The Chinese are not “tolerant”: they are preparing a global counteroffensive
by Yuri Tavrovsky
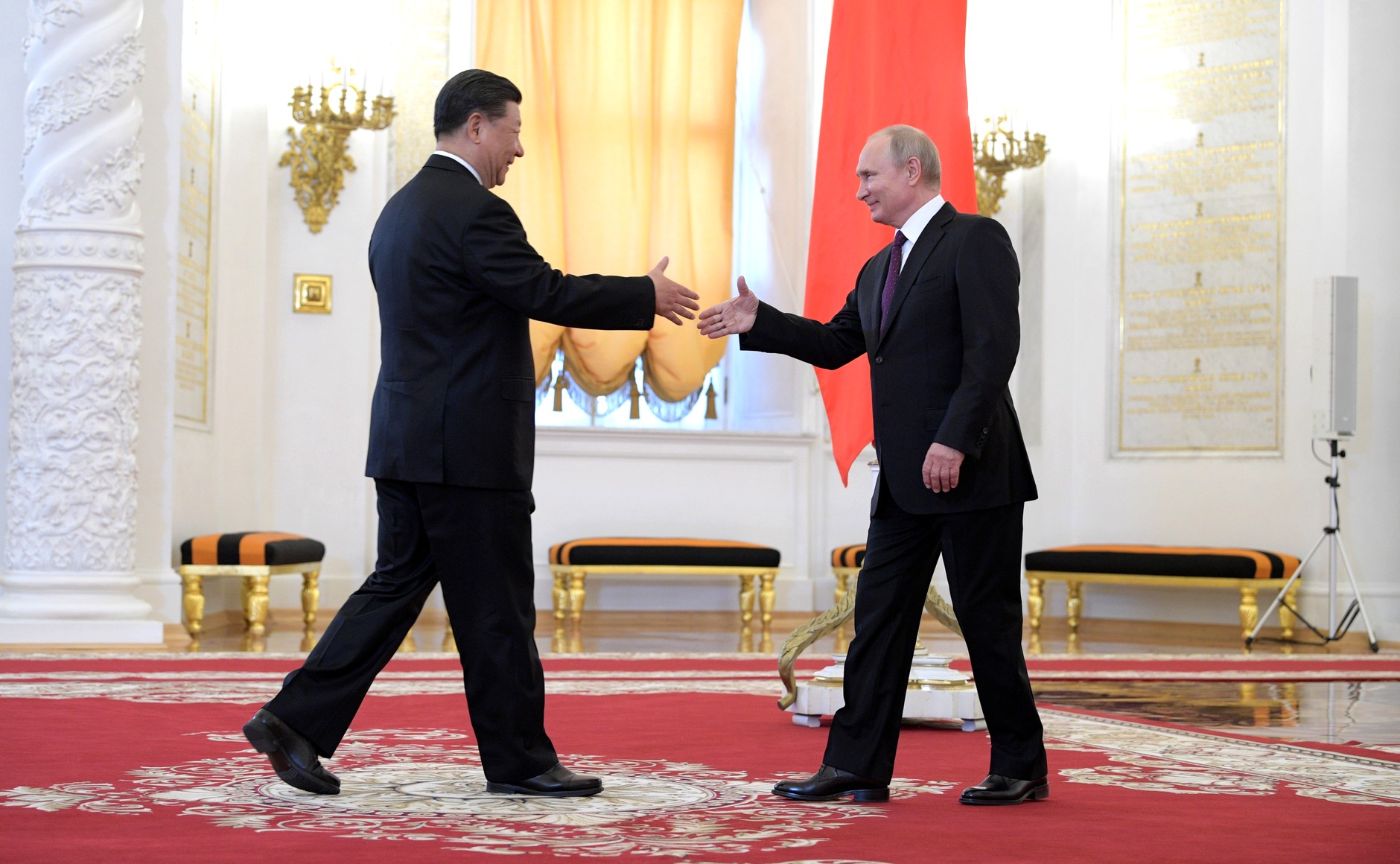
Moscow-Beijing: combat coordination is growing. Powerful cold currents from the West determine the political atmosphere of the planet. Efforts are being made to counter them with warm currents from the East. Only the synergy of actions between Russia and China prevents the the consolidated camp of hegemony from entering the "final and decisive battle" against each of these recalcitrant powers individually. We are well aware of the situation on the western front of the global Cold War. However, on the eastern front, where there is no Ukrainian-scale conflict yet, tensions are approaching critical levels. Defense-related Chinese trade publications have published some very disturbing material in recent weeks. ... To destroy the latest American nuclear aircraft carrier Gerald Ford and the battle group accompanying it from a cruiser and 5 missile frigates, 24 hypersonic missiles without nuclear warheads were enough. In a computer simulation, rocket launches were carried out from 6 different areas, including even the Gobi Desert in Northwest China. Considered unsinkable, the carrier group was completely destroyed by a series of launches of distracting and damaging missiles. The Chinese took into account the capabilities of both the standard set of anti-aircraft weapons and the latest American SM-3 anti-missiles. According to the scenario described in the Chinese-language Journal of Test and Measurement, the American armada entered the waters of the South China Sea and continued to move in a menacing course, despite warnings. Similar scenarios play out regularly near Chinese shores. Another Chinese publication spoke about the mortal danger of such actions. The South China Morning Post, published in Hong Kong in English, reported that the war between China and the United States could begin in the South China Sea. On January 5, 2021, three US Navy anti-submarine aircraft searched for Chinese submarines near the Dongsha Qundao (Pratas) archipelago. Reconnaissance aircraft, as always, dropped electronic buoys and tracked the routes of Chinese submarines that were participating in major exercises. However, one plane flew too close to China, and Chinese fighters flew in from there. The Chinese regarded the situation as a huge threat to national security. There was a possibility of an armed conflict, and the Americans, taking into account the unfolding actions of the PRC Air Force and Navy, began to prepare for the worst and even destroyed expensive buoys with top-secret equipment. The description of the conflict in the Chinese specialized magazine Shipboard Electronic Countermeasures does not give details of the confrontation. However, everything was very, very serious. No wonder the Chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff of the United States, General Mark Milley, made a phone call to the Chinese Minister of Defense a couple of days later, assuring him that the Pentagon had no intention of provoking a real war. He even promised to inform his counterparts in Beijing in advance about the intentions of policymakers in the event of a critical situation. These two sensational publications did not appear by accident. One can only guess how many