Abstract
This short analysis is based on the Security Complex theorem. Its departure point is the definition of the term, as introduced by Barry Buzan and Ole Wæver.
The author then briefly introduces the historical background of the Caucasus countries (Armenia, Azerbaijan and Georgia) and their relationships with Russia and suggests further readings for those willing to consult the existing scientific literature.
The central part of the analysis focuses on five distinct components of the Caucasus Security Complex, which include interconnected security concerns, a distinctiveness as a geographical region, anarchical structure, shared security dynamics and Social construction of threats.
The paper concludes by examining the geopolitical importance of the Caucasus region for the two Great powers, Russia and the United States of America, and the reference for the European Union.
The introduction
I will start by briefly explaining the notion of a Security Complex for the reader's convenience. The term "security complex" was introduced by Barry Buzan and Ole Wæver in their 1998 book Security: A New Framework for Analysis. This refers to a distinct geographical region in which security concerns are interconnected. In other words, the security of one state in a complex is inextricably linked to that of others, creating a dynamic and often volatile environment. The key elements of this notion include: a) interconnected security concerns - a security complex is characterised by a web of security interdependencies where a threat to one state is perceived as a threat to others, leading to a shared sense of vulnerability and a need for collective security arrangements. b) Distinct geographical region - security complexes are geographically defined. They are typically regional in scope, although they sometimes encompass more significant areas. The geographical proximity of the states within a complex contributes to the interconnectedness of security concerns. c) Anarchical structure - just like the international system, security complexes operate within an anarchical structure. There is no overarching authority to enforce rules or resolve disputes that can lead to heightened tension and conflict. d) States within a security complex share typical security dynamics, such as arms races, alliance formation, and conflict spirals. These dynamics create a self-reinforcing cycle of insecurity. e) Social construction of threats – the concept of security complex recognises that security threats are not objective realities but are socially constructed. States within a complex share a common understanding of what constitutes a threat, which shapes their behaviour and interactions.
At the same time, it would be wise not to confuse the meaning of Security Complex with the notions of Security Community (shared sense of identity and trust among its members) or Security Regime (a set of principles, norms, rules, and decision-making procedures around which actors' expectations converge in a given area of international relations).
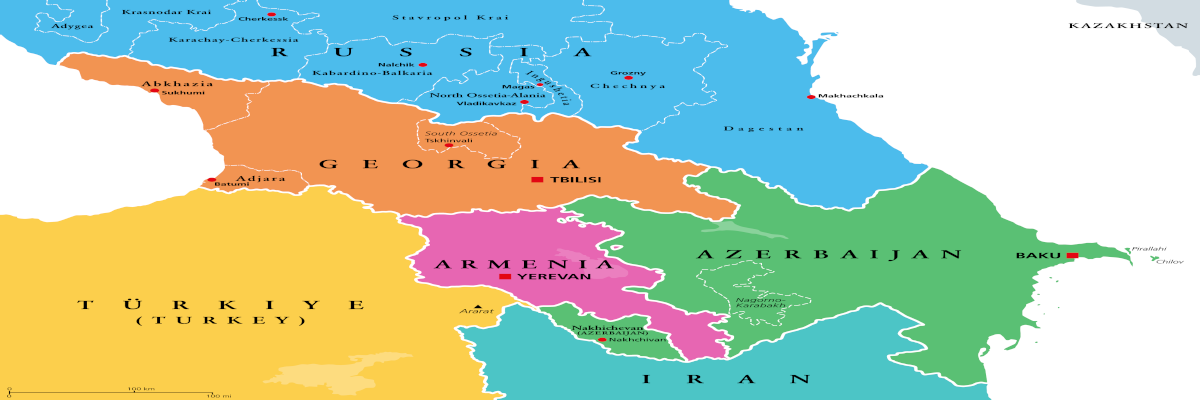
This short analysis will focus on three countries, namely Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Georgia, and explore their geopolitical situation at the beginning of 2025 from the perspective of a security complex theorem, particularly their relationships with Russia.
Historical introduction
The Caucasus, a region nestled between the Black and Caspian Seas, has a rich and tumultuous modern history. Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Georgia, each with distinct cultural and historical trajectories, have navigated a complex landscape of imperial collapse, nation-building, and conflict.
