Israel’s Punitive War on Palestinians in Gaza- Academic Article
by Camilla Boisen, New York University Abu Dhabi
한국어로 읽기
Leer en español
In Deutsch lesen
Gap
اقرأ بالعربية
Lire en français
Читать на русском
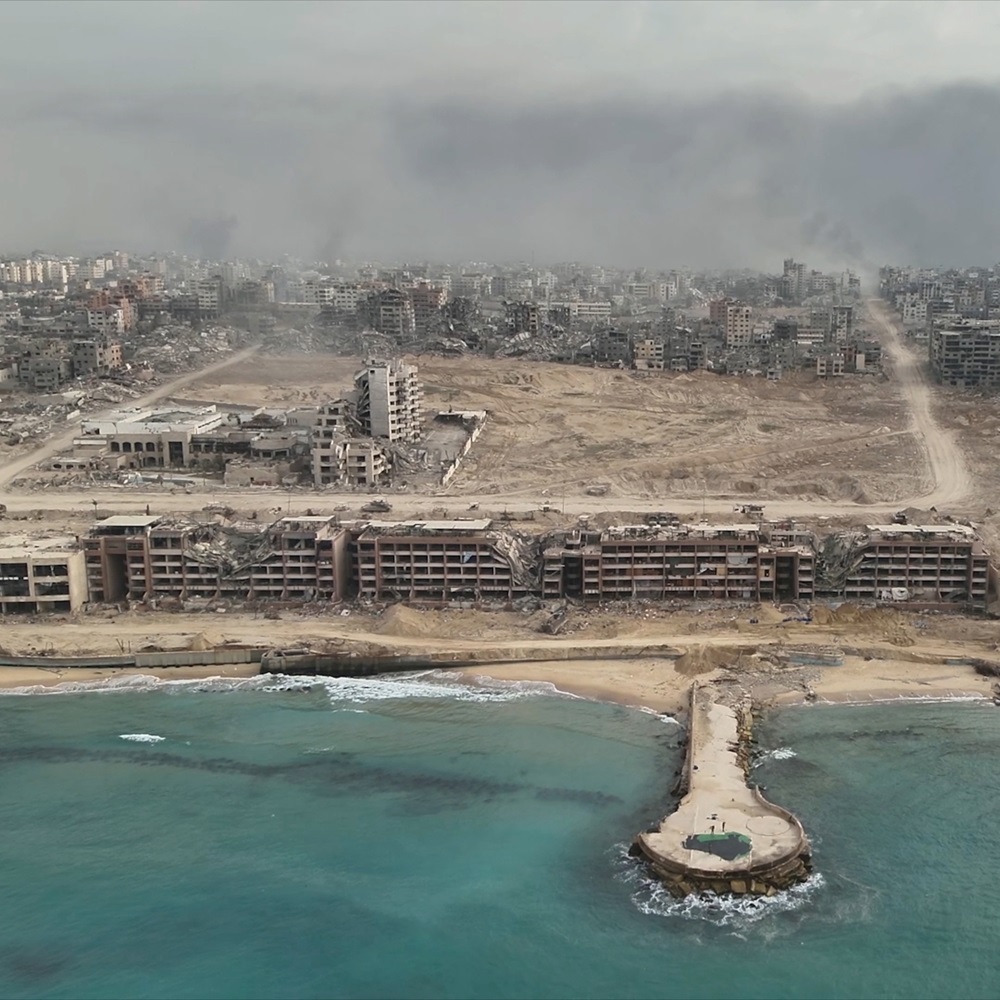
In this article, I consider how Israel’s justifications for war and rationalization of its conduct align with historical justifications for punitive war and unlicenced warfare. Approaches to forcible punishment in early modern writings in the Western Just War Theory tradition (JWT) relate both to defensive and offensive war. In the early modern period, the use of force for self-defence is a type of inter-state punishment justified by the aim of deterrence and the goal of preserving the state. Offensive war, by contrast, is deemed justified to deter aggressors, pre-emptively, or violators of the natural law, even warranting a rejection of a principle of discrimination between perpetrator and innocents.1 Most of the early modern jurists insisted that a right to inflict punishment was integral to claims of just war. For Hugo Grotius (1583–1645), wars were only justified to vindicate rights, which included wars to defend the common good,2 or interventions by a third party when crimes have been committed against another state. Before him, Francisco de Vitoria (1483–1546) warned of the danger associated with resort to the principle of punishment because it allowed space for acts of revenge or vengeance masquerading under the pretext of humanitarian protection – a guise that remains a common feature of contemporary international politics.3 Since the Spanish conquest of the Americas in the sixteenth century, settlers have justified their retaliatory actions against indigenous resistance as necessary for their own “self-preservation.” Furthermore, the “doctrine of double effect” provided moral justification, allowing them to consider the killing of innocents acceptable as an effect of achieving a moral objective such as preservation by means of self-defence.4 In exceptional circumstances where the levels of depravity were deemed abhorrent, the punishment of whole communities for violating the laws of nature was justified.5 The right to punish is no longer a regulative principle of international law. It was gradually replaced by principles of collective security, humanitarian intervention, and the Responsibility to Protect (R2P) doctrine. With its focus on preventative war, modern international law has reduced just causes for war (threat or use of force) to essentially two: first, self-defence under United Nations (UN) Charter Chapter VII: Article 51, and second, when authorized by the UN Security Council to maintain international peace and security (Article 39).6 Even though older theories by jurists in the law of nations have been superseded, international law and the JWT are not discordant doctrines. JWT provides the intellectual framework to international humanitarian law (IHL); minimally, for a war to be considered morally just, it must first and foremost be lawful.7 The Western JWT tradition provides two distinct judgments on war premised on the assumption that war can be justified in certain cases (jus ad bellum), while also establishing ethical limits on how war should be conducted (jus in bello).8 It is no wonder that the philosopher Immanuel Kant would describe its theorizers as “sorry comforters” in that they legitimized (and moralized) the intersection between the demands of morality and the pragmatism of foreign policy. The permissive interpretation of IHL we are witnessing in Gaza since October 2023, as Jessica Whyte aptly describes, by a deliberate starvation policy to depopulate Gaza that also seeks to disavow any intent to do so, reveals Israel (and its allies) as Kant’s “unsorry comforters.”9 The use of starvation as an instrument of war, the imposition of military strategies akin to a scorched earth policy,10 and widespread violence against civilians suggest that Israel is using collective punishment against Palestinians in Gazan.11 This conduct has now led International Criminal Court (ICC) chief prosecutor Karim Khan to seek indictments against Israeli (and Hamas) leaders for war crimes and crimes against humanity. Despite the excessive civilian death toll that has stemmed from Israel’s proclaimed self-defensive and genocide-preventive measures, Israeli authorities have remained steadfast in their military goal of irrevocably destroying Hamas’s military capacity rather than eradicating Palestinian civilians in Gaza. Since the 7 October 2023 attack on southern Israel by Hamas-led forces, Israel has claimed that its military operations in Gaza are justified in two interrelated ways. First, it is executing its right to self-defence in retaliation for the attack on Israeli citizens, including civilians, by a terrorist organization whose avowed aim is to destroy Israel.12 Secondly, in exercising its right to self-defence, it is engaging in “genocide-prevention” – by destroying the capacity of Hamas and Palestine to perpetrate a “second Holocaust.” At the Hague, Tal Becker, legal advisor to the Israeli Defense Forces, insisted “Israel is in a war of defence against Hamas, not against the Palestinianpeople.”13 In international law, deliberate targeting of citizens is not permissible or condoned. Collateral damage is.14 The extent of the death toll and destruction of civilian infrastructure – hospitals, schools, and mosques, in addition to residential neighbourhoods – suggests, however, that these distinctions have largely been ignored.15 Israel’s deployment of advanced Ai systems has allowed its forces to reshape the acceptance of the technology’s margin of error, including the risks of collateral damage and civilian casualties. This is just one of the ways Israel’s actions distort or pervert JWT criteria, prompting new moral (and legal) questions for advanced warfare, including where to draw the boundaries of existing ethical constraints.16 If we reference those boundaries to modern international law, Israel’s counteroffensive in Gaza is punitive because it violates the principle of proportionality. What further confines us to this limited international law framework is the current focus on whether Israel is committing genocide in Gaza. Since 7 October, the devastating civilian casualties caused by Israel, along with destructive rhetoric from Israeli leaders, quickly led to accusations of genocide and counter-accusations that Hamas committed genocide on7 October.17 The question is being considered by the International Court of Justice (ICJ) thanks to a case brought by the Republic of South Africa. In large measure, the acrimonious global debate about genocide in Gaza is mired in legal technicalities due to the stringent requirements of the United Nations Convention on the Prevention and Punishment of Genocide (UNGC). Because the question admits only of a yes/no answer, other aspects of the conflict are missed: maybe we are witnessing an attack on civilians that amounts to “more than genocide”?18 Viewed historically, mass state violence against civilians is not an anomaly or exception in the international system as genocide implies: it is intrinsic to the very idea of statehood, and the kind of natural right of self-defence that Israel is invoking is central to the identity of many western states, whose formation is closely tied to imperial and colonial expansion.19 Early modern just war theorists often discussed wars in colonial contexts. Their theories accepted forms of punishment as well as unlicensed warfare in its normative schema, such as retribution, deterrence, restraint, and reform. They constitute a paradigm of punitive warfare. Whether they realize it or not, commentators today are drawing on this paradigm in relation to Gaza. Edward Luttwak, for instance, arguably