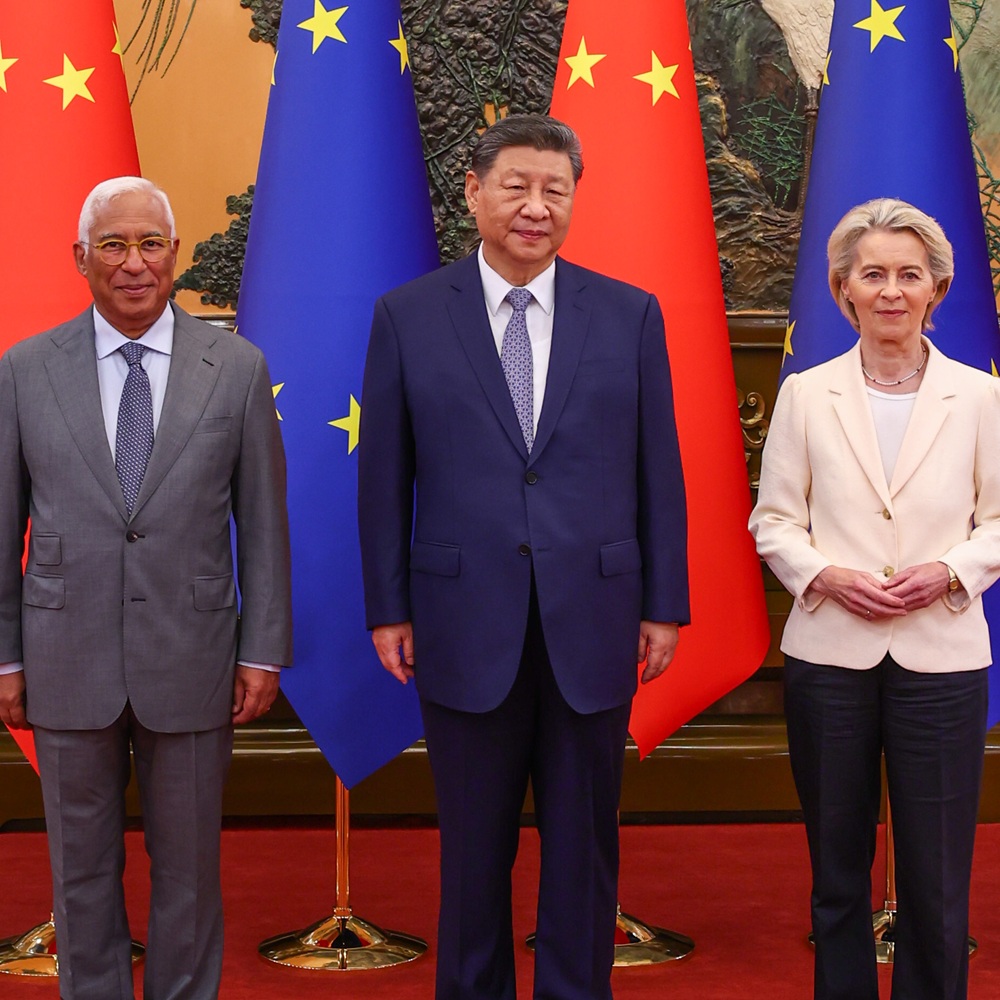
25th EU-China Summit in Beijing
by Johann C. Fuhrmann , Dr. Olaf Wientzek , Jonas Nitschke
A Sobering Anniversary Fifty years of diplomatic relations – and little to celebrate: The 25th EU-China Summit, held in Beijing on July 24, was overshadowed by deep disagreements. From trade disputes to China’s stance on Russia’s war in Ukraine, expectations on both sides were low. While there were symbolic gestures and limited agreements on climate and critical minerals, the meeting highlighted more divergence than convergence. Xi Jinping appeared self-assured; the EU delegation emphasized clarity and unity – but left without substantive concessions. Abstract: The 25th EU-China Summit marked a symbolic milestone – 50 years of diplomatic relations – yet took place in an atmosphere of growing mistrust and confrontation. Geopolitical tensions, an ever-growing trade imbalance, and China’s ongoing support for Russia’s war in Ukraine dominated the agenda. The EU delegation, led by Commission President Ursula von der Leyen and Council President António Costa, sought to recalibrate the relationship and push for concrete outcomes, particularly in trade and global security. Yet Beijing showed little willingness to make concessions. Although both sides agreed on a climate communiqué and a mechanism to address export restrictions on critical raw materials, progress remained limited. China framed the summit as a platform for global cooperation, while the EU left with a renewed sense of caution. Still, the in-person dialogue – the first since 2023 – was seen as diplomatically necessary. For Brussels, the message was clear: without a shift in China’s geopolitical posture, especially towards Russia, meaningful improvement in relations remains elusive. 1. Background The fundamental importance of the relationship was repeatedly emphasized in the run-up to the summit; the EU and China account for nearly 30 percent of global trade in goods and services. Even though there was a slight decline in 2024, bilateral trade still amounted to over 700 billion euros. China is the EU’s second-largest trading partner after the United States.[1] At the same time, discordant tones have increased in recent years: the flooding of the European market with subsidized goods from China, the resulting growing trade imbalance between the two sides, the limitation of market access for European goods, as well as export restrictions on rare earths, are causing dissatisfaction on the European side. While Brussels initially proclaimed at the start of the first von der Leyen Commission that China was—depending on the topic—a partner, competitor, or rival, in recent years the focus has increasingly shifted to competition and rivalry—also due to concerns about excessive dependence on Beijing. The EU’s decision to impose countervailing duties on electric vehicles, in turn, triggered corresponding reactions from China. Politically as well, China’s de facto support for Russia in the war of aggression against Ukraine has significantly changed the EU’s perception of China over the past three years—not to mention concerns about China’s actions toward Taiwan, its support for authoritarian regimes around the world, and its attempts to increasingly shape and shift the discourse in multilateral organizations in its own favor. The statement made in June by Chinese Foreign Minister Wang Yi that China could not afford a Russian defeat, as this would mean that the USA and its Western allies would then turn their attention to Asia[2], reinforced the conviction in Brussels that China supports Russia in the conflict not only in words but also in deeds. Just a few days before the summit, the EU imposed sanctions on Chinese banks for violations of sanctions against Russia, to which China responded with threats of retaliatory measures.[3] In the weeks leading up to the summit, little suggested a resolution to these points of contention. The tougher stance taken by Washington toward both sides in recent months also did not lead to a reduction in dissonance. At the same time, the EU finds itself increasingly under pressure to navigate a balancing act between the strategic interests of the USA and China. China is courting with investments in favor of more “strategic autonomy,” while the USA is pushing for a hard line against Beijing, for example through export controls on critical raw materials. At the G7 summit in Canada, President von der Leyen accused China of using its dominance in raw materials as a weapon against competitors.[4] Beijing rejected the criticism. In Brussels, the fight against climate change is seen as the only somewhat consensual topic, although in the field of green tech—such as electric vehicles or photovoltaics—China is a competitor that challenges the EU. As the controversial vote on tariffs for electric vehicles also showed, EU member states are not always united when it comes to China.