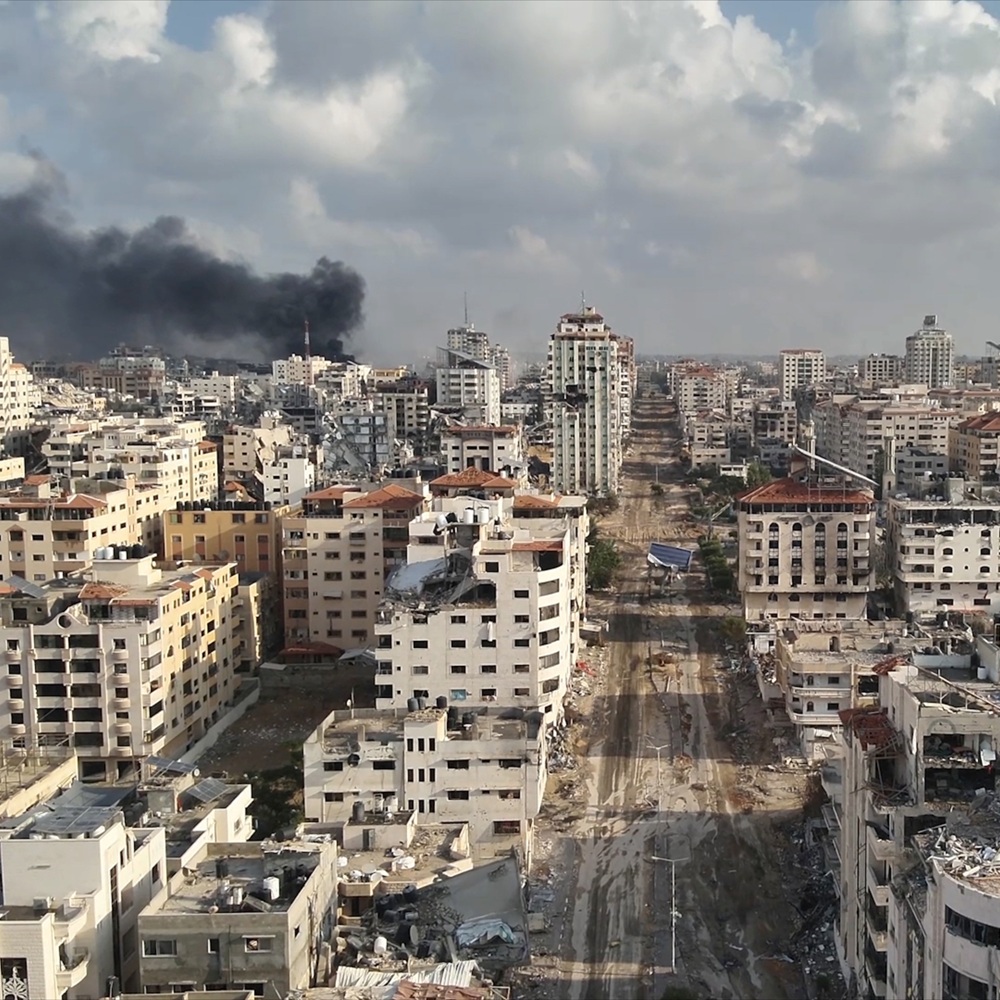
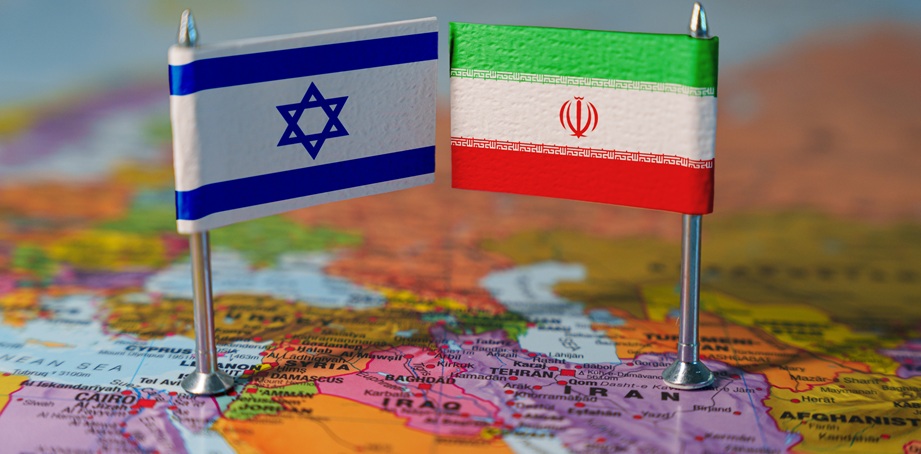
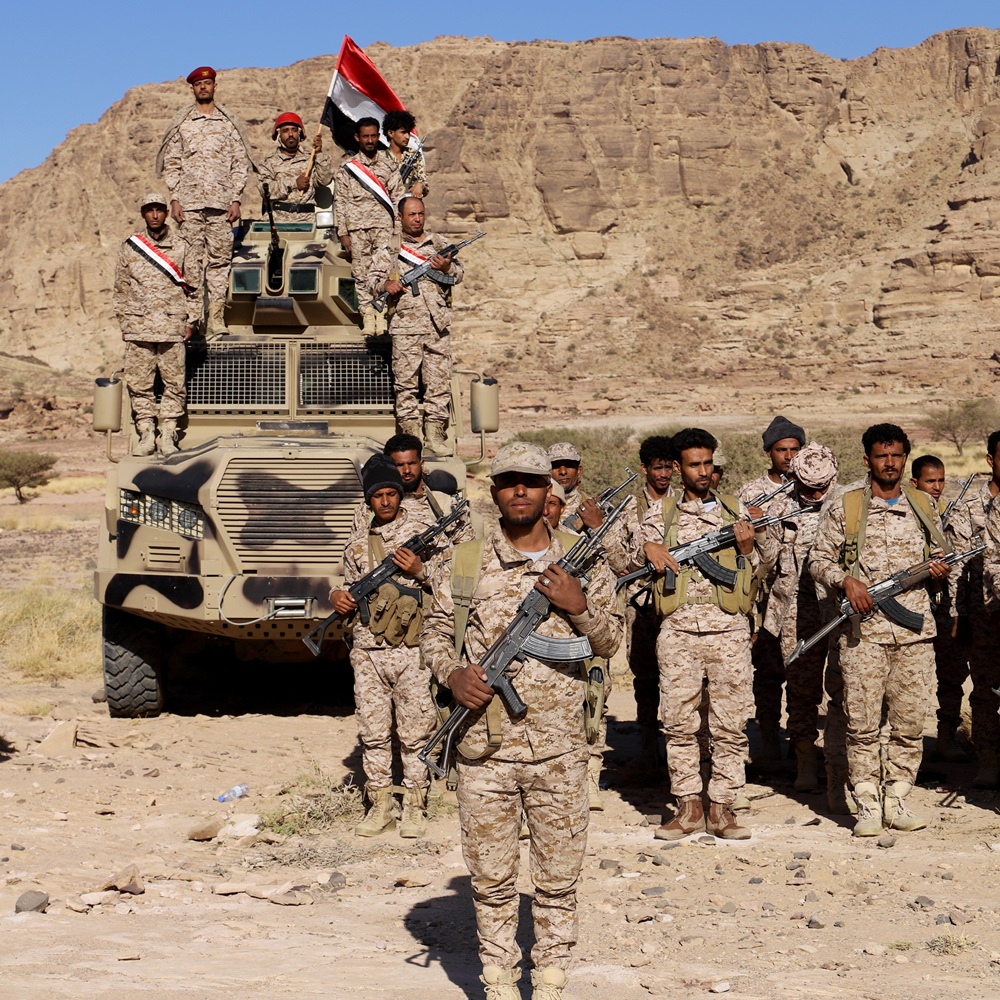
The Yemeni Crisis: Structural Characteristics and Contemporary Developments
by Sergey Serebrov
The structure of the Yemeni crisis (YK) developed step by step throughout the period after the unification in May 1990 of two republican states — the Yemen Arab Republic (YAR) and the People’s Democratic Republic of Yemen (PDRY) — into a unitary state. The rushed and unprepared process of merging the government bodies and armies of two countries with different political systems and ideologies, but related historical, cultural, and ethnic communities, coincided with major global changes: the transformation of the international system, the collapse of the USSR, and the Gulf War, which brought sanctions from the United States and Gulf monarchies against the young state, as well as the expulsion of nearly one million Yemeni labor migrants from these countries. After that, political Islam began to grow stronger across the region. Both countries entered unity carrying a heavy burden of internal social and political problems, hoping that unification would create a new model of development, and that a new source of income from oil exports — from fields recently discovered in the neighboring provinces of Marib and Shabwa — would speed up modernization and help solve these problems. But this did not happen — the democratic institutions, multi-party system, and the first direct presidential elections introduced by the new state’s constitution did not stop the return to power of the conservative coalition from the YAR era, and the oil reserves were not enough to repeat the success of wealthy oil-producing countries. However, the alliance between the General People’s Congress (GPC) and Islah quickly turned into rivalry just a few years after they defeated the former ruling party of the PDRY — the Yemeni Socialist Pa rty (YSP) — in 1994. A religious reform focused on spreading Salafism, led by the Islamist wing of Islah (Yemen’s branch of the Muslim Brotherhood), became a tool of political struggle. It challenged the regime of President Ali Abdullah Saleh (1947–2017), who personally oversaw the state’s security sector but gave Islah control over education and significant legislative functions. The reform led to growing tensions — first due to clashes with the Shafi’i traditions in the South, and then with Zaydi practices in the North. The aggressive spread of a proselytizing version of radical Salafism through a network of religious colleges (ma'ahid ilmiyya) under Islah’s supervision was seen by local communities as an official government policy. This created distance between society and the state. Dissatisfaction with the country’s social, economic, and political situation turned into conflicts of identity of a new kind, with no precedent in Yemen’s history. These conflicts had nothing to do with the traditional Sunni-Shia divide, as Yemen has long been home to two Islamic schools — the Shafi’i (about 60% of the population) and the Zaydi (about 40%) — that are close in theology and law (aqidah and fiqh). In public opinion, the situation was seen as a clash between true Islam rooted in authentic Yemeni traditions and a foreign, radical takfiri current that caused deep divisions. The consequences of this conflict in the South appeared in the idea of a “southern identity,” which replaced the idea of a united Yemeni identity that the republican regimes of the YAR and PDRY had promoted before unification. This idea became the base of the ideology of “southern nationalism,” which set the “southern” society against the “northern” or “Yemeni” one — describing the first as “advanced” and the second as “backward,” tribal, and fundamentalist, and therefore incompatible. Since 2009, political leaders of the South Yemeni separatist movement “Hirak” (Peaceful Southern Movement) have used the slogan of restoring the status quo — independence of the South within the 1990 borders of the PDRY — as the best way to peacefully solve the “southern question.” At the same time, in the northern Zaydi provinces of Yemen, the takfiri practices of the “reformers” caused a similar defensive reaction from Zaydi youth. Against the Salafi proselytism of the international school Dar al-Hadith in Dammaj (near the Zaydi stronghold of Saada since the 9th century), the Zaydi intellectual elite created the “Shabab al-Mu’min” movement, which praised the historical role of Yemenis in Islam. It was led by former MP from Saada province, Sayyid Hussein al-Houthi (1959–2004), who gave lectures in 2001–2002 that formed the base of a new form of political Islam known as “Hussism.” It was a mix of theology and political theory, trying to explain the problems of the Muslim world and offer solutions. Its roots were in Zaydi theology. The idea of the “Qur’anic path” led by a spiritual leader — the ‘alam al-huda — aimed to rebuild