Opinion – As Israel Pushes for Annexation, Is There Hope for Palestinians?
by James Ron
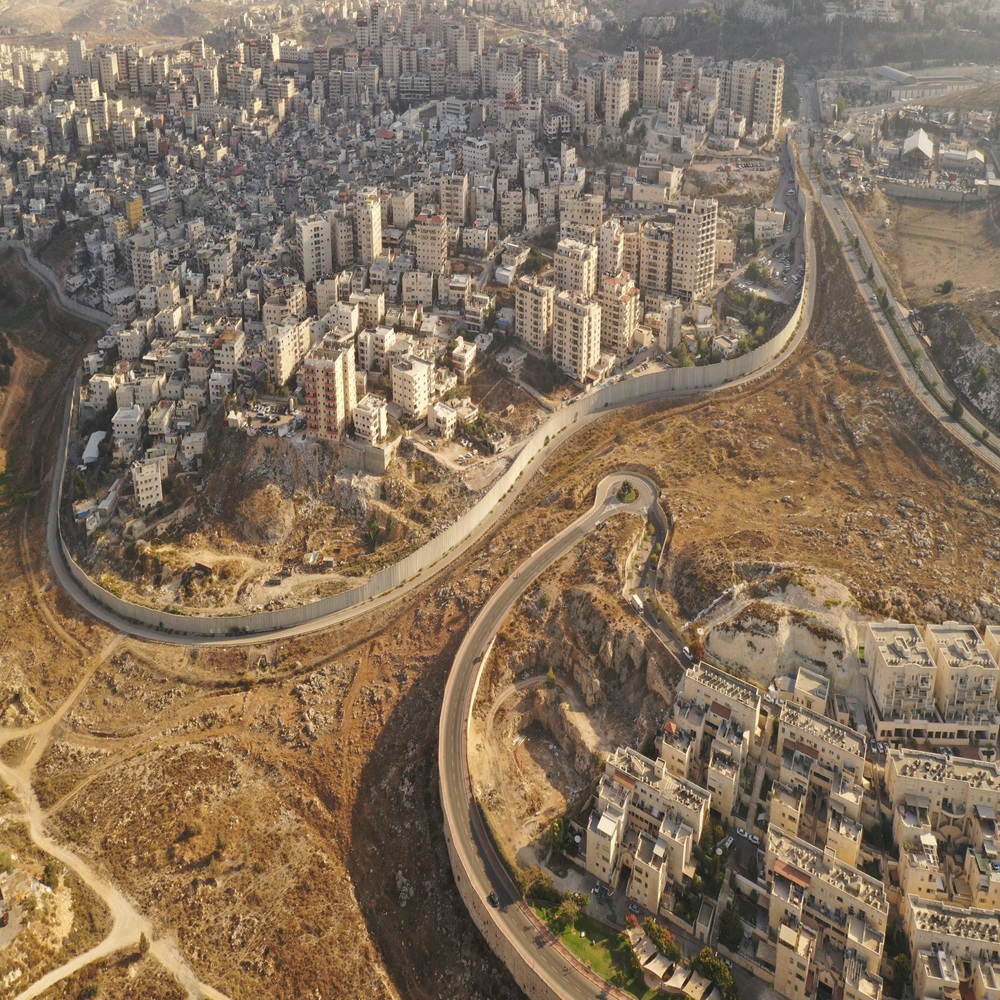
Over the last two weeks, the Israeli website +972 reported, “Six ‘game-changing’ recent cabinet decisions may push the occupation past a tipping point toward permanent Israeli rule.” Many think this will spell political disaster by ending all hope for a negotiated two-state solution. I suggest a different, and perhaps overly optimistic perspective. Maybe – just maybe – these new moves could spark a long-term process ending in a more democratic, egalitarian, and peaceful Israeli-Palestinian space. The current government of Benjamin Netanyahu has been heavily influenced by its ultra-nationalist cabinet members, including Finance Minister Bezalal Smotrich, who leads the political party “Religious Zionism,” and whose responsibilities include administering the Palestinian West Bank (known to his supporters as “Judea and Samaria”). Another key right-wing government figure is National Security Minister Itamar Ben Gvir, head of the Israeli party, “Jewish Power,” who was handed control over the powerful national police. Under the influence of these and other right-wing coalition partners, the Netanyahu government – which won Israel’s national elections in late 2022 – wrote policy guidelines that committed itself to efforts aimed at ensuring the Jewish people’s full and exclusive rights over what they called the entire “Land of Israel.” These guidelines were interpreted by many as commitments to strengthening Israel’s legal and administrative hold over the West Bank in preparation for eventual annexation. In the last week or so, the government has passed new rules enhancing Israel’s ability to take over more West Bank land and tighten its administrative and legal grip over the area. These include: • Declassifying West Bank land ownership records, which would allow settler groups to place pressure on individual Palestinian owners to sell or abandon their property. • Striking down a Jordanian law, long applied to the West Bank, barring private land sales to foreigners, including Israelis. • Mandating a new land registration process, which might allow the government to register more West Bank property as “state land,” which could then be turned over to settlers, and opening the door to fraud during the registration process itself. • Eliminating the need for a special permit to register land sales, again expanding opportunities for skulduggery. • Expanding the Israeli military’s law enforcement role in the West Bank’s “A” and “B” zones, which are supposed to be under the control of the Palestinian Authority, to varying degrees. • Transferring control over some West Bank areas from Israeli military commanders to civilian agencies, normalizing their incorporation into the Israeli state. Until now, the West Bank has been legally defined as an object of “military rule,” although Israel’s civilian ministries have long crept into specific areas of jurisdiction. Taken together, according Ziv Stahl, director of the Israeli human rights organization, Yesh Din, these actions are accelerating processes of de facto West Bank annexation:l by Israel. “Legally speaking,” Stahl told +972, “I don’t know if we can still call it occupation. I think we have been shifting to a reality of annexation. It’s hard to determine where exactly the pivotal moment was, but the physical situation on the ground in the West Bank has completely changed in these three years of this government.” Many regard annexation as an absolutely disastrous political development that will permanently end all hope of a two-state solution. It is this solution, in turn, that is the desired outcome of most European states, the