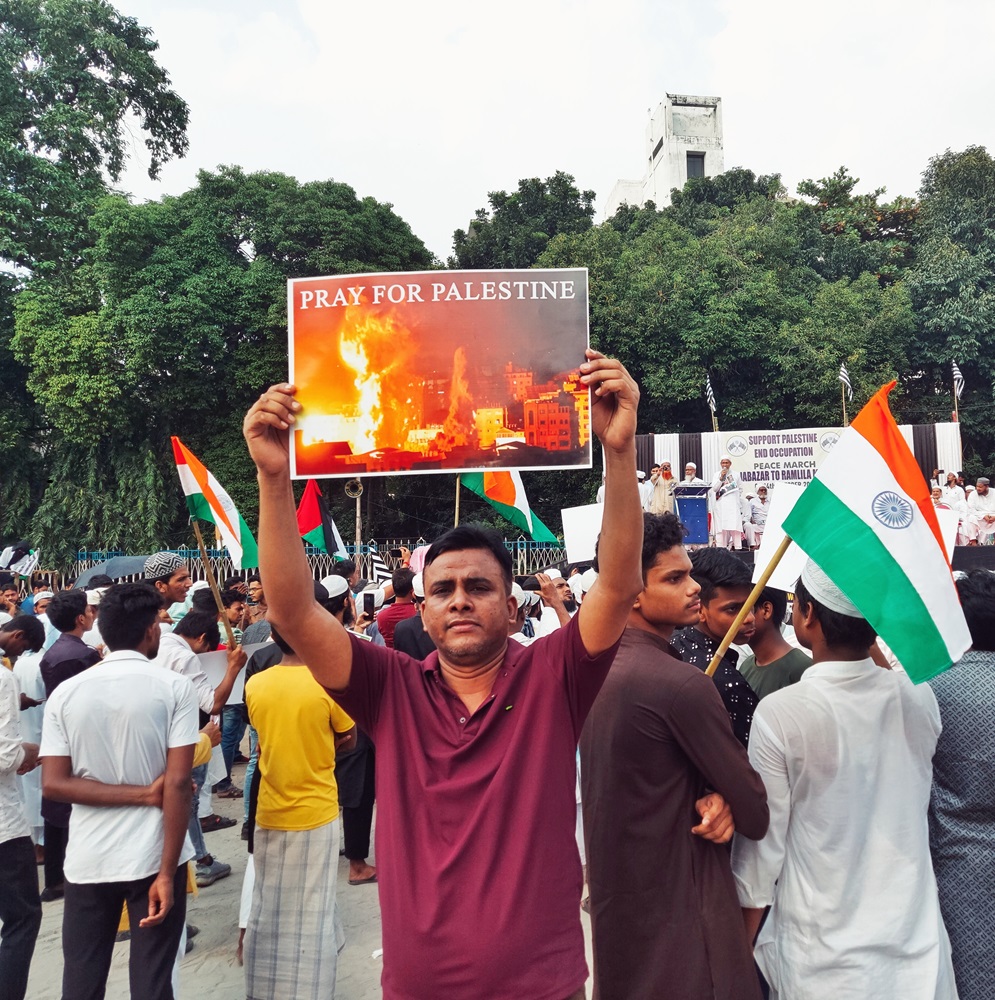
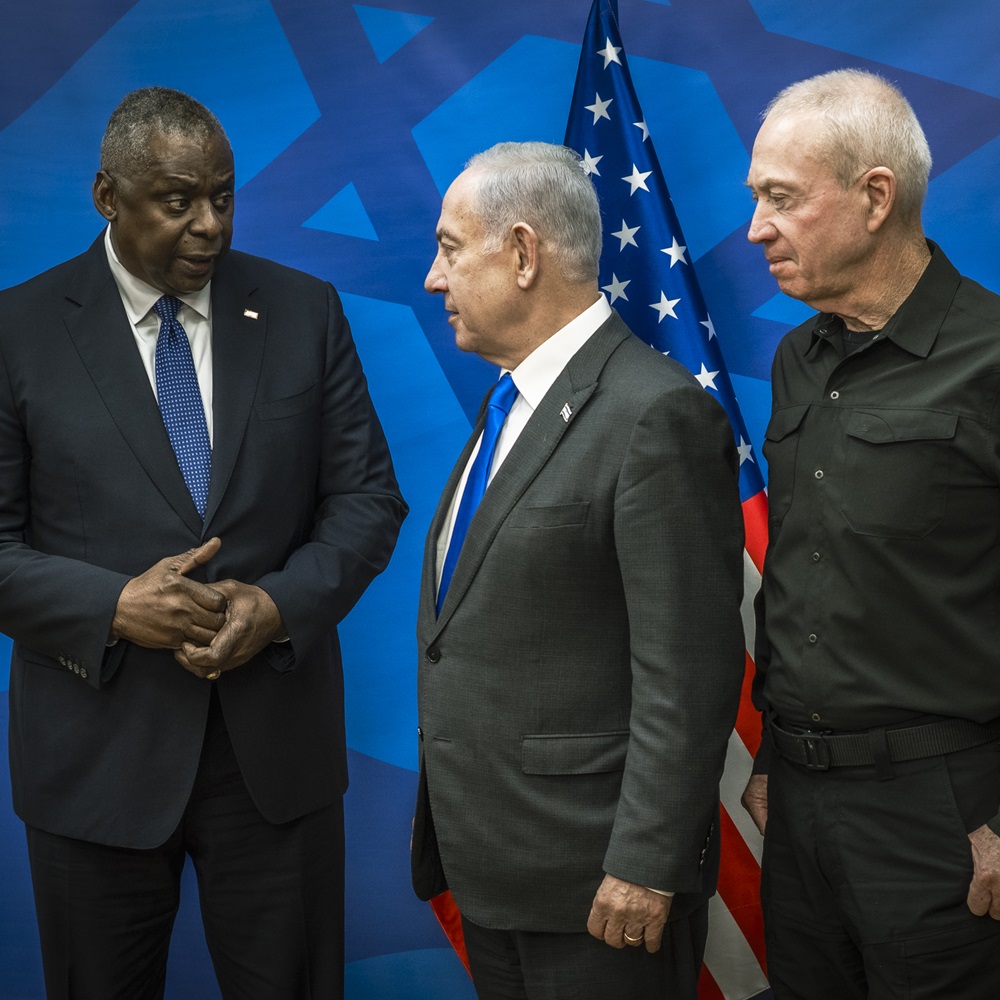
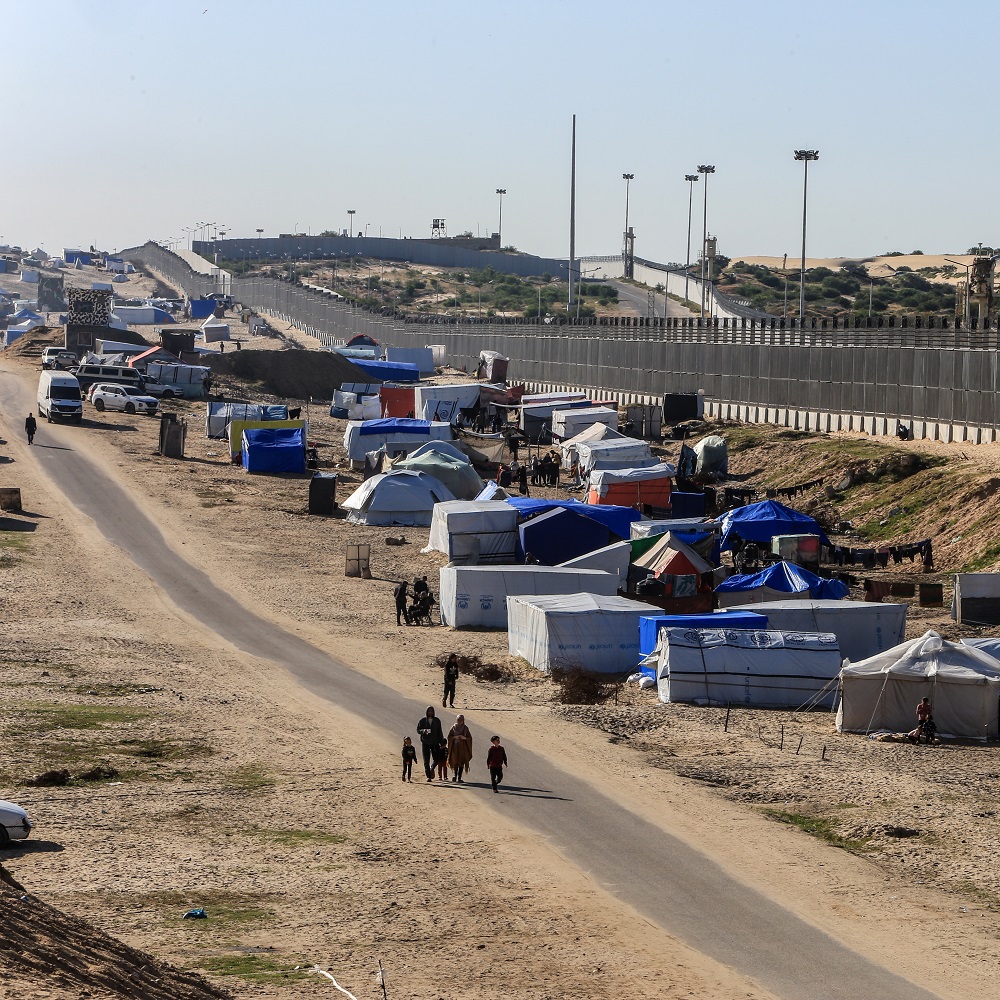
한국어로 읽기 Leer en español In Deutsch lesen Gap اقرأ بالعربية Lire en français Читать на русском When the Israeli–Palestinian conflict escalated dramatically in early October 2023, many observers jumped to a grim conclusion that, from then onward, the Middle East was hurtling at an ever-increasing speed toward another major regional conflict. The military operation of the Israel Defense Forces (IDF) in the Gaza Strip was to be followed by fierce hostilities in the West Bank, then by a large-scale border clash between Israel and Lebanon, and, finally, by an Israeli–Iranian war, which had been looming on the political horizon for years and was literally just a step away, with the likely involvement of several key regional and global actors, including the United States. Limits to escalation But in the 11 months that have passed since the Hamas attack on Israel, no major war has broken out in the Middle East. Israel, as predicted, is stuck in Gaza for long. The death toll among Palestinian civilians has passed 40,000, with the number of wounded approaching 100,000, and the number of refugees and internally displaced persons now in the seven figures. For the people of Gaza, everything happening there is not a targeted anti-terrorist operation, but an all-out war in every sense. While the neighboring West Bank also saw an escalation, it was much more limited—around 600 Palestinians and several dozen Israelis have died there over the past 11 months. This is still many times more than in previous years (28 people were killed there in 2020, 86 in 2021, and 146 in 2022), but it is clear now that the West Bank has not become a second Gaza today, nor is it likely to become one overnight. Along the line of confrontation between the IDF and Hezbollah forces on the Israeli–Lebanese border, nothing extraordinary has occurred so far either, except for a rocket strike at a soccer field in the town of Majdal Shams in the Golan Heights on July 27, which killed 12 Druze teenagers. True, Hezbollah has fired an unprecedented number of missiles at Israel over the past 11 months, up to 6,000 according to some reports. Israel, in response, has launched massive retaliatory and even preemptive strikes on southern Lebanon. But the preliminary results of this duel were