[5] Some primarily view China as an important economic partner, others struggle with China’s punitive tariffs, still others see the country as an authoritarian center of gravity that, through support for Russia or through cyberattacks, threatens their own security. Most recently, alongside Hungary—which has been regarded for years as one of Beijing’s closest partners in the EU—the socialist government of Spain also stood out with a charm offensive toward China. The difficulties in the relationship with China have prompted the EU—especially in the new legislative term—to noticeably diversify its economic and political foreign relations: directly before the EU-China summit, closer cooperation was agreed with Japan—also with the goal of reducing strategic dependence on China.[6] 2. Expectations for the Summit On the Chinese side, expectations for the summit were limited from the outset—at least in terms of making their own concessions. In its official communications, Beijing adopted an unusually sharp tone in the lead-up. The spokesperson of the Chinese Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Guo Jiakun, warned the EU not to harm the interests of Chinese companies. Otherwise, China would take measures to protect their rights. At the same time, Guo criticized the new EU sanctions against Russia, which also affect Chinese banks. The normal exchange between Chinese and Russian companies must not be disrupted. Beijing continues to reject the EU’s formula “partner, competitor, systemic rival”—as well as, from the Chinese perspective, unfounded accusations related to the war in Ukraine.[7] This clear defensive posture is also reflected in the public debate. In state-controlled social media, the summit was sometimes mockingly commented on in advance: the Europeans, it was said, would be begging for rare earths on their knees while a strong China benevolently dictated the rules of the game. This self-portrayal reflects a growing sense of self-confidence in Beijing—and at the same time sends a signal: China does not see itself as a supplicant, but as a shaper. Specifically, Beijing hopes for a withdrawal of the new EU import tariffs on Chinese electric vehicles, for which, according to the Chinese side, they are in the final stages of “price negotiations.” From the perspective of European officials, however, the process has been stagnating for months. Further points of friction lie in China’s response to European sanctions—such as the recent imposition of punitive tariffs on French cognac and new restrictions on the procurement of medical equipment. The looming action against European milk and pork exports also fits into this pattern. At the same time, Beijing highlights the fruits of decades of cooperation: bilateral trade has grown from 2.4 billion to nearly 786 billion US dollars over the past 50 years, and mutual investments have reached nearly 260 billion. President Xi Jinping therefore called on the EU to maintain “open cooperation.” “Decoupling” or even “building walls” would only lead to isolation, he warned. China is therefore insisting on further market access in Europe—particularly in key areas such as automobile manufacturing, high-tech, and medical technology—and sees itself increasingly discriminated against by European protective measures. The preliminary reporting on the meeting in state media, however, was predictably conciliatory. The focus was primarily on powerful imagery, portraying China as a responsible actor on the global stage. In a report by the state news agency Xinhua shortly before the summit, it was stated that the meeting offered an opportunity to “consolidate the common interests of China and Europe in a time of global upheaval.” China Daily also struck a cooperative tone on July 24 and warned against endangering the relationship “through protectionist reflexes or foreign policy proxy conflicts.” Europe, the paper said literally, must decide whether it will “continue to make independent strategic decisions—or blindly follow Washington’s course.”[8] What remains unmentioned in China’s narrative is that many of these shared goals currently exist primarily on paper. Accusations regarding competition-distorting subsidies, China’s role in the war in Ukraine, or restrictions on European companies are at best dismissed as misunderstandings. From Beijing’s perspective, the summit appeared to be primarily a diplomatic showcase—rather than a venue for tangible rapprochement. 