Palestinian Authority, most Arab countries, most UN members, and the US government. Under President Trump, of course, support for the two-state option has grown muddier; he hasn’t endorsed annexation, but hasn’t made any effort to promote the two-state idea either. Among some of Israel’s more moderate political parties – as well as left-of-center Jewish advocacy groups such as J Street or Peace Now – the idea of two separate, sovereign states is also sacrosanct. One would be for Palestinians living in the West Bank and Gaza, and another would be for Israeli Jews living in roughly 70% of Mandatory Palestine. For most international diplomats and many advocacy groups, the two-state option has long been regarded as the best possibility for long-term political stability, justice, and human rights for all. I’d like to offer a different perspective. If Israel were to annex the entire West Bank, the demographics of Israel’s official polity (as opposed to its hybrid ‘internationally recognized state plus militarily occupied Palestinian zones’) would include an additional three million Palestinians. This number includes some 2.8 million Palestinians living in the West Bank’s A and B zones (Palestinian Authority-controlled, in theory), and another 250,000 living in the West Bank’s C zones (controlled by the Israeli military). To these, add another roughly 1.6 million current Palestinian citizens of Israel, living chiefly in the country’s north, along with some 350,000 Palestinians who are permanent residents of Israel, living in East Jerusalem. This combined total of roughly 5 million Palestinians would represent just over 40% of the entire population under direct Israeli sovereignty, using today’s figures. It would not include the roughly 2.2 million Gazan Palestinians now living in utterly dire conditions. (I do not include them here because the Israeli cabinet’s new regulations do not refer to Gaza). Although only 1.6 million of these five million Palestinians currently have Israeli citizenship and the right to vote today in Israeli elections, there might be pressure, over time, to add more Palestinians living in sovereign Israeli territory to the voter rolls. Over the next few decades, newly enfranchised Palestinians could exert increasing influence on Israel’s legislature and governments. With a bit of luck, this pressure might eventually lead to a softening of Israel’s commitment to Jewish political, legal, and cultural supremacy, gradually leading to a more pluralistic and democratic space. Importantly, this could give desperate Palestinians a viable, non-violent alternative for shaping their political fate, relegating the Palestinian Authority’s moribund diplomatic efforts and the violence of Hamas and others to the back of the line. Several authors have discussed the possibility of a “one-state solution” to the Israeli-Palestinian conflict, including a 2010 volume by American academic Virginia Tilley, and the more recent book by Sarah Leah Whitson and Michael Omer-Man. These analysts have identified a fifth option that is distinct from the four possibilities currently on the table for Israelis and Palestinians. These five options include: • The Israeli radical right’s current plan for Jewish annexation and eternal Palestinian subordination. • The two-state solution promoted by the international community and other mainstream actors ever since the Oslo Peace Accords. • A new set of proposals for a political consociation of “two sovereign peoples living in a single land,” promoted, among others, by the Palestinian-Israeli NGO, A Land for All; • The violent status quo, in which the Palestinian Authority continues to crumble, Palestinian militant groups occasionally strike Israelis, and Jewish