endorsed Samuel von Pufendorf’s (1632-1694) call for unrestricted warfare to achieve peace in his controversial 1999 article “Give War a Chance” (despite it being unclear if he has actually read the Saxonian jurist).20 Today he lauds Israel’s counteroffensive in Gaza as a military success, while bemoaning the severity of the constraints “that has been placed on Israel’s combat operations” as “a major impediment to its fight.”21 That any action taken against an enemy other is justified finds support among many Israelis, who have no faith in diplomacy and view Israeli security solely in terms of pre-emption, intimidation, and deterrence. They believe in always supporting the military against a relentless and cruel enemy.22 Israel’s war in Gaza is punitive in the sense meant by some of the early modern international jurists. Here I demonstrate how Israel is reviving archaic forms and justifications of state practice that are deeply rooted in the Western tradition of just war and the justification of punitive wars. By revisiting these ideas, my aim is not to furnish Israel with justifications for its war in Gaza from the archive of the law of nature and of nations, but rather to place it within the intellectual history of punitive war. This contextualization is anything but a consolation, for as I conclude, the genocide concept is an outgrowth of this history. Historicizing the Right to Punitive War The early modern just war theory discourse of punishment opens up at least two ways to think about Israel’s war as punitive. First, for security reasons, that is for reasons of self-preservation, which also include measures of preventative and non-proportional warfare (defensive punitive wars). Secondly, by constructing Palestinians as “barbarians” (see below), as the quintessential host is humani generis, enemy of humankind, thereby legitimating violence in the name of the state and the jus gentium, that affords them a right to punish “crimes against natural law” (offensive punitive wars). For the Europeans, this particular right opened a way to punishment without injury to the state, and thus cemented amoral pathway for colonial ventures and exploitation. Portraying Hamas as Nazis – the archetypical genocidaires – functions to criminalize Palestinians and allows the Israeli leadership to present them as a persistent genocidal threat.23 Defensive Punitive Wars Punitive wars were a common feature in JWT during the medieval period. Pope Innocent IV (1195–1254), for instance, used his universal jurisdiction to include the spiritual care of the souls of infidels, which at this time meant principally Muslims, and retained a right to intervene with impunity in their domestic affairs.24 The medieval concept of punitive war emerged from the rejection of the Roman Law principle of self-defence in early Christian theology. Augustine of Hippo (354–430), for instance, contended that killing in self-defence could not align with God’s law because it stemmed from humans’ attachment to their earthly life. Augustine linked punishment with sin and heresy, advocating for persecution and punishment driven by the desire to do good and eradicate evil, thus framing the punishment of heretics as an act of charity. Gregory the Great (540–604) championed this idea, threatening divine retribution against rulers who did not support the clergy’s efforts to suppress and punish barbarians and heretics. By the eleventh and twelfth centuries, the Church had expanded its authority to punish its enemies, ultimately merging just war theory with the concept of holy war.25 The gradual shift from a punitive to a defensive conception of war is expressed in the thought of sixteenth-century theologians, where the two paradigms coexist. Writing in the context of the Spanish conquest of the Americas, for the Salamanca theologian Vitoria every punitive war has a defensive character, and no defensive war is effective without a punitive element.26 Punishment was not grounded in vengeance, or vendetta; it had to fit the crime, which promoted a principle of proportionality.27 Although we have obligations based on our universal common rights, these do not justify waging war on the Indians, whether to punish them for violating natural law or to convert them to Christianity by force for their eternal salvation. The natural rights of the Indians are inviolable, and it would be unjust for the Spaniards to violate these rights with impunity.28 Yet, Vitoria contemplates the possibility of saving innocents by prohibiting and punishing offenders “from practicing any nefarious custom or rite.”29 Vitoria, nevertheless, imposes strict conditions on such humanitarian endeavours, insisting that they must bedriven by “right intention.” Punishing to save innocents from cannibalism is a noble intention, but using it as a pretext for war is unjustifiable. Slaughtering of innocents is not permissible, however, Vitoria does introduce exceptions to this rule in extenuating circumstances that relate to a prince’s necessity to obtain peace and security.30 Unlike Vitoria, the Italian jurist Alberico Gentili (1552–1608) recognized a state’s right to punish as an instrument of self-preservation.31 Sovereigns are justified in using preemptive force to deter threats, prioritizing state preservation even before these threats fully develop. The kind of state’s right to what Dirk Moses has termed “permanent security” is theorized with a remarkable clarity in Gentili’s writing.32 This also implies that general deterrence can be invoked as a justification for punishment that exceeds the balance between the wrongdoer and the enforcer. While Gentili maintains that war(and post-war punishment) should address a broadly defined injury, the concept of deterrence as a proactive measure can be applied even before any act directly impacts the state.33 Both Vitoria and Gentili acknowledged the reformative and retributive aspects of punishment, as well as punishing an offender to prevent future misconduct by the offender or by others,34 implicitly conflating punishment with deterrence. For Gentili, self-defence falls under the “category of expediency,” which is considered an autonomous source of justice and, as such, is less restrictive about the requirements of predicate injury. Grotius, as we will see, insisted on an even more permissive right to punitive war against those who offend against nature. This implies that a sovereign can justifiably wage war against another state for any violations without needing to prove harm or have that harm be “proportionate.” That is, the anticipation of injury, along with the harm already endured, provides a legitimate justification for war.35 Generally, cruelty in war is forbidden, but harsher warfare against uncivilized peoples is permitted, because “with respect to barbarians violence is more potent than kindness.”36 The reasoning that certain wartime circumstances, like self-defence or genocide, justify exceptions to norms of restraint for war and in war (jus ad bellum and jus in bello) extends to the discussion of Israel’s war in and on Gaza. This JWT archetype has been invoked in the Gaza context by the prominent political theorist Michael Walzer.37 His views are significant because his book, Just and Unjust Wars (1977), revived the JWT in academic and public discourse, and he has applied the doctrine to Israel’s past attacks on Gaza, urging the principle of distinction while defending Israel’s right to retaliate against Hamas’s missiles.38 Because of academic reputation and occasional criticisms of Israeli military retaliation with statements (Israel today does not have cause “for revenge against the people ofGaza”39), he is regarded as a prestigious commentator with moral standing. He has now written about the conflict in Gaza since 7 October 2023. Walzer’s scrupulous regard for civilian