relatively minor: 21 civilian and 20 military deaths on the Israeli side, and around 375 fighters and civilians killed on Hezbollah’s side. Even the latest attack on Sunday, August 25, which was announced in advance and involved 340 rockets along with dozens of Hezbollah drones, seems to have caused no significant damage to Israel. In any case, nothing comparable to the IDF’s deep incursion into southern Lebanon in July 2006 (known as the Second Lebanon War) is happening now or is likely to happen soon. In recent months, Israel has repeatedly demonstrated its willingness to escalate by conducting precision strikes on prominent figures of its adversaries. On April 1, the Israeli Air Force destroyed an Iranian embassy annex building in Damascus, killing 16 people, including Mohammad Reza Zahedi, one of the top military commanders of the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps. On July 30, senior Hezbollah operative Fuad Shukr was killed in a Beirut suburb, and on July 31, Hamas political chief Ismail Haniyeh was assassinated in Tehran (Israel never claimed responsibility for his death). After each of these incidents, experts predicted a sharp increase in the risks of escalation. But the Iranian leadership’s response to these developments was surprisingly restrained (as was Tehran’s earlier response to the assassination of Maj. Gen. Qasem Soleimani in early 2020 by the U.S. military in a Baghdad suburb). The leaders of most Arab states also showed restraint in their response to the events in Gaza. The highly emotional reaction of the Arab street did not translate into decisive actions comparable to the oil embargo imposed on Israel and its allies following the Yom Kippur War in October 1973. Efforts to further promote the Abraham Accords between Israel and the conservative Arab monarchies continued, albeit fading from the public eye. The only consistent supporters of Palestine were the stubborn Yemeni Houthis, who have attacked foreign ships in the Red Sea. However, it was Egypt—not Israel—that suffered the most from these attacks, losing nearly half of its revenues from the Suez Canal. Reasons for restraint Although the trigger of a major regional war was pulled almost a year ago, the bomb itself never exploded. This situation calls for an explanation, particularly to assess the risk that the bomb might eventually detonate in the foreseeable