The Ukraine-Russia conflict: An international humanitarian law review of the involvement of foreign fighters
by Khoirunnisa Khoirunnisa , Brian Matthew , Didi Jubaidi , Agung Yudhistira Nugroho
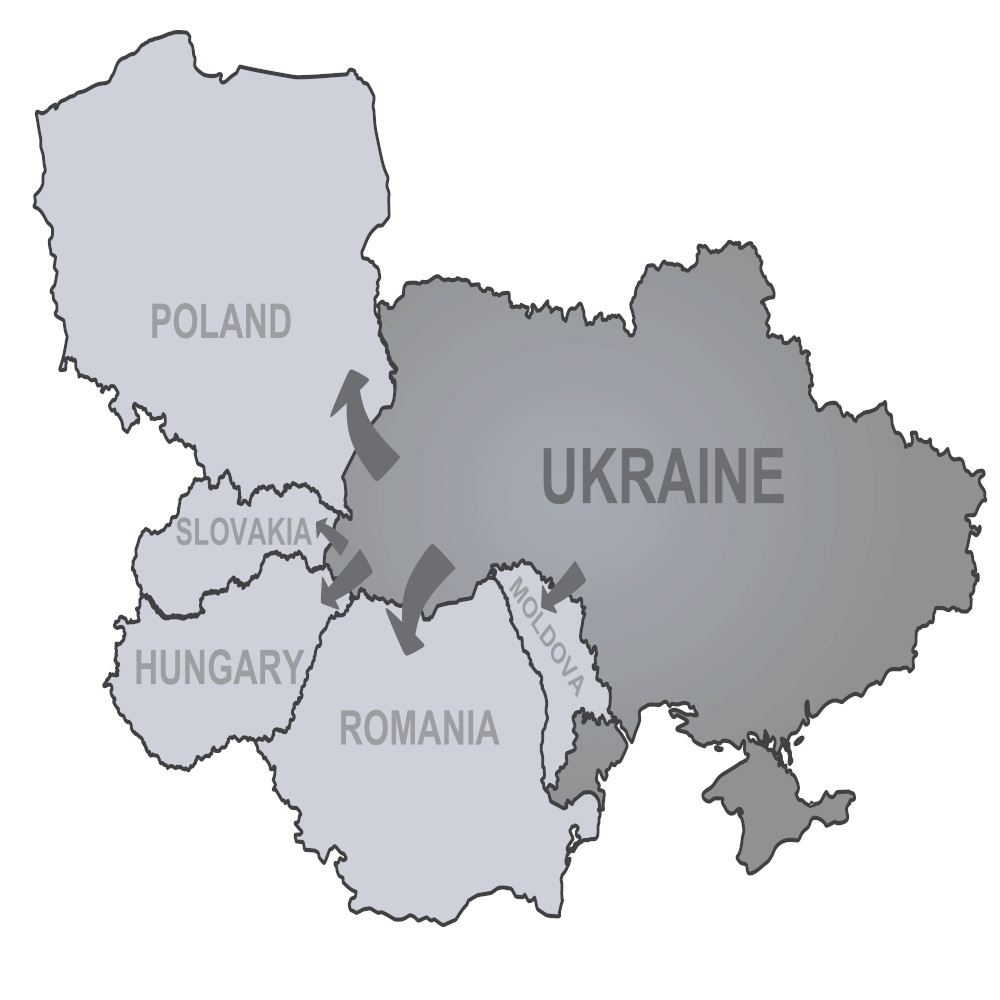
AbstractThe increasing presence of foreign fighters in the armed conflict in Ukraine has posed significant challenges to the application of International Humanitarian Law (IHL). These foreign fighters, often motivated by political, ideological, or religious reasons, do not neatly fit into traditional legal categories such as lawful combatants, civilians, or mercenaries. Their involvement on both sides of the conflict between those supporting either Ukrainian forces or Russian-backed groups, presents a complex issue that requires careful consideration within the context of IHL, which currently lacks clear provisions for addressing their legal status. This study focuses on the research question: Does the involvement of foreign fighters in the armed conflict in Ukraine comply with the principles of International Humanitarian Law? This issue is particularly important as it exposes significant gaps in IHL, revealing its inability to adequately address the complexities of modern armed conflicts involving non-state actors. Employing a juridical-normative approach, this study examines the application of IHL to foreign fighters in the Russia-Ukraine conflict, focusing on their rights, responsibilities, and accountability. The findings show that IHL lacks specific provisions to regulate the legal status of foreign fighters, relying instead on general human rights principles that fail to address their unique circumstances. This creates a legal vacuum, undermining both their protection and the enforcement of accountability for violations. The study concludes that targeted reforms in IHL are urgently needed to establish clear legal standards for the classification, protection, and prosecution of foreign fighters, thereby strengthening the overall humanitarian framework for contemporary armed conflicts.KeywordsForeign fighters, Russia, Armed conflict, Humanitarian law, Ukraine 1. Introduction The Russia-Ukraine conflict, which has been ongoing since Russia's annexation of Crimea in 2014, has escalated into a complex and devastating war. This conflict, deeply rooted in geopolitical tensions, has drawn the attention of the international community, not only due to the implications for regional stability but also for the growing role of foreign fighters. The involvement of foreign fighters in the conflict adds a new layer of complexity to the already volatile situation. These individuals, who join armed conflicts in foreign territories, are often motivated by political, ideological, religious, or financial reasons, and their presence in Ukraine raises serious legal, political, and humanitarian questions (Asya et al., 2024). The role of foreign fighters has become increasingly significant in modern warfare, with their participation often blurring the lines between combatants, civilians, and mercenaries (Anjelika et al., 2024)The primary challenge posed by the involvement of foreign fighters in Ukraine lies in the legal uncertainty surrounding their status under International Humanitarian Law (IHL). IHL, which governs the conduct of armed conflicts and seeks to protect individuals who are not actively participating in hostilities, does not provide clear guidelines for foreign fighters. These fighters, who do not represent a state or recognized party to the conflict, do not neatly fall into categories such as lawful combatants or civilians, making their legal status ambiguous. This creates a gap in the legal framework, complicating the application of IHL to their actions and raising critical questions about accountability, rights, and protections under international law (Alexander, 2023) (see Table 1, Table 2). The significance of this study stems from the need to address these legal uncertainties and to understand how IHL can be adapted to regulate the involvement of foreign fighters in modern conflicts. Despite the growing prevalence of foreign fighters in conflicts around the world, the existing body of IHL has not sufficiently addressed their status or the challenges they pose to the protection of human rights and the enforcement of accountability (Paulussen, 2021). By focusing specifically on the Ukraine conflict, this study aims to fill a significant gap in current legal scholarship by analyzing the implications of foreign fighters' participation through the lens of IHL. The involvement of foreign fighters in the Ukraine conflict has profound implications not only for the legal treatment of these individuals but also for the broader geopolitical context (Idris & Mu'tashim, 2023). Their participation exacerbates tensions between Russia and Western countries, as foreign fighters supporting Ukraine often come from nations with opposing political interests to Russia. This dynamic further complicates diplomatic efforts aimed at resolving the conflict and maintaining international peace. Additionally, the presence of foreign fighters contributes to the growing trend of non-state actors engaging in warfare, challenging traditional notions of state sovereignty and complicating international efforts to regulate armed conflict (Lekatompessy et al., 2024). From a humanitarian perspective, the presence of foreign fighters increases the risks of violations of IHL and human rights, as these individuals may not be subject to the same legal frameworks as state actors. The lack of clear legal provisions for foreign fighters leaves them vulnerable to exploitation, abuse, and violations of their rights, while also creating a situation in which accountability for violations becomes difficult to enforce (Akbar & Sadiawati, 2023). This not only undermines the protection of civilians but also weakens the enforcement of humanitarian norms, further complicating the efforts of international organizations and states to address violations of IHL. This study is particularly important because it seeks to address the legal vacuum that exists concerning foreign fighters in the Ukraine conflict. By examining the application of IHL to foreign fighters, this research contributes to the broader field of international law by proposing a more comprehensive framework for regulating their involvement. Through this examination, the study aims to provide concrete recommendations for legal reforms within IHL that would better address the challenges posed by foreign fighters in modern armed conflicts. The rationale for this study lies in the growing recognition that IHL, as it currently stands, is insufficient to address the complexities of modern warfare, particularly when it comes to the participation of non-state actors like foreign fighters. As the world witnesses an increasing number of foreign fighters engaging in conflicts worldwide, it is essential to adapt international legal frameworks to these new realities. This study not only contributes to the understanding of IHL's limitations but also proposes practical legal reforms that could enhance its effectiveness in protecting human rights and ensuring accountability in future conflicts. The involvement of foreign fighters in Ukraine represents a critical point at which the gaps in IHL are laid bare. As such, this study holds significant relevance for policymakers, international legal scholars, and human rights advocates, as it highlights the urgent need for reform and provides insights into how IHL can evolve to better respond to contemporary challenges. By addressing the legal status and accountability of foreign fighters, this study aims to contribute to the development of a more robust and responsive international legal system that can effectively address the complexities of modern warfare and uphold humanitarian principles in the face of emerging threats. 