unity in the Muslim community (ummah), combining ideas from different Sunni and Shia political movements and adding an element of Yemeni nationalism. Despite its originality, it had some similarities with Khomeinism, Salafism, the Muslim Brotherhood, nationalism, and other ideologies, making it a subject of criticism and speculation, even from other Zaydis. It focused on the civilizational injustice of global politics. In this teaching, takfirism was seen both as a distortion of Islamic values and a tool of US and Israeli (Zionist) policies to block a peaceful solution to the Palestinian issue. After the US invasion of Iraq in 2003, Hussein al-Houthi saw this as a sign that the Arab-Muslim world should mobilize to defend itself from future invasions aimed at taking resources by removing identity. In domestic politics, the Houthi movement followed only legal methods: they called for removing the religious reform (and the Islah party) from state privileges, and excluding the security sector from US cooperation. This idea went against President Saleh’s policy of strategic partnership with the US, which started in 2001 when Yemen joined the global US-led counterterror campaign after 9/11. This partnership gave mixed results: it helped build anti-American feelings in society, even as it made Yemen seem more important regionally and gave Saleh’s relatives in the security agencies close contact with US partners. In 2004, President Saleh declared war on the Houthis after they refused to stop chanting their slogan in mosques in Sanaa: “Death to America! Death to Israel! Curse the Jews! Victory to Islam!” — which became a symbol of the movement and expressed its main ideas. The bloody and failed Saada wars of 2004–2010, and the death of their respected leader in 2004, weakened the regime and brought more armed tribes and other groups to join the Houthi resistance. This made them a strong local opposition force. A year before the peaceful uprising of 2011 that shook Saleh’s regime, the so-called “Houthi problem” had already become one of the country’s top national issues, next to the “southern question.” Experts described Yemen in the 1990s and 2000s as unstable. Many American political scientists saw it as a “fragile state,” a term used by the World Bank in the early 1990s. In the 2000s, Yemen gained the image of a global center of “terrorist threats” and became a testing ground for the military and political actions of US intelligence. The “fragile state” concept helped justify direct foreign intervention. At an international conference in London in January 2010 about Yemen, the focus was on security, not reform, as Yemenis had hoped. In 2011, Yemen became one of the key places hit by the wave of protests known as the “Arab Spring.” The idea of a “fragile state,” military spending, and the weakening of national sovereignty all led to the shift of conflicts into violent areas instead of using the democratic tools in the constitution. But the crisis in the relationship between society and the state, and among political actors, could also be seen as a natural immune response of a healthy cultural system — reacting to political problems: Islah still had support from the kingdom that backed the religious reform, while the US became more involved in Yemen’s security agencies despite public anger. Even though the protests in February 2011 were spontaneous and had no central leadership, they had the signs of a real social revolution. There were clear problems at both the top and bottom of society. The Yemeni revolution followed a unique peaceful transition plan — the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) Initiative, launched on 23 November 2011 under the UN Secretary-General’s special envoy. The plan gave the task of creating a new constitution to an inclusive National Dialogue (ND) in Sanaa (March 2013 – January 2014), which showed that civil society was alive and strong in Yemen — something not possible in a truly “fragile state.” The organizers of the ND focused its agenda on the two key issues — the “southern question” and the “Houthi problem” — showing that internal Yemeni problems were the main priority in the transition. The only outside part of the plan was the proposed reform to decentralize and federalize the state, seen as a solution to these problems. A unique part of Yemen’s transition was that President Saleh remained head of the ruling party (GPC) even after officially handing over the presidency to his deputy — interim president Abdrabbuh Mansour Hadi — in February 2012. An attack on Saleh in June 2011 turned the former partners and rivals — the GPC and Islah — into true enemies. This attack also left Islah’s leadership without support in 2014, as the Hashid tribal confederation (which included Saleh himself) no longer backed them. A new alliance formed in 2014, with the GPC and the Houthi movement “Ansar Allah,” combining “conservatives” and “revolutionaries.” This gave