3. Expectations of the EU Whoever on the EU side may have expected major breakthroughs in light of the anniversary was likely disillusioned by early July at the latest: the reduction of the summit, originally scheduled for two days, to just a single day was an initial dampener; the statements from Chinese ministerial officials and top EU personnel in the weeks leading up to the summit did not suggest that anything fundamental would change regarding the divergences in foreign, economic, and trade policy. The EU is seeking a rebalancing of the relationship. According to Commission President von der Leyen ahead of the summit, the relationship had reached a turning point and now required concrete solutions. Among the EU’s top priorities in the economic sphere are: the rollback of China’s punitive tariffs, measures to reduce the massive trade deficit and counter the redirection of Chinese overcapacities toward the European market, the creation of a level playing field, and export licensing requirements for critical raw materials.[9] In the weeks prior to the summit, there were no signs of Chinese willingness to accommodate any of these demands. Expectations were equally low with regard to geopolitical conflicts, even though the EU’s High Representative had again clearly appealed to China in early July to end its support for Russia. Observers no longer expected a comprehensive joint communiqué ahead of the summit; at most, a joint statement on climate policy with regard to COP30 in Belém, Brazil, was still considered possible. The prevailing opinion: the primary goal was to contain the worsening of relations. Some observers still hoped for minor progress on economic issues. At least there were some diplomatic signals from Beijing in the run-up to the EU-China summit. For example, Mikko Huotari, Director of the German think tank Merics, was allowed to travel to China for the first time in four years. Merics had been subjected to a travel ban in 2021 as part of Chinese counter-sanctions against the EU over its human rights criticism regarding Xinjiang. The lifting of sanctions against individual (former) EU parliamentarians was also interpreted in Brussels as a positive political signal.[10] However, a full lifting of the sanctions is still pending, and travel currently remains possible only under certain conditions—such as by invitation from Chinese institutions, without a guarantee of academic freedom. Observers emphasized that these relaxations were “low-cost” concessions for China. 4. Outcomes of the Summit The low expectations ahead of the summit were at least not disappointed.[11] In their choice of words before and after the summit, both sides made efforts to maintain a respectful tone. Commission President von der Leyen and European Council President Costa did address the well-known critical issues (the need for concrete solutions to recalibrate trade relations, market access for European companies, an end to China’s material support for Russia’s war), but at the same time emphasized the immense importance of the relationship, the shared responsibility for a rules-based international order, and expressed respect for China’s tremendous achievements over the past years and decades.[12] Xi Jinping, on the other hand, did not directly address the divergences between the two sides at all, but instead highlighted the importance of mutual respect, the consolidation of cooperation, an open approach to differences of opinion, and collaboration at the multilateral level. Contrary to some particularly pessimistic forecasts, there were two reasonably concrete outcomes at the summit: First, a supply mechanism for rare earth exports is to be established in order to address supply issues faced by European companies. This would allow companies to contact the EU directly to clarify the causes of delayed exports of critical raw materials.[13] It remains unclear exactly what this mechanism will look like in practice. Second, both sides agreed on a communiqué on climate policy, in which both reaffirmed their cooperation in the climate sector, including on the reduction of greenhouse gases. The communiqué expresses support for the Paris Agreement and the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change. Both sides commit to fair and effective implementation in line with national circumstances. The goal is to advance a just global climate transformation, to support Brazil at COP30, and to improve global access to green technology. By COP30, both sides agreed to present new climate targets for 2035 and to expand cooperation in areas such as the energy transition, methane reduction, and low-carbon technologies.[14] Small steps forward were also made toward closer cooperation in emissions trading, the circular economy, financial regulation, drug control, and geographical indications. A new roadmap for regional policy (2024–2029) was adopted. On the sidelines of the summit, a roundtable was also held with around sixty representatives of European and Chinese companies. In its post-summit remarks, the EU expressed concern about China’s opaque data protection rules and cyberattacks. It also voiced concern about the situation in Xinjiang, Tibet, and Hong Kong, as well as the persecution of human rights defenders. Furthermore, the EU expressed concern about tensions in the Taiwan Strait and the East and South China Seas. It rejected any unilateral violent changes to the status quo and called for peaceful solutions in accordance with international law.