Armenia
In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, Armenians, then part of the Russian Empire, faced increasing tensions with their neighbours, particularly the Ottoman Empire. The Armenian Genocide, perpetrated by the Ottoman government during World War I, resulted in the systematic extermination of 1.5 million Armenians. Following the collapse of the Russian Empire, Armenia briefly experienced independence before being incorporated into the Soviet Union in 1922. In 1988, the country was devastated by an earthquake and rising tensions with Azerbaijan over the Nagorno-Karabakh region. The collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991 led to Armenia's renewed independence but also to the First Nagorno-Karabakh War with Azerbaijan.
Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan, also part of the Russian Empire, declared independence in 1918, establishing the Azerbaijan Democratic Republic. This short-lived independence ended in 1920 with incorporation into the Soviet Union. Similar to Armenia, Azerbaijan regained independence in 1991. The Nagorno-Karabakh conflict dominated much of Azerbaijan's post-Soviet history, resulting in significant displacement and ongoing tensions.
Georgia
Georgia, too, declared independence following the collapse of the Russian Empire in 1917. This independence was short-lived, as Georgia was invaded by the Red Army in 1921 and became part of the Soviet Union. The country regained its independence in 1991. The post-Soviet period has been marked by internal conflicts, including the wars in Abkhazia and South Ossetia, and efforts to establish democratic institutions and closer ties with the West.
The Security Complex of South Caucasus
Regional Dynamics and Conflicts – Major issues
The Caucasus region has been plagued by ethno-territorial conflicts, particularly the Nagorno-Karabakh conflict between Armenia and Azerbaijan. This conflict, rooted in historical territorial claims and ethnic tensions, has resulted in significant human suffering and remains a major obstacle to regional stability. Readers interested in in-depth analysis performed by scholars researching the region are advised to consult Jansiz & Khojaste. Their thought-provoking paper discusses the history of the Caucasus crisis and its impact on regional security. Börzel & Pamuk examine the challenges of Europeanization and fighting corruption in the Southern Caucasus. The region's geopolitical significance, located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and the Middle East, has also led to great power involvement, further complicating regional dynamics.
The following part of the analysis will look at the region through the lens of the Security Complex theorem to analyse its dynamics of security interrelationship. This will, in turn, allow us to understand the role of the Caucasus for the Great Powers and the European Union.
Interconnected security concerns
A security complex is characterised by a web of security interdependencies where a threat to one state is perceived as a threat to others, leading to a shared sense of vulnerability and a need for collective security arrangements. According to Natalie Tavadze, “It is important to understand that Eurasianinism and Moscow’s approaches toward the Caucasus correspond to each other. In this regard, the Central Caucasus is considered as Russia’s backyard. Georgia, Azerbaijan, and Armenia, the Black Sea, and the Caspian Sea constitute strategic dimensions for Russia. The latter is determined to dominate the region and uses the “ethnic card” to keep the countries of the Central Caucasus off balance. From the Russian standpoint, any foreign influence in its “near abroad” is seen through the prism of its national security. Such a menace should be thwarted by any means, as Moscow made clear more than once that it does not entertain any notion of conceding territories of its utmost geopolitical interests.” This extended but thought-provoking quote from one of the local experts pretty well sketches the region's security dynamics. Now, let us look at its geographical dynamics.
Distinct geographical region.
Security complexes are geographically defined. They are typically regional in scope, although they sometimes encompass more significant areas. The geographical proximity of the states within a complex contributes to the interconnectedness of security concerns.