a political defeat to Islah, whose spiritual leader saw the revolution as the start of a coming caliphate. President Hadi signed the “Peace and National Partnership Agreement” on 21 September 2014, which the UN Security Council supported. It allowed him to shift his regime’s support from Islah to the new alliance and to form a new technocratic government under Khaled Bahah in December 2014. With this change, the foreign actors’ bets on Islah’s victory failed, and Ansar Allah became one of the expected winners of the transition, along with the GPC. Only in late January 2015 did interim president Hadi show signs of crisis by offering his resignation. But the UN envoy Jamal Benomar still believed in the peaceful plan until 24 March 2015, staying in the capital Sanaa, which was controlled by the new alliance, even after Hadi fled to the separatist-held city of Aden on 21 February 2015. The peaceful project fell apart dramatically in March 2015, and many actors offered different explanations. The idea of a “Houthi coup” (with no exact date) became official after the Arab Coalition launched its military intervention on 26 March 2015. This version was confirmed by UN Security Council resolutions and became part of the Yemeni discourse, now shaped more by the regional rivalry between Saudi Arabia and Iran than by Yemen’s own internal problems. Among the lessons of the transition process, along with proof of the effectiveness of the inclusive National Dialogue (ND), we can also point to the doubt it created about the expert community’s firm belief in decentralization and federalization of Yemen. The debate between Yemeni participants on this issue almost caused the conference to collapse, showing the deep disagreement between major Yemeni actors on how many federal regions there should be and how they should relate to the central government. Strong traditions of regionalism in the young Yemeni state raised real concerns that the result of this idea could be state collapse instead of unity (as seen in the countries the reform authors wanted to copy). By mid-2025, the Yemeni crisis (YC) had gone through four stages: two mentioned earlier — during President Saleh’s rule and the implementation of the Initiative — formed its internal (endogenous) stage; and two newer stages after the Arab Coalition (AC) intervention in March 2015 — the geopolitical (military) stage. The AC military campaign in Yemen lasted seven years before entering a phase of steady de-escalation in April 2022. The current “Palestinian” stage began in October 2023, when the YC shifted into a new kind of conflict — a combined armed conflict of supra-regional level (mixing regional and global elements). What makes it unique is its direct link to the situation in the Palestinian-Israeli conflict (PIC) zone and Israel’s war in Gaza. The leading actors in this stage were first the US and the UK, who formed a naval coalition in December 2023 to stop anti-Israeli Houthi actions, and later Israel itself. We recall the prophetic comparison of the YC to a “ticking bomb” made in summer 2015 by UN Secretary-General Ban Ki-moon, warning that it could explode unless stopped early through political settlement. By summer 2025, the YC had absorbed not only unresolved internal problems but also several layers of subregional and regional issues, becoming a military-political “ticking bomb” for the whole region. Discussions about the cause of the YC’s new military phase range from security threats to shipping in the Red Sea by the Houthis and threats to Israel by the “Axis of Resistance” led by Iran, to opposing claims that the US and Israel are to blame for aggressive actions and blocking a legal settlement to the Gaza war. But for our study of the YC’s structure, another point is more important — the ongoing failure to resolve the YC during all its earlier stages, mostly due to outside geopolitical interference. The new stage stands out because the line between Yemen’s internal and external problems has disappeared. It is now part of a larger ethnic and religious conflict in another part of the region. Still, this link, through an ideological concept born in Yemen, does not feel artificial. Houthism, long under pressure since 2004, has now returned as a form of political will of the population — worn out by war but still determined. This fact again shows how unsuitable military methods are for solving the Yemeni conflict. Another unusual aspect of this new geopolitical stage is the inconsistent way the Houthis are labeled as international terrorists — depending on the mood of the US administration. Regional actors also switch between accepting and ignoring this label based on the situation. The accusation creates a legal problem regarding the status of the second major actor in Yemen’s ruling coalition — the core of the GPC party, which recognized the constitution and formed a government in Sanaa in August 2016. This unrecognized government controls