1.1. Literature review Previous research by Akbar and Sadiawati (2023), titled "Analysis of the Russian Invasion of Ukraine in Terms of Humanitarian Law", focuses on examining violations of the 1949 Geneva Conventions during the invasion and emphasizes the role of the United Nations in promoting global peace. The study provides a comprehensive analysis of the international legal framework, particularly humanitarian law, in addressing war crimes and violations committed during the conflict. Similarly, Nasution and Raudia (2022, pp. 361–374), in their article "Analysis of Russian War Violations in the 2022 Ukrainian Conflict Based on the Perspective of International Humanitarian Law", discusses the breaches of humanitarian law committed by Russia during the conflict. Their study highlights key violations under international legal standards and emphasizes the need for accountability based on humanitarian law principles. Masri et al. (2024), in their study titled "Implementation of International Humanitarian Law in the Russia-Ukraine Conflict", explore the application of international humanitarian law (IHL) within the context of the Russia-Ukraine war. Their research delves into how IHL has been enforced and its effectiveness in mitigating harm during the conflict. While these studies extensively analyze IHL violations in the Russia-Ukraine war, they focus primarily on state actors, with limited attention to the role of foreign fighters. This paper fills this gap by analyzing the participation of foreign fighters, their classification under IHL, and the legal protections afforded to them. 1.2. Theoretical framework1.2.1. Theories of state sovereignty and territorial integrity The theory of state sovereignty and territorial integrity originates from classical thinkers like Bodin (2009), Hugo Grotius (1964), and Kant (1991). Bodin defined sovereignty as supreme authority free from external interference, while Grotius emphasized its role as a cornerstone of international law. Kant argued that territorial integrity was vital for peaceful inter-state relations. These principles were codified in Article 2(4) of the UN Charter (1945), prohibiting threats or force against a state's territorial integrity or political independence. In the Russia-Ukraine conflict, these principles are acutely relevant. Russia's annexation of Crimea (2014), support for separatists in Donetsk and Luhansk, and the 2022 invasion breach sovereignty and international law. Moerdijat (2022) highlights these violations' severity, while Pisano (2022) examines their destabilizing effects on regional geopolitics. Thus, this theory offers a legal and analytical lens to assess the conflict's ramifications for the global order. 1.2.2. Theories of international humanitarian law (IHL) The development of IHL stems from contributions by scholars like Jean Pictet, who stressed protecting individuals in conflicts, and Hugo Grotius, whose De Jure Belli ac Pacis advocated for war regulation through moral and legal principles. J.F. Murphy (1982) linked IHL with human rights, Antonio Cassese (2013) explored IHL's role in mitigating human rights violations during war, and Theodor Meron (2006) advanced civilian protections and war crime regulations. These foundations emphasize protecting non-combatants, limiting warfare methods, and clarifying states' obligations. In Ukraine, IHL faces challenges like the ambiguous legal status of foreign fighters. Akbar and Sadiawati (2023) highlight gaps in their protections, while the BBC (2023) reports on the Wagner Group's role in exacerbating violations, such as civilian attacks and disproportionate force. These challenges underscore the need for stricter adherence to IHL to mitigate humanitarian crises and uphold legal standards. 1.2.3. Theories of globalization in modern warfare Theories on globalization's impact on warfare are shaped by thinkers like Mary Kaldor (2013), who contrasts traditional "old wars" with "new wars" involving non-state actors, and Zygmunt Bauman (1998), who links globalization to interconnected dynamics reshaping warfare. Robert D. Kaplan (1994) connects globalization to growing socio-economic inequalities and asymmetric conflicts. These theories argue that globalization's technological, economic, and communicative aspects have transformed war by introducing non-state actors and advanced technologies. The Russia-Ukraine conflict illustrates globalization's role in modern warfare. The participation of foreign fighters, whether aiding Ukraine's International Territorial Defense Legion or Russia's Wagner Group, reflects globalization's influence. Mehra and Thorley (2022) note motivations like ideology and economics, while Chakyan Tang (2022) highlights both solidarity and challenges introduced by non-state actors. Globalization expands conflicts' scope and complexity, complicating regulation while reshaping modern warfare's nature. 2. Methodology This research employs a juridical-normative method using a legal approach to examine the Ukraine-Russia conflict within the framework of International Humanitarian Law (IHL) (Gunawan et al., 2023). The primary objective is to explore how the actions of the parties involved align with the established principles and norms of international law. A juridical-normative approach is used to systematically analyze laws, regulations, and legal principles applicable to the conflict, particularly focusing on how these norms are implemented or potentially violated by the involved actors. The study relies on qualitative normative research methods, which involve document analysis of legal texts and secondary sources to gain a comprehensive understanding of the legal framework governing the conflict. This includes examining court decisions, legal doctrines, international treaties (such as the 1949 Geneva Conventions), and other relevant international instruments. Secondary sources, such as legal theories and expert opinions, also form a key part of the analysis. Through this approach, the research offers a comprehensive analysis of compliance with, or violations of, the principles of International Humanitarian Law (IHL) in the conflict. The document analysis process, as the primary data collection method, incorporates legal hermeneutics to interpret and clarify the meaning of legal texts, ensuring an accurate understanding of their application in the context of the Ukraine conflict. Comparative analysis is also employed to examine how IHL principles have been applied in similar conflicts, providing a benchmark for evaluating their implementation or breach in this case. The analysis focuses on primary legal materials, including treaties, conventions, official communications, and resolutions from international organizations, to establish a foundational understanding of the legal framework. These are complemented by secondary legal materials, such as academic literature, legal commentaries, and expert opinions, which provide critical insights and context. This methodological combination ensures a robust and nuanced evaluation of how IHL principles are being upheld or violated, strengthening the validity and reliability of the findings. 