[15] 5. Outlook Despite all divergences, the tone in public communication remained at least respectful. However, the summit yielded hardly any tangible progress—particularly in the trade issues central to Brussels. As expected, the EU departed without any concrete commitments. Whether the announced mechanism for rare earth exports will provide substantial added value remains to be seen. From the EU's perspective, the summit confirmed one thing above all: the increasingly skeptical—at times alarmed—view of China remains unchanged. Beijing showed no willingness to make substantial concessions. Instead, the Chinese leadership demonstrated confidence and conveyed the message that it need not act in advance toward a weakened Europe. At the same time, the EU succeeded in clearly articulating key concerns—particularly the expectation that Beijing should use its influence on Moscow to enable progress toward peace negotiations. The clear message: China’s relationship with Russia will play a decisive role in future EU-China relations. One positive aspect from Brussels’ point of view: the appearances of Commission President von der Leyen, Council President Costa, and Estonian Prime Minister Kallas came across as coherent and well-coordinated—an important signal of European unity in difficult times. In addition, according to von der Leyen, the Chinese leadership has begun to address domestic industrial overcapacities under the term “involution.” The latter was regarded as another positive development from a European perspective. Until now, Chinese representatives had consistently denied in talks that the massive overcapacities posed any problem, according to media reports from EU circles.[16] Now, President Xi Jinping and Premier Li Qiang have declared their intent to counteract this trend—against what they perceive as a destructive price war in sectors such as steel, electric mobility, and solar panels. The leadership uses the term “involution” to describe the increasingly intense competition caused by price dumping. Even though some observers hailed the joint climate communiqué as a success, from the EU’s perspective it should be clear: in the field of green tech, China causes massive market distortions through state subsidies and targeted industrial policy—with the goal of creating new global dependencies. Nevertheless, it is undoubtedly important that the summit took place. One must assume that the political system in China—similar to Russia or the Trump administration—functions like an echo chamber; that Xi Jinping likely hears little internal criticism. “That’s why it’s important that the EU leadership tells him directly where the shoe pinches,” emphasized Jörg Wuttke, longtime president of the European Chamber of Commerce.[17] At the same time, it speaks volumes about the state of the relationship when even the mere act of speaking with the EU’s second most important trading partner is regarded as a success of the summit. References[1] https://policy.trade.ec.europa.eu/eu-trade-relationships-country-and-region/countries-and-regions/china_en[2] Exclusive | China tells EU it does not want to see Russia lose its war in Ukraine: sources | South China Morning Post[3] Neue Russland-Sanktionen: China droht EU mit Gegenmaßnahmen | tagesschau.de[4] Präsidentin von der Leyen beim G7-Gipfel[5] https://www.kas.de/en/web/mned-bruessel/global-europe-illustrated/detail/-/content/global-europe-illustrated-eu-member-states-voting-on-tariffs-ev-china[6] AGENCE EUROPE - Faced with economic and security challenges, EU emphasises i...[7] Vgl. China.Table: EU-Gipfel: Pekinger Außenministerium schlägt härtere Töne an, 23.07.2025.[8] Link zu Chinadaily[9] Handelskonflikt: China verursacht Rohstoffkrise – Erste Firmen drosseln Produktion[10] Sanctioned German China expert visits Beijing in sign of easing restrictions | South China Morning Post[11] Andere Zusammenfassungen finden sich hier: https://agenceurope.eu/en/bulletin/article/13687/1 oder in diesem Thread: https://x.com/fbermingham/status/1948242830595391697[12] EU warns China to push Putin to end war as relations hit ‘inflection point’ – POLITICO, die Pressekonferenz ist auch hier zu finden: https://newsroom.consilium.europa.eu/permalink/264159 , https://newsroom.consilium.europa.eu/permalink/264160[13] EU-China-Gipfel: Probleme bei Seltenen Erden gelöst?[14] Joint EU-China press statement on climate[15] 25th EU-China summit - EU press release - Consilium[16] Vgl. China.Table: EU-China-Gipfel: Peking will gegen Überkapazitäten vorgehen, 25.07.2025.[17] Experte Wuttke über EU-China-Gipfel: "Xi will Europa dominieren"














.png)