protection would seem to distance him from the likes of Gentili. However, he allows for extensive civilian destruction in two circumstances. First, his advocacy for “emergency ethics” (morally) justifying the targeting of civilians during war indicates a continuation of early modern arguments about punitive warfare. Walzer argues that military leaders may dispense with the ordinary moral constraints, including the prohibition against killing non-combatants, when the political community is existentially threatened, which he calls the “supreme emergency.”40 Supreme emergency requires that two conditions be met, namely, first, that the threat be imminent, and second, that it be a kind of radical threat to human lives and values that is beyond ordinary military defeat.41 Supreme emergency pertains to jus in bello because it considers revisions to the rules that guide conduct in war. The historical context for conceptualizing this doctrine is the Allied carpet bombing of German cities in World War II. Nazism represented an existential threat to British national existence, and the Allies were entitled to bomb German civilians until that immediate security threat passed.42 Second, Walzer goes further and argues in terms of permanent security, reflecting the colonial logic of thinkers like Gentili. He now argues even Hamas does not constitute an immediate threat (“supreme emergency”), massive Palestinian civilian casualties can still be justified in terms of Israel’s longer-term security.43 The justification of a military campaign with a shocking civilian casualty count through reasoning in terms of self-preservation is reminiscent of early modern thinkers: Israel is fighting a war of existential importance, but there was no concrete threat of genocide against the Israeli civilian population. This war is existential in that if Israel does not succeed in securing its borders and deterring future attackers, many citizens would probably leave the country. But at this moment, it is not a supreme emergency. Therefore, the country is bound to the same standards that it adhered to in previous conflicts.44 As of this moment, and according to the International Court of Justice (ICJ) Advisory Opinion of 19 July 2024, Israel is illegally occupying Gaza, and only has the right to enforce immediate security, not permanent security. It can respond to immediate threats but not wage an endless campaign to achieve “absolute victory” to ensure that Gaza “never again” poses a threat. However, Walzer justifies, as Gentili had, an ongoing military campaign that produces a massive civilian casualty count in terms of anticipatory self-preservation (permanent security).45 By arguing for an existential threat exists that satisfies the principles of jus ad bellum, while simultaneously arguing the Israeli state must still satisfy the principles of jus in bello because there is no supreme emergency, Walzer has found a way to justify a war conducted in a manner that results in a massive civilian casualty count. Walzer’s emphasis on self-preservation as a rationale for jus ad bellum is comparable then to Gentili’s “category of exception,” where the harm suffered does not need to be “proportionate,” also a condition for jus ad bellum, to justify and commit warfare.46 So while Walzer insists that Israel’s response is neither genocidal nor punitive, he clearly believes it to be proportionate: “if there were almost 10,000 Hamas fighters among the30,000 Palestinians killed, it’s not a bad ratio for such a war on urban terrain.”47 In order to maintain his view that the war is being conducted ethically, Walzer appears willing to give the Israeli state the benefit of the doubt. He denies, for example, reports that Israel is bombing Hamas targets after they enter their homes, thereby guaranteeing largescale civilian casualties, especially on women and children.48 Gentili’s JWT exposes Walzer’s appetite for offensive war against Hamas, because of the ambiguity between defensive and offensive war when justified for reasons of permanent security. However, permanent security concerns were not the only grounds for offensive war, including those of a punitive kind. Offensive Punitive Wars The issue of whether Europeans had the right to wage war as a means of punishing non-Europeans is a central topic in early modern just war theory discussions. Gentili was adamant that the Spaniards were justified in waging war against the Indians due to their practices of “abominable lewdness even with beasts” and cannibalism. This justification was based on the idea that the Indians, through such actions, had violated the natural and divine laws that form the bonds of union between all people,49 and “it is ordained by nature herself that all sinners should be punished.”50 The issues of European expansion, indigenous rights, moral questions of dignity, safety, self-preservation and humanitarian intervention were manifest in one of the most famous debates of the sixteenth century between the humanist Juan Ginés de Sepúlveda (1494–1573), and the Dominican Bartholomé de Las Casas (1484–1566), at Valladolid in 1550. Here, the Holy Roman Emperor Charles V commanded that all wars of conquest be suspended until a panel of intellectuals convened in the imperial Spanish capital of Valladolid deliberated on the question by what right Spaniards subdue the Amerindians, and subject them topunishment.51 One of the many issues to be resolved was whether the Spanish were justified in punishing the American Indians for their violations of natural law. The contours of Sepúlveda’s argument can be simply stated: Native Americans were barbarians by both habits (e.g. by engaging in human sacrifice) and nature, tainted by their barbarous vices, and by right of nature, people in this state must obey the more civilized and prudent, or be punished for resisting the universal moral order. Designating this supposed natural defect in the capacity for rational thought to the American Indians cemented a strict God sanctioning order of classification. Resistance of this natural order of dominion gave their Spanish overlords grounds for waging just war against them. The American Indians, Sepúlveda insisted, had to be saved from themselves and subjected to their European masters in order to bring them into the fold of Christianity, and to save their souls. His stipulation for just war maintained first, that the American Indians killed innocents among themselves, hailing their salvation as a just enterprise and something to be encouraged. “If anyone doubts,” Sepúlveda contended, “no one who is a real Christian doubts that all men who wander outside the Christian religion die an eternal death.”52 To protect “innocent persons from such injurious acts” would give the Spanish “the right, already granted by God and nature, to wage war against these barbarians to submit them to Spanishrule.”53 And second, that these depraved acts of indecency were sanctioned and systematized by their own public customs and political institutions – a point, which caused Sepúlveda greater concern than individual acts of depravation.54 This institutionalization of evil required nothing less than a regime change and total victory through war and forcible subjection, a method that “is the most expeditious and best suited for accomplishing these ends and securing the salvation of souls.”55 The Spanish duties to humanity were irrefutable, as far as Sepúlveda was concerned, and they were morally obligated to civilize and Christianize the American Indians. It seemed obvious to Sepúlveda that the Indians lacked sufficient reason to be entrusted with their own affairs. The common bond of humanity, established by divinity and the natural law, considers all people as our neighbours, Sepúlveda asserted, “provided we can do so without harm to ourselves.”56 God has