future, among other things. One explanation for the current situation around Palestine lies in the distinct nature of Hamas, which has an ambiguous reputation in the Arab world. Cairo does not hold it in high regard, and Egypt’s current military leadership, not without reason, draws parallels between Palestinian radicals and the Muslim Brotherhood movement (banned in Russia) at home, which has been driven deep underground, but was, alongside Israel, among the founding fathers of Hamas. Damascus has not forgotten that at the beginning of the Syrian civil war, Hamas sided with the political opposition rather than President Bashar Assad. Opinions of Hamas are divided in the Gulf states—while the group can count on some patronage and even political support in Doha, Abu Dhabi is much more skeptical and doubtful of the former rulers of the Gaza Strip. On the other hand, all regional actors are under pressure from the international community, which for various reasons does not want further escalation. The U.S. has no interest in a major regional war in the Middle East with an uncertain outcome, especially in the run-up to the presidential election in November. Thus, Washington is focused on maintaining the regional status quo. China has even less reason to welcome such a conflict, in the first place because it would immediately drive global hydrocarbon prices up and create many transportation and logistics issues for Beijing. Moscow could possibly count on some short-term gains from a major Middle East conflagration. The West would have to shift attention away from Ukraine for a while, while prices for Russian oil and gas would skyrocket. But the negative consequences of long-term destabilization in such an important region for Russia are so great that they undoubtedly outweigh any short-term gains. It is no coincidence that at his meeting with Palestinian leader Mahmoud Abbas on August 13, President Vladimir Putin emphasized Moscow’s commitment to preventing further escalation and promoting a political settlement of the Palestinian issue. It is also plausible that during the visit of Russian Security Council Secretary Sergey Shoigu to Iran on August 5, Moscow urged Supreme Leader Ali Khamenei to refrain from radical responses to Israel—not only to minimize possible civilian casualties but also to avoid provoking a direct conflict with the U.S. Postmodernity as