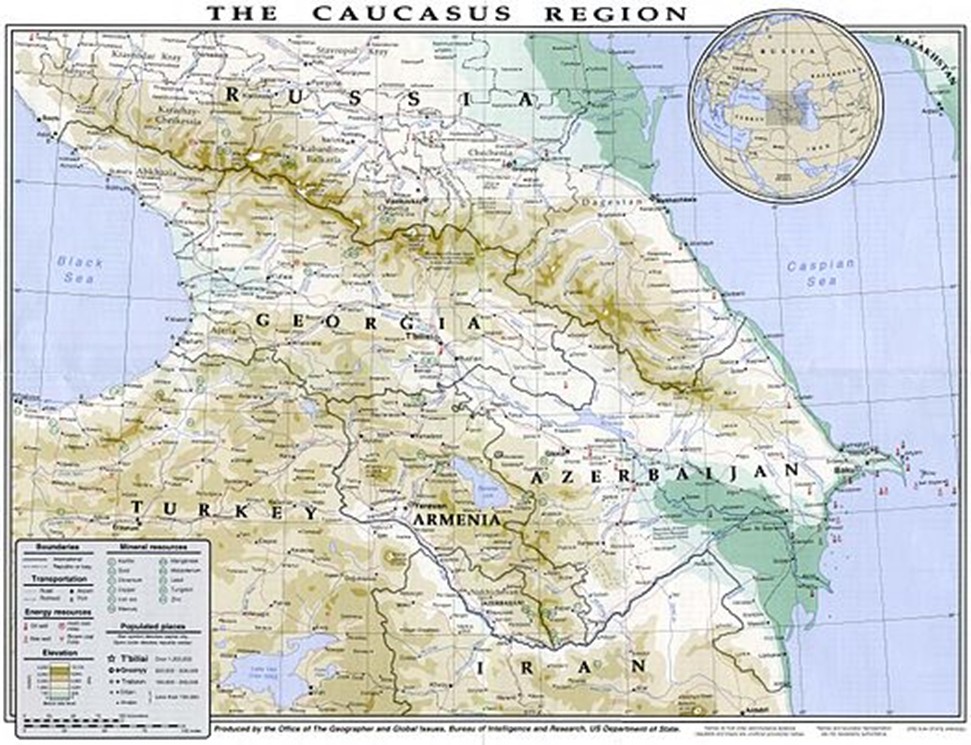
Geographically, the Caucasus is defined by the Caucasus Mountains, a formidable range dividing the region into the North Caucasus and the South Caucasus. The Greater Caucasus, the main range, boasts towering peaks like Mount Elbrus, the highest peak in Europe. This rugged terrain has historically isolated communities, leading to the development of a rich mosaic of languages and cultures. The Lesser Caucasus, located south of the Kura-Aras Lowland, further adds to the region's geographical complexity. This varied topography, ranging from high-altitude glaciers to fertile valleys and semi-desert landscapes, supports a remarkable biodiversity.
The Caucasus's location at the crossroads of continents has made it a historical battleground and a corridor for trade and migration. This strategic importance has left its mark on the region's cultural landscape. The Caucasus is home to many ethnic groups, each with its distinct language, traditions, and history. This diversity, while enriching, has also been a source of conflict and tension. Throughout its history, the region has witnessed numerous internal and external power struggles.
Anarchical structure
Like the international system, security complexes operate within an anarchical structure. There is no overarching authority to enforce rules or resolve disputes that can lead to heightened tension and conflict. As Cornell and Starr adequately observe, “Many states in the Caucasus struggle with weak governance structures. This weakness is characterised by a lack of effective state control over territories, which undermines the rule of law and the provision of public services. The failure to establish strong, sovereign states based on the rule of law leads to corruption and mismanagement, further complicating governance.” At the same time, Russia's role is significant. Russian policies have often destabilised the region, as Moscow's interventions and attempts to maintain dominance can exacerbate local conflicts and governance issues. The reliance on coercive diplomacy and military presence has undermined the sovereignty of local governments and complicated efforts toward conflict resolution.
Shared security dynamics
States within a security complex share typical security dynamics, such as arms races, alliance formation, and conflict spirals. These dynamics create a self-reinforcing cycle of insecurity.
The region has been plagued by unresolved armed conflicts, which create a persistent security deficit. These conflicts destabilise the affected areas and have broader implications for regional peace and security. The ongoing hostilities hinder effective governance and contribute to widespread instability. Partly as a consequence of this, the region has seen a rise in organised crime and radical ideologies, particularly in the North Caucasus, where poverty and unemployment create fertile ground for extremist groups. The intertwining of criminality and political violence poses a significant threat to governance and societal stability.
On top of that, one continues to observe ethnic and national tensions. The presence of various ethnic groups with competing national aspirations exacerbates tensions. This situation is further complicated by external influences and historical grievances, leading to a complex landscape of inter-ethnic relations that can quickly escalate into violence.
Finally, there are serious socio-economic problems. Economic collapse and high poverty levels across the region contribute to governance challenges. The lack of economic opportunities fuels discontent and can lead to social unrest, making governance even more difficult.
The social construction of threats
The concept of security complex recognises that security threats are not objective realities but are socially constructed. States within a complex share a common understanding of what constitutes a threat, which shapes their behaviour and interactions.
In the case of the Caucasus, it is easy to identify a number of threats and challenges that are typical for this security complex. Regional Destabilization - the aftermath of the Chechen war and ongoing frozen conflicts in regions such as Abkhazia, South Ossetia, and Nagorno-Karabakh create instability. These conflicts may still have the potential for spill-over effects and have been exploited by international terrorist networks.
Authoritarian Governance - there is a trend of growing authoritarianism in the region, with Soviet-era power structures maintaining control. Political opposition is often suppressed, leading to a lack of democratic reforms and deteriorating living standards.