settlers, backed by the Israeli army, wield violence against Palestinians. • The “one-state solution,” which involves the creation of a single, unified state from the River Jordan to the Mediterranean Sea, in which all residents are lawful citizens, have the right to vote, are equal before the law, and share in the country’s internal and external defense. If Gaza were to be included in this single state, the new entity’s population would include roughly coequal ethnic populations, although divergent birth rates might, over time, lead to an Arab majority. If Gaza were to be excluded, Palestinians would make up just over 40% of the unified territory’s population, using contemporary numbers. If the Israeli cabinet’s recent annexation-enhancing efforts lead to the eventual annexation of the West Bank’s A, B, and C, this may prepare the ground for an eventual move towards political, cultural, and legal democratization. For West Bank Palestinians to become full-fledged voters would likely take years. It would require repeated cycles of social protest, and might include at least some violence from all sides. Still, the death toll could hardly rival today’s horrific conditions. The radical right is well aware of the one-state possibility. It has spoken of threading that needle by annexing only Area C. Although C includes the vast majority of the West Bank’s landmass, it has only a tiny fraction of the Palestinian population. C is also the zone where most Jewish colonies are currently situated. The radical Jewish right might try to devise a hybrid, “neither fully in, nor fully out” arrangement for Areas A and B, limiting the inclusion of millions of new Palestinians into their newly expanded Greater Israel. Still, the momentum for including all three West Bank areas into Israel’s sovereign territory would persist, both among settlers and Palestinians. A and B zones are small, isolated enclaves, and they will struggle to remain distinct from the C hinterland. The radical right and its associated settler movement, moreover, will continue to cast their eyes over A and B for religious, security, economic, and other reasons. Stripped of the “sea” of Area C, the “islands” of A and B could eventually be incorporated as well. In my optimistic reading, the Israeli radical right’s new turbo-charged efforts to annex more Palestinian land may include a silver lining, offering a more hopeful path forward. In the martial art of ju-jitsu, the weaker party seeks survival by using and redirecting their opponent’s strength. For almost a century, Palestinians have tried to blunt and even reverse the Jewish community’s encroachments by fighting fire with fire: guns, regional alliances, international diplomacy, and UN maneuvering. Those efforts have failed. Israel’s Jewish community is just too strong, too committed, too well-organized, and too capital-intensive. It cannot be overcome with the weapons that Palestinians and their dwindling circle of allies have at their disposal, or by economic boycotts, diplomacy, the International Criminal Court, or UN resolutions. International human rights reporting, after all, did nothing to prevent Gaza’s destruction, Hamas’ horrendous (if briefly successful) October 7 attack yielded nothing good, and the Oslo Peace Accords have, in the end, been spectacularly useless. The UN’s resolutions, moreover, have proved about as useless as everything else. Now, perhaps, the time has come to absorb and gradually metabolize the “blow” of West Bank annexation. Once Palestinians have been incorporated as subjects of the Israeli state, and not as mere objects of military occupation, they can try to transform their opponent’s kinetic energy into something new and more positive for both sides.