inoculation against war However, the core reasons lie not outside, but inside the region. It appears that key actors—from Egypt to Syria, and from Turkey to Iran—are unwilling to engage in a full-blown war. Middle Eastern leaders are reluctant to shoulder the numerous risks and costs associated with a major armed conflict in one way or another. True, the arms race in the Middle East region received a powerful new boost in October 2023 and is likely to accelerate later. Belligerent anti-Israeli rhetoric—not only in the Arab world but also in Iran and Turkey—will also persist. Isolated tragic incidents—both planned and accidental—will continue. Yet a major war is a different matter. This is not because all Middle Eastern leaders are exceptionally compassionate and peace-loving, but because almost none of them today can be fully confident in their own power and resilience. It is still possible to maintain a limited military presence near and far, as Recep Tayyip Erdogan does in Syria and Libya. But repeating the experience of the Iran–Iraq War of the 1980s, with hundreds of thousands killed and millions wounded, is now a no-go: Middle Eastern societies have changed too much over the past 40 years, and the region has advanced too far down the path of postmodernity. It is hardly a coincidence that the strongest proponents of escalation are the Houthis, who are the least affected by the postmodern values and lifestyle in the Middle East. Perhaps even Tehran can no longer count on the unconditional loyalty of the new generation of Iranian citizens, who would have to pay with their own blood for the decisions of the political and military elite leading to a major regional war. In any case, the victory of the only “reformist” candidate, Masoud Pezeshkian, in the recent presidential election is a clear signal from society to the leadership of the Islamic Republic that people want peace, stability and economic development, rather than new military exploits or social and political upheavals that invariably accompany them. Even Israel—for all the outward determination of the current cabinet to see things through to the end—is no exception to this rule. The costs of the Gaza operation have already topped $60 billion, a staggering sum for a relatively small country, meaning inevitable budget deficits, tax hikes and cuts to social programs. Israel’s call-up of reservists has