Ecological Issues - the region faces significant ecological challenges, such as the deterioration of the Aral Sea and limited agricultural land, which contribute to instability and can exacerbate existing tensions.
Militant and Radical Islam - the rise of militant Islamic groups, partly due to the exclusionary tactics of local regimes, poses a security threat, although it is currently considered a lesser factor compared to issues like drug trafficking.
The remaining part of the article will focus on the Caucasus region's geopolitical importance for Russia, the USA, and the EU.
Geopolitical Importance
For Russia
Russian Federation has been a significant power in the region for many years. "Retying the Caucasian Knot: Russia’s Evolving Approach to the South Caucasus" by Neil Melvin (published by Royal United Services Institute) explores Russia's changing role in the South Caucasus amid shifting geopolitical dynamics. Historically, Russia has viewed the region as a buffer against Western influence and as integral to its ambitions in the Black Sea and the Middle East. However, the emergence of multipolarity and the involvement of new international actors, such as Turkey, Iran, and China, have challenged Russia's dominance. The 2020 and 2023 Nagorno-Karabakh conflicts further shifted the balance of power, diminishing Russia's leverage, particularly with Armenia.
In response, Russia is reconfiguring its strategy, emphasising economic and transport ties while maintaining a security presence. The document argues that Russia seeks to reassert its influence by fostering relationships with regional powers and adapting to the new geopolitical landscape. The Euro-Atlantic community faces challenges in countering Russia's efforts as regional states pursue multi-alignment policies, and the prospect of NATO and EU integration diminishes. Ultimately, the paper highlights the need for the West to recalibrate its approaches to effectively engage with the evolving realities of the South Caucasus.
Additionally, the South Caucasus is significant for Russia for several reasons. Firstly, Russian troops in the South Caucasus allow Russia to project military power and influence regional security dynamics. Following the Second Karabakh War, Russia positioned peacekeepers in Azerbaijan and has military bases in Armenia, reinforcing its role as a key security provider in the area. Economically, the South Caucasus is strategically important for energy transit routes. Russia aims to maintain control over energy supplies and infrastructure that pass through the region, ensuring its leverage over energy distribution to Europe and other markets. Finally, Russia's involvement in mediating conflicts, such as the Nagorno-Karabakh dispute, allows it to assert its role as a key player in regional stability. By doing so, Russia can prevent conflicts from escalating that might threaten its interests or lead to Western intervention.
For the USA
In 2017, the Carnegie Endowment for International Peace published an interesting analysis by Rumer Sokolsky and Stronsky. According to the authors, the importance of the South Caucasus region for the U.S. is undisputable and rests on several arguments. According to the document, the main interests of the U.S. in the South Caucasus include: preserving regional stability (preventing the resumption of frozen conflicts and promoting a peaceful environment among Armenia, Azerbaijan, and Georgia), supporting democratic change and governance (the U.S. seeks to support democratic transformations and better governance in the South Caucasus states, facilitating their integration into the international community), economic development (the U.S. is interested in fostering economic growth and development within the South Caucasus, recognizing that economic prosperity can contribute to stability), energy security (although the significance of Caspian energy resources is noted, allegedly the U.S. interest in energy from the region has become less vital due to changes in global energy markets) and finally, countering illicit activities (the U.S. is concerned with combating transnational crime and illegal trafficking, which poses risks to regional stability and security).
According to James Carafano (Vice President of the Kathryn and Shelby Cullom Davis Institute for National Security and Foreign Policy and the E. W. Richardson Fellow Davis Institute for National Security and Foreign Policy, The Heritage Foundation), the Russian Invasion of Ukraine, which started in February 2022, caused the United States to reconsider its global interests and responsibilities diametrically. Accordingly, the conflict has highlighted the need for energy diversification in Europe, leading to renewed interest in the Southern Gas Corridor (SGC) and other regional partnerships. The SGC, which connects gas fields in Azerbaijan to Europe, is crucial for reducing reliance on Russian energy and enhancing European energy security. Next, regional integration. Projects like the modernization of ports in Georgia and Azerbaijan are vital for developing logistics and transport networks and promoting regional cooperation. Turkey is expected to play an increasingly significant role in the South Caucasus, supporting regional integration and security as Georgia seeks alternatives to NATO and EU membership.
The remaining challenges from the perspective of the US include: geopolitical Tensions (Russia, China, and Iran continue to exert influence in the region, although their capacities may be overstretched due to the ongoing war and sanctions), economic viability (the middle corridor faces challenges such as customs and border control issues and the need for modern infrastructure. However, it presents an alternative logistical route that is gaining interest from various stakeholders); climate policy Implications (the ongoing energy crisis due to the war in Ukraine may prompt changes in climate policies, potentially favouring increased investments in oil and gas infrastructure).