given human beings commandments concerning his or her neighbour, and we have a duty to obey such divine laws. If we do not, then we commit heresy. Sepúlveda grounded this enlargement of just war theory beyond a principle of self-defence. Even if the Indians possessed natural rights (afforded to all humankind by the Natural Law) – to for instance self-defence, property and political autonomy, they had so blatantly misused them that they are now forfeited as a result of their ungodly practices.57 Wars were a necessary mean to combat their resistance in obeying the Natural Law. These crimes were a direct affront to God, and it was incumbent upon the Spanish to avenge, punish and restrain such crimes. Punitive wars such as these were salutary, but nothing to be celebrated.58 Sepúlveda was not concerned, as Las Casas had been, about the collateral damage of punitive wars, exactly because Natural Law permits collective punishment of those who violate its tenets. In fact, there is a slippage between what we might term collateral damage (unfortunate, but legitimate violence) and collective punishment (moral imperative to reform or deter) because the category of “innocent” is suspended. Sepúlveda is expounding the latter: And the point he [Las Casas] makes about being obliged to refrain from waging a war aimed at punishing the few guilty parties if it cannot be accomplished without a much larger number of innocent people coming to grief is irrelevant. For in a city or community where human sacrifice was performed by public authority, all are guilty, since all approve of the practice.59, As evidenced further below, Israel’s claim that there are no “uninvolved civilians,” and that any casualties among “human shields” are morally the responsibility of Gazans, aligns with Sepúlveda’s reasoning. In a recent Israel Affairs article, the philosopher Per Bauhn adjudicates on the question of moral responsibility for non-combatants’ death in Gaza. He exonerates Israel and attributes all culpability to Hamas. By posing an “unjust danger to the state of Israel”, Bauhn says, “Hamas has created a situation in which Israel is morally justified in waging a war of self-defence that puts Palestinian non-combatants at risk of being accidentally killed.”60 This claim is not only deeply rooted in permanent security reasoning, it also presupposes that moral responsibility is a zero-sum concept. Yet, the Israeli leadership and the IDF are not exempt from moral scrutiny by the culpability attributed to Hamas for the conflict in Gaza, which the two morally distinct judgements of just war theory also implies. What we have seen so far is that the idea of placing belligerents outside of the moral realm is a central framework for that of extreme emergency exceptions but also for offensive punitive wars. One of the fundamental presuppositions of theorizing about war is the belief that civilization consists in the gradual elimination of force from our relations with others. Thus, to uphold civilization means finding a way of regulating and humanizing armed conflict. However, there are those who do not fight under the auspice of a state; those who fall outside or are deemed to be outside of the civilized world. Laws of war do not apply to them to the same degree as actors within the society of civilized states, and these can be punished. Pirates, barbarians, and non-Europeans all fell within this exclusionary category among many classic international jurists. Sonja Schilling describes how this narrative logic of deviance is closely associated with punitive war.61 Civilized humanity stands against a brutal, barbaric invader. The loser faces annihilation, and if civilization is defeated, humanity will revert to a dreadful state of constant warfare. The hostis humani generis idea assumes a consistent and unquestioned conflict between civilization and the Other, situated in a marginal area between the empire and a non-white wilderness. Evidenced below, Israeli officials frequently invoke the term wilderness, as an imposing “nature,” meaning it is a space where, due to its inherent characteristics, the state of nature exists.62 The act of claiming ownership achieves something important as it brings land into the legal or civilized domain for the first time.63 From the 1980s onwards, Palestinian violence against Israel was increasingly depicted not as a negotiable territorial dispute, but as a fundamental conflict between civilization and its inherent Other.64 As Schilling remarks “[t]he civil societies of both the United States and Israel are constructed as conceivable institutional enablers of civilization because these countries adhere to the universal and international principles of human rights.”65 Grotius prominently asserted the limitations of recognizing belligerency with whom we cannot hope to build moral relations, maintaining a strict distinction between lawful and unlawful enemies.66 For him “unlawful” enemies ultimately demarcated the boundary of international society, and the lingering problem remained whether they can be transformed into legal combatants recognized and protected by the law of nations. Grotius would – reluctantly – insist that promises and good faith should be kept even with pirates and brigands. Given that both Hamas, as an unlawful enemy (violent non-state actor), and Israel (recognized sovereign state) continue to be impervious to the ethical and legal standards of war, the importance of Grotius’s distinction seems less relevant. Wars against unlawful enemies cannot retain recognition that confers legal validation. Pirates are a particular kind of enemy. Pirates violate the commercial rights of humankind. In defending these commercial rights no declaration of war, for instance, is needed, since these violators have already declared war against all.67 In fact, Grotius writes that determining the “manner” of a war is best done on account of the enemy you are fighting: “they are Enemies, who publicly denounce War against us, or we against them; the rest are but Pirates, or Robbers.”68 Pirates and atheists are outside the moral community. War between “lawful” enemies implies that there is a thin aspect of respect that requires explanation when they are acting coercively against one another (one does not need to like one’s neighbour to have a binding social relationship). We can imagine that if a lawful enemy commits heinous crimes against humanity that warrant punitive action, it would need to be declared and follow the rules of the laws of war as a recognition of that relationship. The right of punishment was fundamental for Grotius to determine how to enforce rights and duties to regulate relationships between states.69 The right to inflict punishment follows from the right to defend oneself, the right to recover property and the right to exact debt. Grotius specified four just causes of war, self-defence, recovery of property, obtaining what is owed, and the exacting of punishment.70 The first, afforded by natural law, arising “directly and immediately from the Care of our own Preservation.”71The latter was in effect punitive wars to address uncorrected wrongs – a state right he positioned as central to upholding international order and peace. States have permissive rights to punish human beings or peoples who grievously transgress or sin against natural law by engaging in acts of cannibalism, unnecessary killings, inhumanity toward parents, piracy, as well as religious impiety in public.72 Given that Grotius allows a permissive right to punish violations of the natural law, what exactly is the purpose of the punishment? There are a number of possibilities, of course. It could be retribution for committing a moral wrong, or a deterrent to prevent future violations, or indeed, it could be to reform the character of peoples, to force them to