dangerous situations arise on the line of contact between the military of China and America in the Asia-Pacific basin. But, as the Chinese proverb says, “Heaven proposes, Xi Jinping disposes.” The Supreme Commander, acting at the strategic level of planning and decision-making, is responding to Washington's growing aggressiveness by demonstrating readiness for retaliatory actions on the battlefield and intensifying combat coordination with Russia. Planned for April, Xi Jinping's visit to Moscow was postponed to the end of March, and negotiations with Vladimir Putin lasted a total of 8 hours. Even not so much the published documents as the subsequent events showed qualitative changes in the partnership between Moscow and Beijing. The time has come for all-round combat coordination. It began with hours of face-to-face talks between the two supreme commanders. Soon, Chinese Defense Minister Li Shangfu came to Moscow. After the visit of an experienced and energetic military commander, Chen Wenqing, curator of internal and external intelligence services, arrived in Moscow. Reports of his meetings with the secretary of our Security Council, Nikolai Patrushev, showed the resolute attitude of the chief intelligence officer of the Celestial Empire towards the West. For its part, the Kremlin decided to reinforce the dynamics of combat coordination with a "volley of the main guns." A delegation of high-ranking officials and business leaders headed by Prime Minister Mikhail Mishustin headed to Beijing, unprecedented in size and level. The visit was prepared in a hurry and took place under the vigilant eye of the Western intelligence services. Therefore, the number and quality of signed agreements disappointed the optimists. But the bilateral meetings of officials, bankers and experts of the two countries that took place on the sidelines advanced the ongoing negotiations on strategic areas of cooperation and prepared serious deals. During the visit, influential publications noted the mutual interest of both countries in the accelerated growth of trade. Thus, the Global Times, which is close to the CCP Central Committee, noted the synergy of the two trends. Russia needs to increase the export of raw materials, especially energy. Against the backdrop of a rapid economic recovery, China needs to expand imports of the same oil and gas, agricultural products and other types of raw materials. The development of China's relations with the West repeats the history of the deterioration of Russia's relations with the West. The sanctions already imposed on China will be tightened. Access to sources of raw materials and markets will become a priority for Beijing for the foreseeable future. We should not turn a blind eye to the reaction of some Chinese experts and blogosphere activists to the arrival in Beijing of Mikhail Mishustin at the head of a thousandth army of the Russian elite. The emphasis is not even so much on the vital need for Moscow to receive income from trade with China as on the desirability of not offending the West, leaving the door open for relations with America. However, after 40 years of Chinese-American marriage of convenience, it would be naive to expect a quick change of shoes. There does not seem to be any improvement in relations between America and China, despite Biden's hints