3. Results and discussion3.1. Legal framework for foreign fighters The status of foreign fighters under International Humanitarian Law (IHL) remains contentious and ambiguous. While the Geneva Conventions and their Additional Protocols primarily regulate the conduct of state actors and recognized combatants, they offer limited guidance for non-state participants, such as foreign fighters. These individuals find themselves in a legal gray area, as the Geneva Conventions focus mainly on the protection of civilians and combatants who are part of a state's armed forces or organized resistance groups. Common Article 3 of the Geneva Conventions and Additional Protocol II extend limited protections to non-state actors involved in non-international armed conflicts, emphasizing humane treatment and prohibiting acts like torture or degrading treatment (M, 2001). However, these provisions do not explicitly address the legal status, rights, or obligations of foreign fighters who may not be formally part of an organized state or non-state armed force. Additional Protocol I further complicates this issue. For example, Article 47 of Protocol I explicitly excludes mercenaries from the status of combatants or prisoners of war (POWs), effectively denying them the legal protections afforded to lawful combatants (Geraldy Diandra Aditya, Soekotjo Hardiwinoto, 2017). This exclusion raises questions regarding the legal status of foreign fighters who may not fit neatly into the categories of lawful combatant, civilian, or unlawful belligerent. As a result, the legal position of foreign fighters in modern armed conflicts, such as the Ukraine-Russia conflict, remains unclear and potentially subject to exploitation or abuse. A table listing key international treaties, conventions, and resolutions relevant to foreign fighters could illustrate the legal tools available for regulating their conduct and holding them accountable. The table could include categories such as. 3.1.1. Legal status and responsibilities of foreign fighters Foreign fighters have become a notable element of modern conflicts, including in Ukraine, where individuals from various countries have joined both sides of the conflict. Their participation raises significant legal and ethical questions, particularly regarding their status under International Humanitarian Law (IHL) and the accountability for their actions. IHL, as defined by the Geneva Conventions and the Hague Conventions, does not explicitly mention "foreign fighters" but provides a legal framework for determining their status based on their activities and allegiance. Foreign fighters are typically categorized as either lawful combatants, unlawful combatants, or civilians, and their rights and responsibilities are governed by the laws of war (Hasan & Haque, 2023). a. Lawful Combatants, foreign fighters who join the armed forces of a state party to the conflict (e.g., Ukraine in the context of the Russian invasion) may be considered lawful combatants. As lawful combatants, they are entitled to the protections of IHL, including protection from being targeted and humane treatment if captured. They are subject to the laws of armed conflict, particularly the Geneva Conventions, and must adhere to principles such as distinction, proportionality, and the prohibition of unnecessary suffering. However, this status is contingent upon them being members of an organized military force that follows IHL regulations.b. Unlawful Combatans, foreign fighters who join non-state armed groups, such as mercenaries or irregular militias not recognized under IHL, are considered unlawful combatants. They are not entitled to the same protections as lawful combatants and may be prosecuted for violations of IHL, including acts that could constitute war crimes. The status of unlawful combatants often leads to challenges in terms of legal accountability, as their actions may not be adequately covered by state-based military tribunals or national courts. International efforts to hold foreign fighters accountable for violations such as the targeting of civilians or the use of prohibited weapons can be complicated by the lack of a clear framework for prosecuting non-state actors.c. Civilians, foreign nationals who participate in the conflict but do not take a direct part in hostilities are considered civilians and are protected by IHL. Their involvement in combat can alter their status, and they may lose their protection from direct targeting once they engage in hostilities. This creates a complex dynamic for the prosecution and accountability of foreign fighters, as their status may change based on their activities in the field. A table that compares the legal status of foreign fighters in different contexts could help clarify the varying rights and responsibilities under International Humanitarian Law (IHL). The table could include categories such as: Here is the map illustrating the geographical origins of foreign fighters in the Ukraine conflict, showing their involvement with either the Ukrainian or Russian side. This visual provides a global context to their participation. 3.2. Ukraine's historical struggle: Russia's colonialism and imperialistic attitudes The relationship between Russia and Ukraine stretches back for centuries, characterized by a complex and often turbulent history. From the medieval period to modern times, Ukraine has faced numerous instances of Russian dominance and interference, which has shaped its national identity and its ongoing struggle for independence. This historical context is essential to understanding Ukraine's motivations to fight, as it reflects a long-standing resistance to Russian colonialism and imperialism. In the 17th and 18th centuries, Russia began consolidating its control over Ukrainian territories, particularly after the Treaty of Pereyaslav in 1654, which marked the beginning of Ukrainian subordination to the Tsarist empire (Britannica, 2025). Over the centuries, Ukraine's autonomy was eroded, and it became an integral part of the Russian Empire, with many Ukrainians subjected to harsh policies of Russification. The suppression of Ukrainian culture, language, and national identity under Tsarist rule set the stage for future tensions. The most devastating chapter of this colonial history came under Soviet rule, which exacerbated the sense of Russian imperialism. The Holodomor, a man-made famine in the early 1930s, is one of the darkest episodes in Ukrainian history. Millions of Ukrainians perished as a result of Stalin's policies, which sought to enforce collectivization at the cost of the Ukrainian people. This tragedy has left a lasting scar on the collective memory of Ukraine, fueling a deep-seated distrust of Russia and reinforcing the narrative of Ukrainian victimhood under Russian imperialism. Even after the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991 and Ukraine's declaration of independence, Russia has continually sought to exert influence over Ukraine, often invoking its imperial past to justify intervention. Russia's annexation of Crimea in 2014 and its ongoing military actions in eastern Ukraine are seen by many as a continuation of the imperialistic attitude that has defined Russia's relationship with Ukraine for centuries. Ukraine's motivation to fight in the current conflict is deeply rooted in its desire to protect its sovereignty and preserve its cultural and political independence from Russian influence. This struggle is not just a response to Russia's aggression but a continuation of a centuries-long fight for self-determination, dating back to the period of Tsarist colonialism and reinforced by the Soviet era. The ongoing war represents Ukraine's determination to break free from the chains of Russian imperialism and secure its future as an independent, sovereign nation. 