about 30% of the territory, where more than 70% of Yemen’s population lives. The equal participation of Ansar Allah and the GPC in fully restored state institutions leaves open the question of how the US defines the GPC’s role in terrorism, especially since the party, led by ex-president Saleh, was a US partner for nearly 10 years before 2011. In the Supreme Political Council — the top body of the Sanaa government — there are 10 members, five from each group. The head of the council has always been from Ansar Allah, but the posts of prime minister, foreign minister, and some military and security positions were mostly held by GPC members. Another problem is linked to UN Security Council Resolution 2216, which demands the Houthis give up heavy weapons and leave Sanaa — in other words, surrender. But since the ruling coalition in Sanaa is joint, it is unclear whether the same demand applies to the GPC, which traditionally controlled the army and security services. There is no doubt about the status of the internationally recognized government (IRG), which is officially accepted, even by Russia — although Russia criticized Resolution 2216 during discussions and did not vote for it. Still, there is a question about the realism of demanding the Houthis hand over all weapons (meaning the arsenal collected during Saleh’s time) to Hadi’s government in exile, which was located entirely in a neighboring country with a complex past in its relations with Yemen. The main reasons the YC shifted to a new phase in October 2023 likely include: 1) the outdated UN framework for conflict resolution; 2) the limited and misleading use of the “proxy war” model to explain a complex conflict involving the AC, framing it only as a Saudi-Iranian proxy war; 3) the competition of many foreign powers for geopolitical influence in Yemen while ignoring Yemenis' own right to sovereignty. Before the transition of the YC to the "Palestinian" phase, two approaches to its settlement had formed in the discourse on YC — the official one (but non-functional) and the pragmatic one (but not acceptable to several internal, and especially external, powerful actors). The specific nature of this division, reflecting the mixed endogenously-geopolitical nature of YC itself, lies in the attempts by powerful interest groups behind them to implement incompatible approaches through the same permanent special mission appointed by the UN Secretary-General. The first approach was set by UN Security Council Resolution 2216 (April 2015), which formally became the legal basis for the UN mission’s work and focused on a military solution to the “Houthi problem” — applying pressure on the unrecognized regime in Sana'a until the Houthis surrendered completely. The second approach, which emerged almost immediately after the war began in March 2015, came from the expert community. It largely agreed with the criticism of Resolution 2216 voiced by the Russian Permanent Representative to the UN Security Council (2006–2017) V. I. Churkin and was based on an understanding of Yemeni realities rather than the wishes of foreign actors. It has long served as the practical guide for the current head of the UN mission in Yemen, Hans Grundberg, and includes two main elements: a) assisting in the prompt end of foreign military intervention in YC; and b) launching a comprehensive political peace process in an inclusive Yemeni format under UN auspices. This scenario gave a “green light,” in particular, to the Omani track and the de-escalation regime that began in April 2022. The UN mission and Russian diplomacy actively supported its progress at every stage. The de-escalation regime and the Omani track of direct talks between Riyadh and Sana'a on the terms of ending the war became the main outcome of the years-long war in Yemen and one of the most important achievements of the reform policy of the Saudi Crown Prince Mohammed bin Salman. The new leader of the Kingdom began his involvement in YC as the commander of Operation “Decisive Storm” conducted by the AC, and in 2021–2022, thanks to him, Saudi Arabia became the initiator of the process to end the conflict based on its own model and using a regional format. Liberal reforms in Saudi Arabia, which affected the religious sphere starting in 2017, the threatening dynamics of the military conflict in Yemen, which hindered Saudi Arabia’s strategy to achieve leadership under the “Vision 2030” concept, and finally, the revision of approaches to the regional security system involving Iran — all came before this shift toward de-escalation in the YC zone. Its intellectual basis was a scholarly monograph published in 2022 by the respected King Faisal Center for Research and Islamic Studies (KFCRIS) in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia titled “The Houthi Movement in Yemen: Ideology, Ambitions, and Security.” Most of the articles were written by well-known representatives of various Western schools