see the error of their ways. Grotius’s underlying assertion is that punishment has to have a deterrent effect; and this is where punishment may be considered a moral power. To deter someone from consorting with animals, for example, would be to prevent them from committing amortal sin, and to prevent an indelible stain on their soul.73 Punishment, then, is not exacted for retaliation or vengeance, but rather as precaution. With his doctrine of a natural right to punish, Grotius recognized that there are some violations of the law of nature which affect us all, and for the sake of humankind should not go unpunished.74 Barbarians, who are more “beasts than men” are to all the world “a Foe,” and “such abominable Crimes do they allow of in their public Decrees, that if any City upon Earth should enjoin, or had enjoined, the like, it ought to have been, by the general Voice of Mankind, lain in ruin.”75 Gentili had pressed this permissibility even further. Not only were wars undertaken for the common interest of humankind and on behalf of others more honourable, upholding fundamental standards of justice for humanity, violators who commit the kind of crimes that legitimises such wars, must be defeated through a form of violence aimed at total destruction.76 The kinds of enemies that warrant this kind of punitive measures, as we have seen, are unjust or unlawful enemies. However, in “solemn wars,” those that are fought against a lawful enemy, Grotius generally cautions moderation in situations of war against women and children:“[W]e must not attempt any Thing which may prove the Destruction of Innocents,” Grotius says, “unless for some extraordinary Reasons, and for the Safety of many.”77 Retaliation, or collective punishment, against a whole people is forbidden, and to pretend that “Enemies are but one entire Body engaged against us” is absurd,78 because disproportionate punitive actions exceeded the need to maintain the peace.Recovering the Pufendorian Perspective on Licence for War Unlike Grotius, Pufendorf denies that, in times of war, there are any moral jus in bello rules. The end of war is peace, and peace is most effectively achieved by unconstrained vengeance. There is a rich history to consider concerning the relationship between jus ad bellum and jus in bello – and, as David Boucher shows, we can see how this relationship fluctuates. Since 9/11, the growing emphasis had been on jus ad bellum, and less emphasis on the principles of jus in bello.79 The disastrous consequences of Afghanistan, Iraq, Libya and now Israel, the balance seems to have swung the other way towards jus in bello. It is Israel’s conduct of the war that has come under severe scrutiny, not its right to go to war on the basis of a just cause (self-defence).80 For Pufendorf, such jus in bello scrutiny was unnecessary, as he allowed for unrestricted use of force in wars of self-defence. Wars for Pufendorf could never really be properly punitive. Pufendorf is famous for denying the reality of independent international law, because ultimately law needs an author and an enforcer, and for Pufendorf it is God. International Law is for him the law of nature as applied to states.81 It is the law of nature that regulates the relations among states, and states are regulated by the moral constraints of the natural law. Pufendorf is much more preoccupied by the morality of war, and not its legality. As such, pace the arguments of Sepúlveda and Grotius, there could be no justifiable grounds for reforming the practices of the American Indians.82 Because the force of inflicting “punishment” in the international context does not emanate from a (temporal) authoritative superior, states cannot have the right to punish, but they may, of course, have just cause for war. If a belligerent puts itself outside the protection of the natural law, by for instance being an aggressor –and thereby violating the fundamental law of nature it has placed itself outside of its protection. This opens up a sort of licence for unrestricted war of self-defence. It is, in essence, defence against “unjust” violence. Pufendorf is very clear on the fact that “a state of hostility of itself grants one the license to do another injury without limit.”83 The very violation of the duty of peace against another provokes the licence of any force necessary to bring the war to an end and achieve peace; without this licence, Pufendorf argues, the end of war could never be feasible. Pufendorf conceptualizes states the same way as individuals in the state of nature. To protect one’s own security, Pufendorf prescribes any means necessary that “will best prevail against such a person, who, by the injury done to me, has made it impossible for me to do him an injury, however Imay treat him, until we have come to a new agreement to refrain from injuries in thefuture.”84 According to Pufendorf, the violation of the law of nature releases the victims from the obligation to observe it in relation to the violator. Excess in war is justifiable, and without this permission to go to extremes, the war will never have an end in sight. The aim of force is not to reform the offender by punishing them, but to protect our security, property, and rights. Pufendorf does, however, caution those states who engage in gratuitous violence against the enemy. On prudential grounds restraint should be exercised. One never knows when the table might turn, and the enemy becomes dominant and acts gratuitously towards you. As such, behaving in a manner that is considered inappropriate by other civilized nations can be counterproductive as one’s own reprehensible or cruel acts may be emulated and then used against them. Other reasons to observe the customs of warfare are that they can add to the prestige and honour of a ruler and ultimately it is in the interest of countries to be cooperative and not to cause unnecessary damage to states they may find themselves in alliance with again once the conflict is over, despite the fact that, in a state of war, they have a legal right to do as they please.85 Information: Here is a part called “Israel’s Justification for War against Gazans” – To read the full Article please visit the Original Source under: https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/14623528.2024.2406098?scroll=top&needAccess=true Conclusion Andrew Fitzmaurice has convincingly demonstrated how Raphael Lemkin developed the concept of genocide out of a critique of colonialism, thus inverting the Genocide Studies and Settler Colonial Studies preoccupation with the deployment of the genocide concept to explain 500 years of colonialism. This reframing allows Fitzmaurice to ask important questions about how colonialism has impacted the concept of genocide itself.133 “It is a moot point,” Fitzmaurice remarks “whether the word ‘genocide’ can be meaningfully used to describe the horrors of colonization in centuries that preceded the context in which Lemkin coined the term.”134 To comprehend the dispossession and destruction experienced by occupied peoples in the colonies, Lemkin aligns with the tradition of anti-imperial thought, wherein the framework of universal human rights and therefore also genocide emerged in response to issues concerning the status of colonized population. In these concluding remarks, I draw kinship with Fitzmaurice’s thought in positing the notion of genocide as a product of the history of the critique of colonialism that began with Las Casas, one of Lemkin’s heroes. However, I diverge from his emphasis on genocide as a concept emerging from the anti-imperial tradition, instead viewing genocide (as a practice), as an extension of what Benton calls “projects of peace making.” Colonial wars were invariably punitive wars, and genocide is a product of the punitive war theory tradition. Israel’s arguments for