3.3. International humanitarian law review of Russia's armed attack in Ukraine After the Russian annexation of Crimea, tensions in relations between Russia and Ukraine continued until February 2022. These tensions began when NATO sought to expand its membership into Eastern Europe by inviting Ukraine to join as a member (Andi Antara Putra & Dantes, 2022). NATO has expressed its commitment to Ukraine's future membership, stating: "We reaffirm that we will be in a position to extend an invitation to Ukraine to join the Alliance when Allies agree and conditions are met (NATO, 2024b)." This position underscores NATO's openness to Ukraine's membership, contingent upon unanimous agreement among current member states and Ukraine's fulfillment of specified criteria. While NATO has not issued a formal invitation to Ukraine, it acknowledges Ukraine's aspirations and is actively supporting its progress toward potential membership. This support includes enhancing interoperability and implementing democratic and security sector reforms (NATO, 2024a). This represents an escalation of tensions between Russia and Western countries, especially NATO, as Eastern Europe has become a critical arena for competing geopolitical interests. NATO's post-Cold War expansion, which saw the inclusion of former Eastern Bloc countries such as Poland, Hungary, and the Baltic states, has been interpreted by Russia as a direct encroachment on its sphere of influence and a threat to its security. This tension was further amplified by NATO's 2008 declaration that Ukraine and Georgia would eventually become members, which Russia perceived as a red line. The strategic importance of Eastern Europe, both as a buffer zone and as a transit corridor for energy resources, adds to the stakes for both NATO and Russia. Russia's aggressive actions, including the 2014 annexation of Crimea and its ongoing involvement in Eastern Ukraine, can be seen as attempts to counterbalance NATO's growing presence in the region. Conversely, NATO's military support to Eastern European nations underscores its commitment to collective defense and the deterrence of Russian aggression, further fueling the geopolitical rivalry. Geopolitical influence and efforts to strengthen military presence in the region are important factors in the dynamics of the ongoing conflict between Russia and Ukraine. Russia's insistence that it will not allow Ukraine to "break away," viewing it as a threat to its interests and security (Mamfaluthy, 2014), raises significant tensions with international law principles, particularly the respect for national sovereignty. The United Nations Charter guarantees every state the right to sovereignty, territorial integrity, and political independence, which includes Ukraine's right to determine its domestic and foreign policies without external interference. While Russia argues that Ukraine's potential NATO membership or Western alignment threatens its security, such concerns do not justify actions that violate Ukraine's sovereignty, such as the annexation of Crimea or support for separatist movements in Eastern Ukraine. Although international law permits states to take measures to protect legitimate security interests, these must align with legal norms and avoid infringing on the sovereignty of other states. Russia's actions contravene these principles, as reaffirmed by UN General Assembly resolutions recognizing Ukraine's territorial integrity. This tension highlights a clash between Russia's realpolitik approach to securing its strategic interests and the international legal obligation to respect the sovereignty and independence of other nations. In Putin's view, all countries that are members of NATO have the full right to organize and protect their territories from all threats, both from within and outside the country (Pradana & Ramadhoan, 2022). Putin's opinion reflects the view that NATO membership by countries surrounding Russia, including Ukraine, is perceived as a threat to Russia's security. This is reflected in concerns over the deployment of NATO military infrastructure near Russia's borders, which could be perceived as a direct threat to Russia's strategic interests. Putin has therefore insisted on taking measures he deems necessary to protect Russia's interests and sovereignty. This has led to increased tensions between Russia and Western countries that support Ukraine's membership in NATO. Russia's response to Finland's NATO membership contrasts sharply with its actions toward Ukraine, mainly due to the differing historical and cultural ties with each country. Finland views its NATO membership primarily as a defensive strategy, while Ukraine's relationship with Russia has deep historical and cultural roots. Finland's strong military, combined with NATO's collective defense principles, serves as a deterrent to Russian aggression, whereas Russia, already heavily engaged in Ukraine, avoids provoking NATO. This difference highlights that Russia's actions toward Ukraine are driven by regional dominance ambitions, rather than NATO expansion. Russia's intervention in Ukraine violates the principle of non-intervention, which is a fundamental tenet of international law. Non-intervention asserts that each state has the right to manage its internal affairs without external interference (Octavia & Husniyah, 2023). Article 2, paragraph 4 of the UN Charter emphasizes the importance of peaceful dispute resolution and the avoidance of armed conflict. Russia's actions also contravene the Declaration on Principles of International Law (A/RES/25/2625, 1970), which upholds the national sovereignty, territorial integrity, and political independence of states, emphasizing that disputes should be resolved peacefully and without violence (Mahfud, 2015; Rudy, 2011). Furthermore, Article 38 of the Statute of the International Court of Justice broadens the sources of international humanitarian law (IHL), allowing for inclusion of legal principles recognized by civilized nations, international organizations, and expert opinions, not limited to international treaties (Budisantosa, 2021). This further underscores the importance of respecting IHL and the sovereignty of states in the global legal framework. While the international treaties that are the main foundation of IHL are the Hague Conventionand the Geneva Convention (Pasorong et al., 2023). The Hague Convention regulates the laws of war governing the treatment of individuals and property in armed