of Oriental studies and Yemeni research centers. They reached a common conclusion that the concept of “proxy” does not apply to the Yemeni Houthis. According to them, this very construct contributed more to the development of relations between the Sana'a regime and Iran and the “Axis of Resistance” during the war years than it reflected any prior allegiance to Tehran’s interests before the conflict began. The authors agreed that the roots of Houthism lie both in Yemeni history and traditions and in the distressing modern political situation in the Middle East after the September 11 attacks, which, in the view of Sayyid Hussein al-Houthi and his brother — Sayyid Abdul-Malik al-Houthi, the current leader of Ansar Allah — was largely caused by US policy that threw the region into chaos. Of course, these “findings” in the monograph did not make the relationship between Saudi Arabia and Ansar Allah friendly, but removing the label of “enemy agent” from the movement allowed both sides to sit at the negotiating table and return the “Houthi problem” (among others) to the agenda of general YC settlement in the Yemeni format. The stable de-escalation regime received support from the UN mission but faced strong opposition from various competing centers of political influence (CPI), who feared losing status and were united in April 2022 into the Presidential Leadership Council (PLC) headed by the new president of the MPP — Rashad al-Alimi. The United States also supported their discontent out of fear that regional actors might take over the initiative in the Yemeni settlement. US President Biden’s Special Representative for Yemen, Tim Lenderking (2021–2025), repeatedly spoke of the leading role of the US, indirectly blaming the UN mission for its support of the Oman talks. A telling example is his statement at the Foreign Affairs Committee hearings in December 2022: “The Houthis’ last-minute demand to direct limited oil export revenues, received by the Yemeni government, to pay salaries of active Houthi combatants, even though the Houthis refused to commit to a ceasefire, prevented the UN from concluding a new truce agreement between the parties in October… These actions are an insult to the entire international community and completely unacceptable. ” The two official visits exchanged between Riyadh and Sana’a in April and September 2023, after the normalization of relations between Saudi Arabia and Iran with Beijing’s mediation in March, differed significantly in the atmosphere of negotiations: the enthusiasm clearly declined, increasing Sana’a’s uncertainty about the outcomes and timing. If the agreement on a "roadmap" within the framework of the Omani track — whose readiness was only announced by H. Grundberg on December 23, 2023 — had been reached earlier, a new escalation in YC might not have occurred at all or would have taken a much less aggressive form. The new stage of the military phase in YC covers the period from October 7, 2023, to May 6, 2025, and is divided into three phases. The de-escalation regime along the military contact line between AC and SA forces remained in effect, although in all other aspects of the process it noticeably deteriorated, pushing the humanitarian and economic situation to the brink of collapse. It should be noted that the initiative to link YC with the situation in the PIC zone came solely from the unrecognized regime in Sana’a and had nothing to do with the policy of Yemen’s official authorities — the MPP, which expressed itself in supporting resolutions of international summits, the Arab League (AL), and the Organization of Islamic Cooperation (OIC), condemning Israel for the genocide of Gaza’s Palestinian population but prioritizing the goal of preventing conflict escalation. Many members of the Presidential Leadership Council (PLC) sharply criticized the Houthis’ policy, describing them as a terrorist group, and their actions in the Red Sea against Israel as harmful to Yemen. This nuance should be taken into account, especially when encountering media headlines like “Yemen enters war with Israel,” which rather reflect the strong resonance of Sana’a’s policy in the Arab-Muslim world, coordinated with members of the so-called “Axis of Resistance.” The following refers specifically to the policy of the unrecognized regime — the initiator of the new stage. The push to move to a new phase in YC was triggered by the sudden raid of Hamas fighters on October 7 — “Al-Aqsa Flood” — and the large-scale, well-prepared Israeli army operation in Gaza “Iron Swords,” which led to near-total destruction of the city and raised the number of victims to about 9% of its population by June 2025. During the first phase from October 7 to December 18, 2023, the leaders of Ansar Allah took full control over shaping the domestic and foreign policy of the unrecognized Sana’a regime, achieving a significant breakthrough in unifying its ideological base on the Houthi doctrine. The