and the visit of Chinese Commerce Minister Wang Wentao to the United States. Overcoming the pathological hatred of politicians for China, business people in Washington continue to do business even in the most adverse conditions. In 2022, bilateral trade reached an all-time high of $691 billion. At the same time, the Americans were able to sell their goods to the Chinese for less than 154 billion. The reduction or abolition of duties, which President Trump began to introduce back in 2018 and President Biden is increasing, could help improve the quality and further increase trade. They cost each American family $1,000 a year. However, the prospects for curtailing the trade war are very illusory. The White House and both houses of the US Congress are on the warpath. Any attempt to improve US-China relations ends in scandal—Pelosi's scandalous trip, the big white ball... The same fate awaits current hopes. The visit of Pelosi's heir, Speaker of the House of Representatives Kevin McCarthy to Taiwan is being prepared. At the G7 summit in Tokyo, there was a military coordination between NATO and Japan. China, along with Russia, is designated in the final documents as the main enemy. The bloc's regional headquarters is to be opened in Tokyo. It is impossible to get rid of historical parallels. Similarly, in 1936, Japan concluded the Anti-Comintern Pact with Nazi Germany, directed against the Soviet Union. A few months later, the emboldened Japanese began an all-out war against the Celestial Empire, capturing Beijing, Shanghai, Wuhan and Nanjing in 1937. Only the diplomatic, military and financial assistance of the Soviet Union prevented the capitulation of the Republic of China along the lines of France. Stubbornly resisting China, in turn, prevented Tokyo from attacking the USSR at the already appointed time - August 29, 1941. Then there were two fronts - Soviet and Chinese. Now the situation is repeating itself. The Chinese were not patient. They were defending then. Now, relying on a reliable Russian rear, they launched a counteroffensive. Thanks to Beijing's 12-point peace plan for Ukraine and Xi Jinping's phone call with Zelensky, China is destroying the Yellow Threat stereotype at minimal cost in the European theater and strengthening its image as a peacemaker. There is competition with America. The first study trip to Kyiv, Paris, Berlin, Brussels and Moscow of Special Representative Xi Jinping, Ambassador Li Hui, has just ended. It was preceded by trips of "heavyweights" - Chinese Vice President Han Zheng, foreign policy curator on the party line Wang Yi, Foreign Minister Qin Gang. Another area of China's global counteroffensive is to prevent the West from filling the strategic vacuum in Central Asia. That was the task of the summit of the five countries of this region and China in Xi'an, the ancient capital of several Chinese dynasties. This also meets the strategic interests of Moscow. The combat coordination of the two mighty powers of the Eurasian continent is gaining momentum and taking on new forms. How can one not recall that in March, Xi Jinping, when saying goodbye to Vladimir Putin on the steps of the Grand Kremlin Palace, said: “Now there are changes that have not happened in 100 years, and we are driving these changes.” Putin's answer was short but meaningful: "I agree."