conflicts, while the Geneva Convention sets minimum standards for the treatment of war victims, including the protection of civilians, prisoners of war, and medical personnel. These two conventions form an important legal framework for safeguarding humanity during armed conflicts and have been the main basis for the formation of further IHL rules. IHL cannot cover all actions in international wars, but parties to armed conflicts are obliged to respect and uphold the basic principles of IHL these include (Danial, 2017). a. The Humanitarian Principle: Demands that actions in armed conflict should take into account the interests of humanity and avoid unnecessary suffering of individuals not involved in the conflict.b. Military Interests: Recognizes that military actions taken should be proportionate to the military objectives to be achieved and should minimize unnecessary losses.c. Proportionality: States that military actions must be in accordance with legitimate military interests and must be proportionate to the threat faced.d. Distinction: Stipulates that parties to a conflict must distinguish between individuals participating in the conflict (military) and those not participating (civilians), as well as between military and non-military objects.e. Prohibition of Unnecessary Suffering: Prohibits acts that cause unnecessary suffering or that are incompatible with legitimate military objectives.f. Separation of Ius ad Bellum and Ius in Bello: Distinguishes between the law governing the authority to use military force (Ius ad Bellum) and the law governing the behavior of the parties to the conflict (Ius in Bello). Russia's armed attack on Ukraine violated several fundamental principles of international humanitarian law (IHL). First, it breached the principle of state sovereignty by violating Ukraine's territorial integrity and political independence, contravening Article 2, paragraph 4 of the UN Charter, which prohibits the use of force against another state's territorial integrity. Second, the attack violated the principle of distinction, as there have been reports of civilian casualties from Russian military strikes, which should have been targeted at combatants and military objectives. Third, the strikes caused unnecessary suffering to the civilian population and infrastructure, violating the prohibition against unnecessary suffering in IHL. Overall, Russia's actions are considered serious violations of IHL and universally recognized humanitarian principles. 3.4. Foreign fighters in the context of international humanitarian law The conflict in Ukraine has brought attention to the complexities of international law, particularly regarding foreign fighters in armed conflicts. According to Common Article 3 of the Geneva Conventions, the conflict qualifies as a Non-International Armed Conflict (NIAC), which involves non-state armed groups like insurgents or separatists against state forces (Brits, 2017; Mehra & Thorley, 2017; Mehra & Thorley, 2022). However, the involvement of Russia complicates this classification, leading some to argue the conflict may be an International Armed Conflict (IAC) governed by the Geneva Conventions and the First Additional Protocol, which set standards for the protection of civilians and prisoners of war (Susetio & Muliawan, 2023). The Second Additional Protocol (APII) further outlines protections for civilians and individuals not directly participating in hostilities, providing essential legal instruments for the Ukraine conflict (Ismail, 2018). Despite the ongoing debate over the conflict's classification, IHL standards, including protections against torture and inhumane treatment, apply. These standards include principles such as proportionality and distinction, aiming to safeguard civilians and regulate military conduct (Gisel et al., 2020; Murray, 2019). The classification of the conflict is crucial in determining the application of IHL, especially regarding civilian protection, and distinguishing between military targets and non-combatants (Diakonia, 2022). The influx of foreign fighters, particularly through the International Territorial Defense Legion initiated by Ukrainian President Volodymyr Zelensky, has further complicated the conflict. Since 2014, thousands of foreign fighters from 55 nations have joined the conflict, which could escalate tensions and potentially violate IHL if human rights abuses occur (Egle E. Murauskaite, 2022; Nigel Walker, 2023). The presence of foreign fighters raises significant questions regarding their legal status and responsibilities within the conflict. The term "Foreign Fighters" lacks a universally accepted definition in international law. The most authoritative definition originates from UN Security Council Resolution 2178, which references "foreign terrorist fighters." A foreign terrorist fighter is defined as an individual who travels to a country other than their own to engage in activities that support terrorism, including (Bramantyo, 2023). a. Committing acts of terrorism, characterized by violence or threats aimed at instilling fear or causing harm to civilians for political objectives.b. Planning or preparing acts of terrorism, such as target surveillance, recruitment, or weapon acquisition.c. Participating directly in acts of terrorism, providing logistical support, or harboring perpetrators.d. Receiving or providing terrorism-related training, which includes the use of weapons, explosives, or guerrilla tactics. The UN Security Council's approach to foreign fighters emphasizes counterterrorism, evident in the focus of Resolution 2178 on their roles in terrorism. However, this counterterrorism perspective has been adopted at the national level by various member states, shaping their responses to foreign fighters. Various definitions of "foreign combatants" have emerged in academic literature, with one prevalent definition describing individuals motivated by ideology, religion, or kinship to leave their country to join an armed conflict abroad (Van Poecke & Cuyckens, 2023). Key aspects of this definition include. 1) Motivation, foreign combatants are driven by ideological, religious, or familial factors rather than personal gain.2) Movement, they travel from their home country to engage in conflict in another nation.3) Active involvement, their participation extends to combat or related activities. The classification of "foreign combatants" specifically refers to individuals joining non-state armed groups in conflicts abroad, often motivated by ideological, religious, or kinship ties (Baker-Beall, 2023). This classification excludes mercenaries or volunteers driven by other factors. While national security and counterterrorism are frequently the focus of discussions about foreign fighters, categorizing them as terrorists does not negate the application of International Humanitarian Law (IHL), which applies equally to all belligerents, including foreign fighters. Their actions in armed conflicts should be evaluated according to IHL principles (Ho, 2019). The term "foreign terrorist fighters" may complicate legal proceedings by focusing primarily on counterterrorism rather than recognizing the nuances of foreign fighter involvement in armed conflicts. These individuals often participate in both non-state armed conflicts and terrorist activities (Karska & Karski, 2016). The distinction between "foreign fighters" and "mercenaries" is also important, as foreign fighters typically join armed groups for ideological reasons, whereas mercenaries are financially motivated (Floress, 2016; Dano, 2022). Russia's use of the term "mercenaries" may be intended to influence public perception and emphasize the economic aspects of their participation. Article 47 of the 1977 First Additional Protocol (API) to the Geneva Conventions outlines the legal status of foreign fighters and the limitations on applying the Convention's provisions to individuals from non-signatory states. However, Article 47(2) reinforces that human rights protections remain in effect for foreign fighters, and the responsibilities of conflict parties under IHL are unaffected (Gregorious, 2023). As foreign fighter involvement in conflicts like Ukraine increases, challenges arise regarding their legal status and protections under IHL, necessitating careful consideration of both legal and humanitarian aspects in addressing these issues. 