the war in Gaza rely on an indiscriminate use between both defensive and offensive moral justifications for war. Previously, just war was seen as a punishment for an injustice committed by an adversary, with a jurisdictional enlargement of the right to punish that also included violations of natural law without being limited to direct injury. Now our focus on the right to self-defence, which categorizes wars as either “defensive” or “aggressive” to justify them, shows a noticeable absence of the normative application of the right to punish in modern international law.135 However, rather than absence between the older conception of punishment and modern international law and practice, Israel’s military actions in Gaza expose its continuity. The formal disappearance of the principle of the right to punish as an articulated objective of modern international law has not, therefore, meant the disappearance of punitive wars. Instead, punitive measures are often undertaken under a different guise as modern international law continues to implement measures addressing behaviour that violates its norms. Since7 October 2023, we have seen Israel reasserting this right in justification and conduct by measures of collective punitive actions, deterrence, and punishment of the unlawful genocidal enemy other. We have seen a justification for actions that place the responsibility for the immoral act of violating the laws of wars onto the victims, that is Palestinians, of that immoral act. The genocide concept has had a central role to play for this kind of political deceit, not least because of the way that “genocide prevention” that Israel purports its war to be is unavoidably punitive. The problem of caging in punitive action in the language of justification is that it places the argument into a sacrosanct place that causes hesitation in obligatory and legal frameworks meant to prevent it. Calling something justified does not make it so even when something bares the character but not the spirit of an idea. Just war theories have nuance and contingency not simply to be flexible to permissibility, but also the opposite, to redraw what is impermissible. In practice, however, the intent to punish and deter, which is integral to JWT tradition, is hard to distinguish from the intent to destroy, as the punishing and deterring we are witnessing in Gaza, often involves causing significant destruction to many people. Acknowledgements I am grateful to A. Dirk Moses, David Boucher, Andrew Fitzmaurice, and Matthew C. Murray for making invaluable comments and suggestions on earlier drafts. Also, to Katia Yesiyeva and Salaam Farhan for their research support. Lastly, to the Fall 23 Saving Strangers FYWS students, whose critical engagement with Walzer and Luttwak in the context of Gaza war prompted me to write this article. It goes without saying that any infelicities are mine alone. Disclosure Statement No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s). Notes on Contributor Camilla Boisen is a senior lecturer in the Writing Program at New York University, Abu Dhabi. She is a historian of political thought, and has published widely on the intellectual history of empire and humanitarian intervention. She is also the co-author of Justice, Merit, and the Political Theory of Academic Knowledge Production (Palgrave Macmillan, 2024). Notes 1 The organising terms “defensive” and “offensive” punitive war is loosely derived from Alexis Blane and Benedict Kingsbury, “Punishment and the ius post bellum,” in The Roman Foundations of the Law of Nations, ed. Benedict Kingsbury and Benjamin Straumann (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2010), 241–65. For example, “[p]urely defensive uses of force are permissible to both individuals and states alike; each has the right to forceful self-defence when not the aggressor. However, once the immediate threat abates, only the state has the right to use force for a punitive end, to revenge a wrong that it suffers. […] The right to offensive uses of force belongs solely to the state and can be employed beyond its own borders in defence both of the interests of its citizens and of its own interests as a collectivity” (249).2 Hugo Grotius, The Rights of War and Peace, ed. Richard Tuck, trans. John Morrice et al. (Indianapolis: Liberty Fund, 2005), ii, xx, II, viii.3 Rajan Menon, The Conceit of Humanitarian Intervention (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2016).4 A. Dirk Moses, The Problems of Genocide: Permanent Security and the Language of Transgression (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2021), 2. For discussion on the doctrine of double effect, see Alison McIntyre, “Doing Away with Double Effect,” Ethics 111, no. 2 (2001): 219–55.5 Natural law was a (perceived) shared framework that yielded ever-revealing truths of natural design to create rules and establish the just and right conduct of individuals and governments. Its content and prescriptions changed, but it was always presented as a set of transfixed immutable laws sanctioned by God.6 Essentially, starting a war without UN Security Council approval is illegal, so states must demonstrate either that they acted in self-defence or had the host government’s consent. In recent decades some states have opted for another permissible justification, claiming that their use of force was implicitly authorized by the Security Council, as seen with some NATO members in Kosovo and the US, UK, and Australia in Iraq or that it was done for humanitarian purposes. See also Alex Bellamy, “The Responsibilities of Victory: ‘Jus Post Bellum’ and the Just War,” Review of International Studies 34, no. 4 (2008): 601–25; Kevin Jon Heller, “The Illegality of ‘Genuine’ Unilateral Humanitarian Intervention,” Journal of International Law 32, no. 2 (2021): 613–47; Jennifer M. Welsh, ed., Humanitarian Intervention and International Relations (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2003); Philip Cunliffe, “The Doctrine of the ‘Responsibility to Protect’ as a Practice of Political Exceptionalism,” European Journal of International Relations 23, no. 2 (2017): 466–86.7 Mary E. O’Connell, “The Just War Tradition and International Law against War: The Myth of Discordant Doctrines,” Journal of the Society of Christian Ethics 35, no. 2 (2015): 33–51.8 In the classical just war theory, the principles of proportionality and necessity are applied twice: first, in the criteria for deciding to go to war (jus ad bellum), and second, in the rules for how war is conducted (jus in bello). This means the theory demands that both the war as a whole and each specific action within it must be proportionate and necessary. See Jeff McMahan, “Proportionality and Necessity in Jus in Bello,” in The Oxford Handbook of Ethics of War, ed. Seth Lazar and Helen Frowe (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2015), 418–39.9 Jessica Whyte, “A ‘Tragic Humanitarian Crisis’: Israel’s Weaponization of Starvation and the Question of Intent,” Journal of Genocide Research (17 April 2024), https://doi.org/10.1080/14623528.2024.2339637. On the “foundational myth” of the Geneva Conventions see Boyd van Dijk’s excellent work, Preparing for War: The Making of the Geneva Conventions (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2022).10 Eiland quoted in ibid., 14.11 Collective punishment refers to any non-individual punitive measure or sanction imposed on all members of a group for actions they did not commit. Article 33(1) of the Fourth Geneva Convention declares a war crime: “Collective penalties and likewise all measures of intimidation or of terrorism are prohibited.”12 Commentators have consistently challenged the legality of Israel’s excessive use of force in Gaza. See, for example, Ralph Wilde, “Israel’s War in Gaza is Not a Valid Act of Self-defence in