already drained the national economy, and its effects will be felt for a long time. Most importantly, as the Gaza offensive has once again shown, starting a war is easy, but ending it is very difficult. The prospect of a second Gaza in the West Bank or southern Lebanon is far from appealing, even for a politician as determined as Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu. Armageddon is off the table? It is fair to assume that the current situation in the Middle East reflects the broader state of global politics. After February 24, 2022, many experts expressed a gloomy belief that “the world is entering a new era of big wars” and that the confrontation between Russia and the West would inevitably lead to a chain reaction of major armed conflicts all over the planet. They predicted an imminent U.S.–China military clash over Taiwan, an armed standoff between China and India in the Himalayas or between India and Pakistan in Kashmir, a rapid escalation on the Korean Peninsula and numerous new conflicts across Africa, among others. Fortunately, none of the above scenarios have so far come to pass. Many other ominous predictions have not come true either. ECOWAS member states opted out of a military intervention in Niger. The Libyan National Army’s threat of a border conflict with Algeria never materialized. Even Venezuela’s eccentric leader Nicolas Maduro seems to have changed his mind about going to war with neighboring Guyana over disputed territories. The number of conflicts in the world has not decreased, but the ongoing ones are predominantly low-intensity conflicts rather than conventional wars, after all. The international system, though shaken, has overall remained standing—for now. Of course, it is too early to sit back. The situation can explode at any moment and almost anywhere: there are more than enough flashpoints around the world, while the level of trust or even basic communication between the great powers has dropped to near zero. In today’s international environment, any negative scenarios are possible, down to the most apocalyptic ones. And this unsettling uncertainty is now very much felt in the Middle East as well. But for now, there is still hope that the unfolding transition to a new world order will be less destructive and less costly for humanity than many professional pessimists have imagined in recent years.

