3.5. Human rights of foreign fighters in the context of international humanitarian law The ongoing conflict between Ukraine and Russia has resulted in severe material and psychological consequences for both the civilian population and combatants. Amidst this turmoil, the participation of foreign fighters has garnered significant attention, raising questions about their status and human rights within the framework of International Humanitarian Law (IHL). Despite their involvement in armed conflict, foreign fighters retain certain rights and protections under IHL, necessitating a thorough assessment of their legal status, actions during the conflict, and involvement in armed groups. Thus, the protection of their human rights must be carefully considered in accordance with the principles of IHL, which guarantee fair and humane treatment for all parties involved. 3.5.1. Concerns regarding due process and human rights violations The recent sentencing of three foreign fighters to death by the Supreme Court of the Donetsk Republic has raised serious concerns about adherence to international legal standards. These sentences were issued after proceedings criticized for being swift and unfair, raising alarms about violations of the right to a fair trial, including access to legal counsel and the right to present a defense. The United Nations Commission on Human Rights has previously reported violations in the region, indicating a troubling disregard for internationally recognized human rights norms. In response, the European Court of Human Rights (ECHR) intervened, directing Russia to halt the use of the death penalty and to respect the rights of foreign fighters. This underscores the critical need to uphold fundamental human rights, even amidst armed conflict, and to ensure that individuals engaged in hostilities receive basic protections recognized by international law. 3.5.2. The issue of citizenship and nationality The citizenship status of foreign fighters in the Ukraine conflict is complex due to varying national legal frameworks and policies regarding participation in foreign armed conflicts. Some countries have enacted laws revoking citizenship for involvement in terrorist activities or foreign conflicts, citing national security concerns, though critics argue these measures often lack transparency and due process, risking arbitrary deprivation of nationality. The revocation of citizenship leaves individuals in a legal limbo, vulnerable to prosecution or ill-treatment in other states. Statelessness, a common outcome of citizenship loss, exacerbates vulnerability by denying individuals access to basic rights like education, healthcare, and employment. This issue has significant implications for international human rights. The UN plays a key role in addressing these challenges by facilitating dialogue, monitoring compliance with international law, and advocating for human rights protections. Regional organizations, such as the EU, are also critical in promoting unified approaches and adherence to human rights standards in the treatment of foreign fighters. 3.5.3. Human rights protections under IHL The Geneva Conventions, particularly the Fourth Geneva Convention, emphasize the humane treatment of all individuals in conflict, including civilians and those detained. Article 3 requires non-participants in hostilities, such as civilians and prisoners, to be treated humanely, ensuring respect for basic human rights regardless of nationality or political affiliation. In light of citizenship revocation, states involved in armed conflict must assess their obligations under International Humanitarian Law (IHL) to avoid human rights violations. Revoking citizenship can undermine protections for prisoners of war (POWs), who are entitled to humane treatment, a fair trial, and protection from torture. Arbitrary revocation of nationality risks violating due process, leaving individuals stateless and vulnerable to ill-treatment. States must ensure that national security policies do not compromise fundamental rights. Upholding human rights is not just a legal requirement but a reflection of a state's commitment to justice. International organizations, such as the United Nations and regional bodies, have a crucial role in monitoring compliance and advocating for the rights of those affected by armed conflict. 3.5.4. Obligations of states and international accountability The right to return is a fundamental principle in international law, safeguarding individuals from arbitrary state actions that could lead to statelessness or human rights violations. This right is especially relevant for foreign fighters, who may face citizenship revocation upon returning from conflict zones, further exacerbating their vulnerabilities. The International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC) stresses that states are obligated to investigate war crimes committed by their nationals and ensure accountability. Revoking citizenship and transferring legal responsibility to other states can create a culture of impunity and hinder accountability for war crimes. Denying the right to return can lead to further human rights abuses, including inhumane detention or exposure to violence in conflict zones. Article 12 of the ICCPR affirms that all individuals have the right to return to their own country, emphasizing that this right is not contingent on actions or affiliations. States must avoid arbitrary deprivation of nationality, particularly in conflict contexts, to preserve these rights. Adhering to International Humanitarian Law (IHL) and human rights standards is crucial to maintaining trust and accountability within the international community. A balanced approach that considers both security and humanitarian principles is necessary in addressing modern conflicts. 