Palestinian issue had already played a major role in the rhetoric of Ansar Allah leaders when condemning the military intervention in Yemen by Saudi Arabia and the UAE — which they called “unprovoked aggression,” staged by their common enemies — the US, Britain, and Israel (referred to as the “unholy trinity” in the regime’s rhetoric), aimed at preparing a strategic base in the Red Sea under the hostile New Middle East project. Now the topic of Palestine and Jerusalem became dominant. The solidarity campaign with the Palestinians under the name “Battle of the Promised Victory and the Holy Jihad” covered all areas of the unrecognized regime’s policy and filled the entire internal discourse. Weekly, well-organized mass marches with slogans from the Demonstration Organizing Committee, accompanied by public lectures and religious sermons by the movement’s leader Sayyid Abdul-Malik al-Houthi broadcast on screens, served as the official manifestation of the Yemeni people’s will and determination to stand firm in defending the rights of the Palestinian people. They included not only threats against enemies but also criticism of Arab and Islamic states’ policies for their “negligence,” and of the MPP, described as “anti-people.” In October–November 2023, the campaign of civilian solidarity with the people of Gaza was supplemented by military-political actions of the Houthi regime under the slogan directed to Hamas organizations, “You are not alone!” The unrecognized authorities blocked Israeli shipping through Bab-el-Mandeb, launched missiles toward the Israeli Red Sea port of Eilat, significantly disrupting its operations. At the same time, combat training courses were organized to prepare “hundreds of thousands of Yemenis” for voluntary entry into the war against Israel. Expressions of loyalty to the “leader of the revolution” — Sayyid Abdul-Malik al-Houthi — reached unprecedented levels, spreading across the military leadership at all levels. The head of the Supreme Political Council (SPC) of the Sana’a regime, Mahdi al-Mashat, emphasized that the countermeasures he introduced against Israel were tied exclusively to the war and blockade in the Gaza Strip, with no intention to obstruct freedom of navigation through the Bab-el-Mandeb strait for other companies and ships. Overall, the ban affected about 1–1.5% of the cargo flow. The second phase, from December 18, 2023, to January 19, 2025, covers the conduct of the “Poseidon Archer” military operation with the participation of the US-UK Maritime Coalition (USUKMC) during the Biden administration. In a joint statement from the US government and several of its partners dated January 3, 2024, referring to attacks on about 10 cargo ships using around 100 drones from Yemen’s shores, it stated: “... the attacks threaten the lives of innocent people around the world and pose a serious international problem requiring collective action. Nearly 15% of global maritime trade passes through the Red Sea, including 8% of global grain trade, 12% of maritime oil trade, and 8% of liquefied natural gas. International shipping companies continue to reroute their vessels around the Cape of Good Hope, resulting in significant costs and weeks-long delays in deliveries, ultimately putting at risk the transportation of essential food, fuel, and humanitarian aid worldwide. Let our message be clear: we call for an immediate end to these illegal attacks and the release of unlawfully detained ships and crews. The Houthis will be held accountable for the consequences if they continue to threaten lives, the global economy, and the free movement of trade along key regional waterways.” The strikes launched by USUKMC on January 11, 2024, aimed to “restore freedom of navigation” through the strait and deprive Sana’a of the military capability to continue its ship attacks. Israel was not mentioned, but within Yemen, the openly pro-Israel orientation of the campaign against the Sana’a alliance (SA) seriously complicated the MPP’s position. The operation ended on January 19, 2025, without achieving its objectives, following Biden’s departure from the presidency. U.S. partners in the EU and the region refused to operate under U.S. command. The EU’s “Aspides” operation focused on covering and escorting merchant ships. Among the Gulf countries, only Bahrain participated in the US-UK Maritime Coalition (USUKMC), providing a base for U.S. and British fleets and CENTCOM’s command headquarters. The U.S. invoked Article 51 of Chapter VII “Action with respect to threats to the peace, breaches of the peace, and acts of aggression” of the UN Charter (the right of self-defense) to justify its aggression in Yemen. The legal side of the USUKMC operation was extensively criticized by the Russian Ministry of Foreign Affairs and Russia’s Permanent Representative to the UN Security Council, V.A. Nebenzya. In his detailed letter to UN members dated January 22, 2024, he presented Russia’s