International Law,” Opinio Juris, (9 November 2023), http://opiniojuris.org/2023/11/09/israels-war-in-gaza-is-not-a-valid-act-of-self-defence-in-international-law/. The second ruling of 24 May 2024 by the ICJ that Israel should with immediate effect cease the military offensive in Rafah points now to the danger of excessive force amounting to genocide, and therefore military action should cease. One judge, however, underlined that the court could not ban Israel from taking legitimate action in self-defence.13 “War against Hamas in Gaza is act of self-defence, Israel tells world court,” UN News, 12 January 2024, https://news.un.org/en/story/2024/01/1145452.14 The principle of collateral damage forms part of the necessary criteria that has to be met to establish wars legitimacy. According to IHL, civilians cannot be directly targeted, but they may be lawfully killed as collateral damage. Although numbers are classified, militaries used a specific value of the collateral damage estimation (CDE), which gauges the accepted number of civilian casualties for any military action. From an ethical standpoint of how much collateral can be accepted in order to obtain the purpose of a war or military humanitarian intervention is the question. Charles P. IV Trumbull, “Proportionality, Double Effects, and the Innocent Bystander Problem in War,” Stanford Journal of International Law 59, no. 1 (2023): 35–74. Regardless, the principle of collateral damage continues to be morally troubling. See also F. M. Kamm, “Terror and Collateral Damage: Are They Permissible?,” Journal of Ethics 9, nos. 3–4 (2005): 381–401.15 Israeli President Isaac Herzog remarked on 13 October that the entire people of Gaza are responsible for the 7 October attacks as part of a wider phenomenon of modern war where the targeting of civilians is increasingly prevalent. Elyse Semerdjian, “Gazification and Genocide by Attrition in Artsakh/Nagorno Karabakh and the Occupied Palestinian Territories,” Journal of Genocide Research (17 July 2024): 1–22, https://doi.org/10.1080/14623528.2024.2377871.16 Bethan McKernan and Harry Davies, “‘The Machine Did it Coldly’: Israel used AI to Identify 37,000 Hamas Targets,” The Guardian, 4 April 2024, https://www.theguardian.com/world/2024/apr/03/israel-gaza-ai-database-hamas-airstrikes.17 Raz Segal, for example, is vocal in labelling Israel’s war in Gaza a genocide. See Raz Segal, “A Textbook Case of Genocide,” Jewish Currents Magazine, 13 October 2023, https://jewishcurrents.org/a-textbook-case-of-genocide.18 A. Dirk Moses, “More than Genocide,” Boston Review, 14 November 2023. https://www.bostonreview.net/articles/more-than-genocide/.19 See Moses, The Problems of Genocide.20 Edward N. Luttwak, “Give War a Chance,” Foreign Affairs, no. 78 (1999): 36–44.21 Edward N. Luttwak, “Why Israel is Winning in Gaza,” Tablet, 9 February 2024, https://www.tabletmag.com/sections/israel-middle-east/articles/israel-winning-gaza.22 Comments by American-Israeli analyst and cited in Steven Erlanger, “Netanyahu, Defiant, Appears to Have Gone Rogue, Risking a Regional War,” New York Times, 2 August 2024.23 Zoé Samudzi, “‘We are Fighting Nazis’: Genocidal Fashionings of Gaza(ns) After 7 October,” Journal of Genocide Research (18 January 2024): https://doi.org/10.1080/14623528.2024.2305524.24 F. E. Peters, The Monotheists: Jews, Christians, and Muslims in Conflict and Competition (Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press, 2005), 146; James Muldoon, Popes, Lawyers, and Infidels (Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press, 1979), chaps. 1–2. I have laid out aspects of the early modern theories of punishment in JWT before. See Camilla Boisen and David Boucher, “The medieval and early modern legacy of rights: The rights to punish and to property,” in Medieval Foundations of International Law, ed. William Bain (New York: Routledge, 2017), 148–65.25 Frederick H. Russell, The Just War in the Middle Ages (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1977), 24–25.26 Pärtel Piirimäe, “Alberico Gentili’s Doctrine of Defensive War and its Impact on Seventeenth-Century Normative Views” in The Roman Foundations of the Law of Nations: Alberico Gentili and the Justice of Empire, ed. Benedict Kingsbury and Benjamin Straumann (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2010), 187–209, 189–93.27 See Stephen C. Neff, War and the Law of Nations: A General History (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2005), 68; Blane and Kingsbury, “Punishment and the ius post bellum,” 248.28 Francisco Vitoria, Political Writings, ed. Anthony Pagden and Jeremy Lawrence (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1991), 219.29 Vitoria, Political Writings, 288. Emphasis in original. The connection between the right of property and Vitoria’s argument concerning saving the innocent is explored in William Bain, “Saving the Innocent, Then and Now: Vitoria, Dominion, and World Order,” History of Political Thought 34 (2013): 588–613.30 A. Dirk Moses, “Empire, Resistance, and Security: International Law and the Transformative Occupation of Palestine,” Humanity: An International Journal of Human Rights, Humanitarianism and Development 8, no. 2 (2017): 384. See also Vitoria, Political Writings, 324.31 Blane and Kingsbury, “Punishment and the ius post bellum,” 250.32 Moses, The Problems of Genocide.33 Ibid., 251; Alberico Gentili, Three Books on the Law of War, trans. John C. Rolfe (Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1933), i, chapter xiv, 62.34 It is worthwhile to consider the underlying metaphysical differences between Vitoria and his protestant successors. As a Thomist, Vitoria was deeply invested in the idea of human sociability, rooted in mutual affection within society, including between different peoples. Consequently, wars of retribution and reprisal conflicted with these core beliefs. In contrast, Grotius, along with other seventeenth-century natural law theorists, adhered to what Kant described as a theory of "unsociable sociability," which underpinned the social contract – a concept unnecessary for Vitoria, who, following Aristotle, believed societies naturally predate the individual. Contrarily, for someone like Grotius, the notion of unsociable sociability was based on the assumption that self-preservation is humanity's primary goal, and this was considered the first law of nature. It should, therefore, come as no surprise that these seventeenth-century natural law writers would allow for a more aggressive pursuit of self-interest than Vitoria, for instance, had endorsed. I thank Andrew Fitzmaurice for bringing this important difference to my attention.35 Blane and Kingsbury, “Punishment and the ius post bellum,” 251–2. See also fn.8 above.36 Gentili, On the Law of War, iii, chap ii, 293.37 Recently also by Per Bauhn, “Just War, Human Shields, and the 2023–24 Gaza War,” Israel Affairs (21 August 2024): https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/13537121.2024.2394289?src = .38 Michael Walzer, Just and Unjust Wars: A Moral Argument with Historical Illustrations (Boston: Basic Books, 2015); Avishai Margalit and Michael Walzer, “Israel: Civilians & Combatants,” New York Review of Books, 14 May 2009; Michael Walzer, “Israel Must Defeat Hamas, But Also Must Do More to Limit Civilian Deaths,” New Republic, 30 July 2014.39 Michael Walzer, “Justice Demands the Defeat of Hamas, Not Revenge against the Palestinians,” K. Jews, Europe, XXIst Century, 19 October 2023, https://k-larevue.com/en/michael-walzer-justice-demands-the-defeat-of-hamas-not-revenge-against-the-palestinians/.40 Walzer’s doctrine of supreme emergency has met with understandable criticism over the years. Especially Walzer’s moral exercise of it. See for example Alex J. Bellamy, “Supreme Emergencies and the Protection of Non-Combatants