4. Research limitations While this study provides valuable insights into the legal frameworks surrounding foreign fighters in the context of the Russia-Ukraine conflict, it is important to acknowledge several limitations. First, the study is limited to a normative analysis of IHL, focusing primarily on the legal aspects of Russia's military aggression against Ukraine, without delving deeply into the political and social dynamics that also play a significant role in shaping the conflict. Second, the sources of data utilized are predominantly drawn from international legal documents and reports issued by international organizations, which may not fully capture the perspectives of all parties involved, particularly those who are underrepresented in global discourse. Third, while the study adheres to established international legal approaches, it faces challenges in assessing the practical application of IHL in the field, due to difficulties in obtaining sensitive or potentially biased information from diverse sources. Fourth, the research does not specifically address the role of third-party states supporting one of the conflicting parties, a dimension that could significantly complicate the interpretation of IHL. In light of these constraints, it is recommended that future research adopt a more holistic and inclusive approach to explore these complexities in greater depth. 5. Conclusion The ongoing conflict between Russia and Ukraine involves direct military engagements between Russian and Ukrainian forces, along with the participation of pro-Russian separatist groups in eastern Ukraine. Foreign combatants have also become a significant factor on both sides of the conflict. Individuals from various countries have joined the Ukrainian side, either as volunteers or part of organized military units, while Russia has provided support to pro-Russian factions, including involvement of Russian foreign combatants. The legal status of foreign combatants is unclear under International Humanitarian Law (IHL), which primarily addresses the rights and obligations of states, military forces, and civilians, leaving ambiguous the status of foreign combatants, whether they act on behalf of non-state armed groups or as independent volunteers. There is a need to avoid misusing terrorism laws that do not differentiate between foreign volunteers, combatants, and mercenaries, as this could undermine the core objectives of IHL, which include ensuring humane conduct in war. IHL's primary goal is to mitigate human suffering during war, not to prevent conflict. It aims to make warfare more humane, ensuring that all combatants, including foreign ones, enjoy the same human rights as nationals. Violations of these rights, such as deprivation of citizenship or the right to life, cannot be justified under any circumstances. As the conflict persists, all parties must respect IHL to safeguard the dignity of individuals and ensure justice and accountability in the conflict. CRediT authorship contribution statementKhoirunnisa Khoirunnisa: Conceptualization. Brian Matthew: Resources. Didi Jubaidi: Conceptualization. Agung Yudhistira Nugroho: Conceptualization.Data availability statementThe data used in this study were obtained from publicly available sources such as the Open Access Library, DOAJ (Directory of Open Access Journals) and , as indicated in the Data section of the article.Funding statementThis research was supported by a grant from xxxxxxxx which had no role in study design, data collection, analysis, interpretation of results, or writing of this article.Declaration of competing interestThe authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest associated with this publication. No financial, personal, or professional relationships with other individuals or organizations have influenced or could potentially influence the work presented in this manuscript.AcknowledgementsThe authors would like to thank all those who have provided technical support and valuable input during this research process.Khoirunnisa Khoirunnisa, Brian Matthew, Didi Jubaidi, Agung Yudhistira Nugroho, The Ukraine-Russia conflict: An international humanitarian law review of the involvement of foreign fighters, Social Sciences & Humanities Open, Volume 11, 2025, 101340, ISSN 2590-2911, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssaho.2025.101340.ReferencesAkbar and Sadiawati, 2023, M.N. Akbar, D. Sadiawati, Analysis of the Russian invasion of Ukraine in terms of humanitarian law, Jurnal Ilmiah Mizani: Wacana Hukum, Ekonomi, Dan Keagamaan, 10 (1) (2023), p. 160, 10.29300/mzn.v10i1.10760Alexander, 2023, A. Alexander, Filling the gaps: The expansion of international humanitarian law and the juridification of the free-fighter, Journal of International Humanitarian Legal Studies, 14 (2) (2023), pp. 274-303, 10.1163/18781527-bja10075Andi Antara Putra and Dantes, 2022, I.K. Andi Antara Putra, K.F. Dantes, Analysis of war crimes in the 2022 Russian-Ukrainian armed conflict according to international humanitarian law, Jurnal Pendidikan Kewarganegaraan Undiksha, 10 (3) (2022), pp. 260-268Anjelika et al., 2024, F. Anjelika, J. Rahayu, T.P. Sari, N. Ratmaningsih, Analisis perang modern pada perang ukrain, Jurnal Ilmu Sosial Politik Dan Humaniora, 6 (2) (2024), pp. 39-48, 10.36624/jisora.v6i2.100Asya et al., 2024, J. Asya, S. Rahayu, A.P. Widianto, Analisis yuridis terjadinya peristiwa konflik bersenjata ukraina dan rusia ditinjau Dari perspektif hukum humaniter internasional, Unes Law Review, 6 (3) (2024), pp. 9421-9433, 10.31933/unesrev.v6i3Baker-Beall, 2023, C. Baker-Beall, The concept of the foreign terrorist fighter: An immanent critique, European Journal of International Security, 8 (1) (2023), pp. 25-46, 10.1017/eis.2022.30Bauman, 1998, Z. Bauman, Globalization: The Human Consequences, University Press, United Kingdom: Columbia (1998)BBC, 2023, BBC, What is the Wagner group in Russia, and what happened to its leader? Bbc, Com (2023), https://www.bbc.com/news/world-60947877Bodin, 2009, J. Bodin, On sovereignty: Six Books of the commonwealth (reprint)Seven Treasures publications (2009), https://books.google.co.id/books/about/On_Sovereignty.html?id=5ELtQQAACAAJ&redir_esc=yBramantyo, 2023, M.H. Bramantyo, Pemahaman tentang munculnya pejuang teroris asing Indonesia : Ekonomi politik , analisis pasar , dan pendekatan teori perubahan,Journal Anti Money Laundring, 2 (1) (2023), pp. 83-99, 10.59593/amlcft.2023.v2i1.147Britannica, 2025, E. Britannica, Pereyaslav Agreement, Britannica (2025), Retrieved January 5, 2025, from, https://www-britannica-com.translate.goog/event/Pereyaslav-AgreementBrits, 2017, P. Brits, When history no longer suffices: Towards uniform rules for armed conflicts, Scientia Militaria, 45 (2) (2017), 10.5787/45-1-1210Budisantosa, 2021, K. Budisantosa, Studi komparatif konflik bersenjata non-internasional dalam hukum humaniter internasional (comparative study on non-international armed conflict in IHL), TerAs Law Review: Jurnal Hukum Humaniter Dan HAM, 2 (2) (2021), pp. 1-32, 10.25105/teras-lrev.v2i1.9051Cassese, 2013, A. Cassese, Cassese's international criminal law, Oxford University Press, USA (2013)Danial, 2017, D. Danial, Efektifitas konsep prinsip pembedaan hukum humaniter internasional sebagai upaya perlindungan korban dalam konflik bersenjata modern, Jurnal Media Hukum, 23 (2) (2017), pp. 200-208, 10.18196/jmh.2016.0080.200-208Dano, 2022, D. Dano, Analysis of the impact of the Russia-Ukraine conflict on material prices, Journal of Science, 2 (3) (2022), pp. 261-269, 10.51878/cendekia.v2i3.1494Diakonia, 2022, Diakonia, Prinsip dasar HHI. IHL center, https://www.diakonia.se/ihl/resources/international-humanitarian-law/basic-principles-ihl/ (2022)Egle, 2022, E.M. Egle, Foreign Fighters in Ukraine: What concerns should really Be on the agenda? Russia