position, describing the actions of the U.S. and Britain as a blatant violation of international law and a threat to peace. Russia did not support the Houthi threats to navigation but, amid the even more explosive situation in Gaza — which the Houthi countermeasures aimed to contain — proposed that both issues be resolved simultaneously through balanced, comprehensive solutions. This approach was also shared by most regional actors, who were primarily concerned about threats to shipping posed by the USUKMC military campaign in the Red Sea itself. According to the 2024 annual report of the Suez Canal Authority, revenue from ship traffic fell by 60%, depriving Egypt of about $7 billion (compared to a 2–3% drop before the formation of the “Guardian” coalition). Almost every quarter during the military phase of the “Palestinian” stage, the Houthis demonstrated new types of weapons and improved tactics for attacking maritime targets, including both commercial and military ships of the U.S. and Britain, which were added to Sana’a’s blacklist after the aggression began. This development triggered threats toward Iran, accused of supplying weapons to the Houthis while bypassing all checkpoints established since March 2015 — long controlled by the U.S. and British navies. On July 20, 2024, Israeli aviation joined the USUKMC “Archer” operations — one day after a Yemeni drone exploded in Tel Aviv. In the second half of the year, Israel launched three more attacks, coordinated with USUKMC combat operations. Meanwhile, strikes on Israeli territory from Yemen intensified. From October 2023 to mid-January 2025, Sana’a media reported 92 air raids on various targets in Israel, including the Haifa port on the Mediterranean (jointly with Iraqi resistance forces) and Ben Gurion International Airport in Tel Aviv. During this period, the Houthis also attacked 24 Israeli ships. They carried out 78 combat operations against the U.S. Navy, attacked 30 American commercial vessels, and 13 British ships. Attacks on Israeli territory involved cruise and ballistic missiles, some with hypersonic capabilities that pierced Israel’s defense systems, as well as large numbers of drones. According to incomplete data, during the first year of the “Archer” operation, USUKMC launched 1,200 strikes on Yemen. The combat experience gained by U.S. forces in the war with Yemen in the Red and Arabian Seas was recognized by many experts as instructive, becoming a subject of close study of a conflict in which drones worth up to $20,000 were countered by air defense missiles costing $1–4.5 million each. The change of administrations in the White House triggered a pause in the Gaza war on January 19, 2025, and a simultaneous halt in Houthi attacks on all ships in the Red and Arabian Seas. However, the arrival of President Trump was accompanied by a major escalation of the U.S. military operation, which was named “Furious Rider.” Trump's designation of the Houthis as a Foreign Terrorist Organization (FTO) on January 22, 2025, coincided with the pause in hostilities and contradicted the call from UN mission head H. Grundberg for a full ceasefire in the Red Sea, citing Yemen’s dire humanitarian situation. At the UN Security Council briefing on February 13, 2025, he began his speech with a call for deescalation. However, on March 15, 2025, the U.S. resumed heavy bombing of Yemen just before the truce in Gaza collapsed due to Israeli actions. The Washington Times wrote: “President Trump warned the Iran-backed terrorist group that it must stop all attacks on commercial shipping in the Red Sea, or ‘you will face a hell like you’ve never seen before.’” The new wave of daily, unprecedentedly intense strikes on Yemen under the “Furious Rider” operation continued from March 15 to May 6, 2025. The beginning of the operation was marked by a loud political scandal — “Signalgate” — related to the leak of confidential information about the planned U.S. military operation in Yemen. The leak was published in an article by The Atlantic’s editor-in-chief Jeffrey Goldberg, who had accidentally joined a messenger chat created by National Security Secretary Mike Watts, who was later dismissed over the incident. The operation involved the aircraft carrier USS Harry S. Truman (CVN-75), which lost three F-18 jets in multiple incidents, each valued at $67 million. The U.S. also lost over a dozen heavy MQ-9 Reaper drones, each worth $30 million, shot down over Yemen. The cost of the U.S. operation in Yemen is estimated at around $7 billion. In late April 2025, British aircraft rejoined the “Rider” operation. On May 5, Israeli aircraft carried out its first large-scale strike of the campaign on sensitive infrastructure and residences of Ansar Allah’s political and military leaders, continuing attacks even after President Trump declared the operation over. At an investment forum in Riyadh in mid-May, the American president gave the following comment on his decision: “In recent weeks, after repeated attacks on American ships and on the freedom of navigation in the Red Sea, the U.S. military carried out more than 1,100 strikes on the Houthis in Yemen. As a result, the Houthis agreed to stop. They said, ‘We don’t want this anymore.’ You’re hearing this from them for the first time. They’re tough guys, they’re fighters. But just a few days ago, we asked them to stop attacking commercial ships. They had no intention whatsoever of targeting trade vessels or anything American, and they were very happy that we stopped. But we had 52 days of thunder and lightning like they’d never seen before. It was fast, fierce, decisive, and an extremely successful use of military force. Not that we wanted it, but they were hitting ships. They were firing at you. They were firing at Saudi Arabia. We were not.” The prospects for further development of the YC remain unpredictable. The linkage of YC with the PIC remains in effect. YC has transitioned into a format of direct confrontation between SA and Israel. A new war front was opened by Israel's attack on Iran on January 13, 2025, and the twelve-day war that followed — ending with a U.S. strike on Iran’s nuclear facilities and Iran’s retaliatory strike on a U.S. Air Force base in Qatar — sparked Sana’a’s willingness to support Iran while continuing to tie YC to the situation in Gaza and maintain the blockade of Israeli shipping through the Bab-el-Mandeb Strait. Russia’s position throughout all phases of the second stage of the military phase was consistently focused on political resolution of YC. On May 14, 2025, Russia’s Permanent Representative to the UN, V.A. Nebenzya, stated that during the nearly two-month confrontation between the U.S. and the Houthis, the death toll had exceeded 200 people, with several hundred more injured. Strikes were carried out almost nightly on the territory of sovereign Yemen, targeting not only military but also civilian infrastructure, with no result — neither the suppression of Ansar Allah’s military capabilities nor their abandonment of their course of action. Welcoming the cessation of U.S. attacks on Yemen, the Russian envoy remarked: “Better late than never, as the saying goes. It seems that Washington has finally acknowledged the futility of the military approach, something we have pointed out repeatedly… This could have been a first step toward general de-escalation around Yemen. But unfortunately, it is not yet the case, because Israel has now begun relay-style bombardments of Yemen.” The U.S.-UK coalition’s military campaign in Yemen bore all the hallmarks of a large-scale neocolonial military adventure. It immediately took the form of a demonstration of military superiority, hardly differing in method or tactics from earlier AC operations, when nearly 250,000 strikes were launched on Yemen from March 2015 to April 2022. The USUKMC's failures to organize a ground operation — necessary for military victory — also echoed past lessons. The AC’s refusal to participate in favor of maintaining the de-escalation regime, and the conditional agreement by Yemeni CPIs in the MPP to join only if supplied with U.S. arms (thus endangering their patrons from the AC), yielded no results. Moreover, the Palestinian backdrop of the new phase raised the risk that all of the accumulated military power of SA’s enemies might eventually pivot against Israel’s allies. The second stage of the geopolitical phase of the crisis cannot be considered fully complete, yet it may transform into a third one if Israel attempts to seize the initiative. * Organization designated as terrorist and banned in the Russian Federation.References:Bokov T.A. The Yemeni Houthi Movement: Causes of Origin, Formation and Development. Dissertation abstract. St. Petersburg, 2023. P. 162.In January 2021, outgoing president D. Trump designated the Houthis as an international terrorist group, which was reversed by incoming president J. Biden in February. In January 2024, the group was re-designated, and Trump began his new term in January 2025 by raising the threat level of the Houthis to a “Foreign Terrorist Organization” (FTO).The Huthi Movement in Yemen: Ideology, Ambition and Security in the Arab Gulf / Abdullah Hamidaddin. London: I.B. Tauris, 2022.The book’s editor was Dr. Abdullah Hamidaddin, Assistant Secretary General of the Center. Contributors included B. Haykel (Princeton), M. Brandt (ISA, Austria), E. Ardemagni (ISPI, Italy), among others.The same article served as the legal reference for launching the AC’s “Decisive Storm” operation in March 2015.United Nations S/2024/90 Security Council Distr.: General 22 January 2024 — Letter dated 22 January 2024 from the Permanent Representative of the Russian Federation to the United Nations addressed to the President of the Security Council.MQ-9 Reaper — remotely piloted UAV, medium-altitude and long-endurance. Primarily used for reconnaissance, surveillance, targeting, and strikes.