in War,” International Affairs 80, no. 5 (2004): 829–50; Robin May Schott, “Just War Theory and the Problem of Evil,” Hypatia 23, no. 2 (2008): 122–40.41 Walzer, Just and Unjust Wars, 251–5.42 Ibid., 253.43 Michael Walzer, “Gaza and the Asymmetry Trap,” Quillette, 1 December 2023, https://quillette.com/2023/12/01/gaza-and-the-asymmetry-trap/.44 Michael Walzer, “What is a Just War,” Zeit Magazine, 17 April 2024, https://www.zeit.de/zeit-magazin/leben/2024-04/michael-walzer-just-war-israel-gaza-english.45 International Criminal Court, “Legal Consequences arising from the Policies and Practices of Israel in the Occupied Palestinian Territory, including East Jerusalem,” 9 July 2024, https://www.icj-cij.org/sites/default/files/case-related/186/186-20240719-adv-01-00-en.pdf.46 Walzer, Just and Unjust Wars, 305.47 Walzer, “What is a Just War.”48 Yuval Abrhaham, “‘A Mass Assassination Factory’: Inside Israel’s Calculated Bombing of Gaza,” 972 Magazine, 30 November 2023, https://www.972mag.com/mass-assassination-factory-israel-calculated-bombing-gaza/; Yuval Abhraham, “‘Lavender’: The AI Machine Directing Israel’s Bombing Spree in Gaza,” 972 Magazine, 3 April 2024, https://www.972mag.com/lavender-ai-israeli-army-gaza/49 Gentili, On the Law of War, i, chap. xxv, 122–123.50 Ibid., iii, chap. xi, 330.51 Diarmaid MacCulloch, Reformation: Europe’s House Divided 1490–1700 (London: Penguin Books, 2004), 69.52 Juan Ginés de Sepúlveda, “The Defence of the Book, On the Just Reasons for War (Apologia pro libro de iustiis belli causis)” in Sepúlveda on the Spanish Invasion of the Americas: Defending Empire, Debating Las Casas, ed. and trans. Luke Glanville, David Lupher, and Maya Feile Tomes (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2023), 191–224, 207.53 Lewis Hanke, All Mankind is One: A Study of the Disputation Between Bartolomé de Las Casas and Juan Ginés de Sepúlveda in 1550 on the Intellectual and Religious Capacity of the American Indian (Dekalb: Northern Illinois University Press, 1994), 86.54 Sepúlveda, “The Defence,” 204–7.55 Ibid., 213.56 Ibid., 210.57 David Boucher, The Limits of Ethics in International Relations: Natural Law, Natural Rights and Human Rights in Transition (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2009), 172; Lewis Hanke, Aristotle and the American Indians: A Study in Race Prejudice in the Modern World (Bloomington and London: Indiana University Press, 1959), 35–42.58 Sepúlveda, “Contained Herein is a Debate or Disputation (Aquí se contiene una disputa o controversia),” Sepúlveda on the Spanish Invasion of the Americas, 225–350, 281.59 Ibid., 283.60 Bauhn, “Just War, Human Shields, and the 23–24 Gaza War,” 3.61 Sonja Schilling, Enemies of All Humankind: Fictions of Legitimate Violence (Hannover, NH: Dartmouth College Press, 2016), 91.62 Ibid.63 Ibid., 100.64 Ibid., 208.65 Ibid., 200.66 I have laid out some of these ideas before in “Hugo Grotius, Declaration of War, and the International Moral Order,” Grotiana 41 (2020): 282–303. It must be said that Grotius is somewhat ambivalent about punishment of violent non-state actors. He advocates for the eradication of pirates and other actors against humanity, but he is, of course, also famous for his tract defending Jacob van Heemskerck, commander of a fleet of eight vessels belonging to the United Amsterdam Company (and Grotius’ cousin), whose actions in attacking the Portuguese in 1603 were performed without authorization from the Dutch state. Grotius would go on to argue that the seizure of the Portuguese ship Santa Catarina and its cargo were good prize in a just war. See also Randall Lesaffer, “Grotius on Reprisals,” Grotiana 41 (2020): 330–48.67 Hans W. Blom and Mark Somos, “Public-Private Concord through Divided Sovereignty: Reframing Societas for International Law,” Journal of the History of International Law 22 (2020): 565–88.68 Grotius, The Rights of War and Peace, iii.ii.i, 1246.69 Piirimäe, “Gentili’s Doctrine of Defensive War,” 202.70 Grotius, The Rights of War and Peace, ii, xx.71 Ibid., ii, i, 397.72 Ibid., ii, xx, 1021–24;1027–31;1051–52.73 Ibid.74 Straumann, Roman Law in the State of Nature, 215. See also Camilla Boisen, “The Law of Nations and The Common Law of Europe: the Case of Edmund Burke,” in International Law in the Long Nineteenth Century 1776—1914 – From the Public Law of Europe to Global International Law?, ed. Randall Lesaffer and Inge Van Hulle (Leiden: Brill, 2019), 20–44. The idea that wars waged for the purpose of self-preservation, including pre-emptive ones and wars undertaken by third parties against those who disrupted the sociability of the international order was commonplace among early modern thinkers. Specifically, Grotius believed this principle was why the society of nations functioned as a society rather than existing in a state of nature, as Hobbes suggested. Grotius contended that what elevated the law of nations to the status of a legal order, rather than a mere convention, was the readiness of its members to sanction those who posed a threat to others.75 Grotius, The Rights of War and Peace, ii, xx, 1024.76 Claire Vergerio, War, States, and International Order: Alberico Gentili and the Foundational Myth of the Laws of War (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2022), 116.77 Ibid., iii, xi, viii, 1439.78 Ibid., xvi, 1452–53.79 David Boucher, “The Just War Tradition and its Modern Legacy: Jus ad bellum and jus in bello,” European Journal of Political Theory 11, no. 2 (2011): 92–111.80 That being said, the ICJ’s Advisory Opinion of 19 July 2024 has many implications for Israel’s claims of a right to self-defense (jus ad bellum). The occupation is per se illegal, and not simply the way it is conducted (jus in bello). Israel cannot claim self-defense when it is committing an ongoing act of aggression through the illegal occupation; moreover, Palestinians have, under international law, a right to resist alien occupation, colonial domination, and racist regimes. See: UNGA resolution 3314 (1974), UNGA resolution 37/43 (1982), and Article 1(4) of API to the 1949 Geneva Conventions. I am grateful to Jinan Bastaki for pointing this out.81 Samuel von Pufendorf, Of the Law of Nature and Nations, Eight Books (1672), trans. C. H. Oldfather and W. A. Oldfather (Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1934), i.ii.6; ii, iii, 23.82 Ibid., viii, iii, 4–7.83 Ibid., viii, vii, 2.84 Ibid., vi, 7.85 Francesca Iurlaro, The Invention of Custom Natural Law and the Law of Nations, ca. 1550–1750 (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2022), 142. It is important not to downplay the significance of natural law by over-focusing on interest and self-preservation as states’ main motivation for agreeing to follow customs. In opposition to Iurlaro, Peter Schröder rightly points to the error in giving too much consideration to interest as a basis for Pufendorf ’s international political thought. Pufendorf thinks that states’ behaviour can be regulated by natural law, the primary concept of which is socialitas. See Peter Schröder, “Sovereignty and Interstate Relations,” in Pufendorf's International Political and Legal Thought, ed. Peter Schröder (Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2024), 155–74. In same volume, see also Boisen, “Pufendorf ’s Enduring Legacy for International Law,” 251–69.133 Andrew Fitzmaurice, “Anticolonialism in Western Political Thought: The Colonial Origins of the Concept of Genocide,” in Moses, Empire, Colony, Genocide, 55–80.134 Ibid., 74.135 Piirimäe, “Alberico Gentili’s Doctrine of Defensive War,” 189. The modern focus on self-defence, and its implications, is explored in detail in James Turner Johnson, “Then and Now: The Medieval Conception of Just War Versus Recent Portrayals of the Just War Idea,” in Medieval Foundations of International Relations, 117–31.