matters, https://www.russiamatters.org/analysis/foreign-fighters-ukraine-what-concerns-should-really-be-agenda (2022)Floress, 2016, M. Floress, Foreign fighters involvement in national and international wars: A historical survey, Foreign fighters under international law and beyond, T.M.C. Asser Press (2016), pp. 27-47, 10.1007/978-94-6265-099-2_3Geraldy and Soekotjo Hardiwinoto, 2017, D.A. Geraldy, J.S. Soekotjo Hardiwinoto, Peran dan status private military companies dalam konflik bersenjata ditinjau Dari hukum humaniter internasional, Diponegoro Law Journal, 6 (1) (2017), pp. 1-18Gisel et al., 2020, L. Gisel, T. Rodenhäuser, K. Dörmann, Twenty years on: IHL and the protection of civilians against the effects of cyber operations during armed conflicts, International Review of the Red Cross, 102 (913) (2020), pp. 287-334, 10.1017/S1816383120000387Gregorious, 2023, Gregorious, Perlindungan terhadap instalasi nuklir dalam wilayah konflik bersenjata internasional berdasarkan hukum internasional, Mataram Journal of International Law, 1 (1) (2023), 10.29303/majilGunawan et al., 2023, Y. Gunawan, G.A. Wibowo, M.H. Arumbinang, Foreign fighters in the Ukrainian armed conflict: An international humanitarian law perspective, Volksgeist: Jurnal Ilmu Hukum Dan Konstitusi, 6 (2) (2023), pp. 145-157, 10.24090/volksgeist.v6i2.9315Hasan and Haque, 2023, M.A. Hasan, M.I. Haque, Should unlawful combatants be considered as prisoners of war when captured?, Journal of Law and Legal Reform, 4 (1) (2023), pp. 123-140, 10.15294/jllr.v4i1.64276Ho, 2019, H. Ho, Penerapan hukum humaniter internasional dalam konflik bersenjata antara palestina dan Israel, Lex Et Societatis, 7 (2) (2019), p. 394, 10.35796/les.v7i2.24668Hugo Grotius, 1964, Hugo Grotius, De jure Belli Ac Pacis libri tres, Oceana Publications (1964), https://lib.ui.ac.id/detail.jsp?id=20133345Idris and Mu’tashim, 2023, F.N. Idris, M.R. Mu’tashim, Sanksi uni eropa terhadap rusia atas pelanggaran teritorial ukraina: Pendekatan multi-tujuan, Jurnal Dinamika Global, 8 (1) (2023), pp. 16-38, 10.36859/jdg.v8i01.1543Ismail, 2018, I. Ismail, Penerapan konvensi jenewa 1949 dan protokol tambahan 1977 dalam hukum nasional Indonesia (studi tentang urgensi dan prosedur ratifikasi protokol tambahan 1977), Jurnal Dinamika Hukum, 13 (3) (2018), pp. 367-378, 10.20884/1.jdh.2013.13.3.243Kaldor, 2013, M. Kaldor, New and old wars: Organised violence in a global era, John Wiley & Sons (2013)Kant, 1991, I. Kant, Perpetual peace: A philosophical sketch, H.S. Reiss, H.B. Nisbet (Eds.), Kant: Political writings, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1991), pp. 93-130 chapterKaplan, 1994, R.D. Kaplan, The coming anarchy, Atlantic Monthly, 273 (2) (1994), pp. 44-76Karska and Karski, 2016, E. Karska, K. Karski, Introduction: The phenomenon of foreign fighters and foreign terrorist fighters, International Community Law Review, 18 (5) (2016), pp. 377-387, 10.1163/18719732-12341337Lekatompessy et al., 2024, L.G. Lekatompessy, J. Augustina, Y. Wattimena, H.U. Pattimura, Tanggung kelompok bersenjata non negara pada wilayah konflik yang di kendalikan dan pertanggung jawabannya, PATTIMURA Law Study Review, 2 (1) (2024), pp. 62-68M, 2001, G. M, Notes and comments common article 3 of Geneva convention, 1949 in the era of international criminal tribunals, http://www.worldlii.org/int/journals/ISILYBIHRL/2001/11.html (2001)Mahfud, 2015 ,Mahfud, Identifikasi jenis konflik bersenjata suriah menurut ketentuan hukum humaniter internasional, Kanun: Jurnal Ilmu Hukum, 17 (2) (2015), pp. 233-245Mamfaluthy, 2014, Mamfaluthy, Legalitas intervensi militer rusia terhadap the autonomous republic of Crimea, ukraina, Al-Ijtima’i, 1 (1) (2014), pp. 29-40Masri et al., 2024, S. Masri, S. Surjaatmadja, S. Anwar, Implementation of IHL in the Russia-Ukraine conflict, International Journal of Progressive Sciences and Technologies (IJPSAT), 42 (2) (2024), pp. 98-104Mehra and Thorley, 2022, T. Mehra, A. Thorley, Foreign fighters, foreign volunteers and mercenaries in the Ukrainian armed conflict ICCT (2022), https://www.icct.nl/publication/foreign-fighters-foreign-volunteers-and-mercenaries-ukrainian-armed-conflictMoerdijat, 2022, L. Moerdijat, Kedepankan Pertimbangan Kemanusiaan untuk Upayakan Perdamaian pada Krisis Rusia-Ukraina, Sekretariat Jenderal MPR RI (2022), https://www.mpr.go.id/berita/Kedepankan-Pertimbangan-Kemanusiaan-untuk-Upayakan-Perdamaian-pada-Krisis-Rusia-UkrainaMurphy, 1982, J.F. Murphy, Human rights and state sovereignty. By richard falk. New York and London: holmes & meier publishers, inc., 1981., paper, American Journal of International Law, 76 (4) (1982), pp. 897-899, 10.2307/2201580Murray, 2019, D. Murray, Organizing rebellion: Non-state armed groups under IHL, human rights law, and international criminal law, International Review of the Red Cross, 101 (910) (2019), pp. 1-6, 10.1017/S1816383119000493Nasution and Raudia, 2022, E.N.D. Nasution, Z. Raudia, Analysis of Russian war violations in the 2022 Ukrainian conflict based on the perspective of IHL, Proceedings of the international conference on sustainable innovation on humanities, education, and social sciences (ICOSI-hess 2022) (2022), 10.2991/978-2-494069-65-7NATO, 2024a, NATO, Relations with Ukraine, https://www.nato.int/cps/en/natohq/topics_37750.htm (2024)NATO, 2024b, NATO, Washington summit declaration, https://www.nato.int/cps/ar/natohq/official_texts_227678.htm (2024)Octavia and Husniyah, 2023, A. Octavia, A. Husniyah, Penyelesaian konflik rusia-ukraina dalam perspektif hukum internasional, Tirtayasa Journal of International Law, 2 (2) (2023), p. 109, 10.51825/tjil.v2i2.21726Pasorong et al., 2023, R. Pasorong, D. Sondakh, F. Karisoh, Implementasi hukum humaniter dalam konflik bersenjata antara rusia dan ukraina, Lex Privatum, 9 (4) (2023)Paulussen, 2021, C. Paulussen, Stripping foreign fighters of their citizenship: International human rights and humanitarian law considerations, International Review of the Red Cross, 103 (916–917) (2021), pp. 605-618, 10.1017/S1816383121000278Pisano, 2022, J. Pisano, How Zelensky has changed Ukraine, Journal of Democracy, 33 (3) (2022), https://www.journalofdemocracy.org/articles/how-zelensky-has-changed-ukraine/Pradana and Ramadhoan, 2022, H.A. Pradana, R. Ramadhoan, Strategi Konfrontatif NATO Terhadap Rusia di Negara-Negara Baltik dan Polandia, Jurnal Ilmiah Hubungan Internasional Fajar, 1 (1) (2022), pp. 1-14, 10.47354/jiihif.v1i1.438, https://www.researchgate.net/publication/366505578_Strategi_Konfrontatif_NATO_Terhadap_Rusia_di_Negara-Negara_Baltik_dan_PolandiaRudy, 2011, T.M. Rudy, International law book 1 (1st printing), Refika Aditama (2011)Susetio and Muliawan, 2023, W. Susetio, A. Muliawan, Pelanggaran hukum internasional dalam perang rusia-ukraina, Lex Jurnalica, 20 (1) (2023), p. 77Theodor Meron, 2006, Theodor Meron, The humanization of international law, Brill | Nijhoff (2006)Van Poecke and Cuyckens, 2023, T. Van Poecke, H. Cuyckens, The qualification of the activities of (returned) foreign fighters under national criminal law, Returning Foreign Fighters: Responses, Legal Challenges and Ways Forward, February (2023), pp. 143-173, 10.1007/978-94-6265-571-3-8Walker, 2023, N. Walker, Conflict in Ukraine: A timeline (2014 - eve of 2022 invasion), House of Commons Library (2023), https://commonslibrary.parliament.uk/research-briefings/cbp-9476/