Last but not least, the path ahead requires the U.S. to consider military cooperation - enhanced US military support for Azerbaijan could signal a deeper commitment to regional stability, Three Seas Initiative (3SI) - success in expanding the 3SI could benefit the South Caucasus by fostering infrastructure development and regional integration, Black Sea security - NATO's evolving role in Black Sea security will be critical in linking to the middle corridor and ensuring regional stability and finally investment in energy resources - interest in the Transcaspian Gas Pipeline and other energy initiatives will be significant for Europe's efforts to diversify energy supplies.
For Europe (The EU)
The South Caucasus is essential for the EU for several reasons. Firstly as a geostrategic gateway. The region is a crucial gateway between Europe and Asia, making it significant for trade routes and connectivity. It is positioned at the intersection of major global trade routes, enhancing the EU's access to East and South markets.
Secondly, in terms of energy supplies. The South Caucasus, particularly Azerbaijan, plays a vital role in the EU's energy strategy, especially as the EU seeks to diversify its energy supplies and reduce dependence on Russian energy. Azerbaijan is a key supplier of natural gas to the EU, which has become increasingly important following Russia's invasion of Ukraine.
Thirdly geopolitically, the region's geopolitical landscape has shifted due to recent conflicts, including the war in Ukraine. The EU's engagement with South Caucasus countries is essential for maintaining stability and influencing regional dynamics, especially as these nations navigate their foreign policy options between the EU and Russia.
Fourthly, as an economic partner. Strengthening ties with the South Caucasus countries can enhance economic collaboration, which is particularly important given the EU's interest in bolstering regional trade and investment. This can also increase economic growth and stability in the EU's neighbourhood.
Finally, The South Caucasus is becoming increasingly significant in the context of EU sanctions against Russia, as it could serve as a transit route for goods. The EU's ability to monitor and influence trade flows through this region is critical for enforcing its sanctions.
Conclusion
This short analysis proves the importance of the Caucasus (South Caucasus, to be more exact) for the international community and its potential to play the role of an essential geopolitical factor that could potentially tip the scale regarding the global balance of power. Recent political developments in Georgia (Georgian Protests 2024 – 2025), where the ruling party, Georgian Dream, won the majority of seats in parliament, were met with protests fueled by claims of the opposition parties that the elections were fraudulent. The winning party has decided to suspend the talks with the European Union about the country’s accession to the EU until 2028. The move is seen as anti-EU (ergo pro-Russian). At the same time, pro-Russian commentators have claimed that the demonstrators have been supported by the CIA (a claim that has been put forward with regard to the Ukrainian Maidan of 2013 or even the HK protests of 2019).
As it appears, the Southern Caucasus plays a crucial role on the geopolitical chessboard attended by the U.S.A., Russia, Turkey, Iran and the EU. All of them are, at least for the time being, interested in peace and stability, which means status quo, at least as long as the war in Ukraine is not decidedly over. The future depends, among others, on the outcome of the end of the Ukrainian war and the visions and actions of the 47th President of the U.S., who already stunned the world with his claims regarding the Panama Canal and Greenland.
References
1 Buzan, B and Wæver, O. 1998. “Security: A New Framework for Analysis.” Lynne Rienner Publishers.
4 Jansiz, Ahmad, and Mohammad Reza Khojaste. 2015. “Conflicts in the Caucasus Region and Its Effects on Regional Security Approach.” Journal of Politics and Law. Canadian Center of Science and Education. https://doi.org/10.5539/jpl.v8n1p83. 7 Jansiz, Ahmad, and Mohammad Reza Khojaste. 2015. “Conflicts in the Caucasus Region and Its Effects on Regional Security Approach.” Journal of Politics and Law. Canadian Center of Science and Education. https://doi.org/10.5539/jpl.v8n1p83. 9 Schmidt, Jürgen. "Security Challenges in the Caucasus and Central Asia - A German and European Perspective." Paper presented at the German-U.S. Conference, Conflicts in the Greater Middle East and the Transatlantic Relationship, Jena, February 28 - March 1, 2003.
12 Rumer, Eugene, Richard Sokolsky, and Paul Stronski. U.S. Policy Toward the South Caucasus: Take Three. Washington, DC: Carnegie Endowment for International Peace, 2017. http://www.jstor.com/stable/resrep13079.