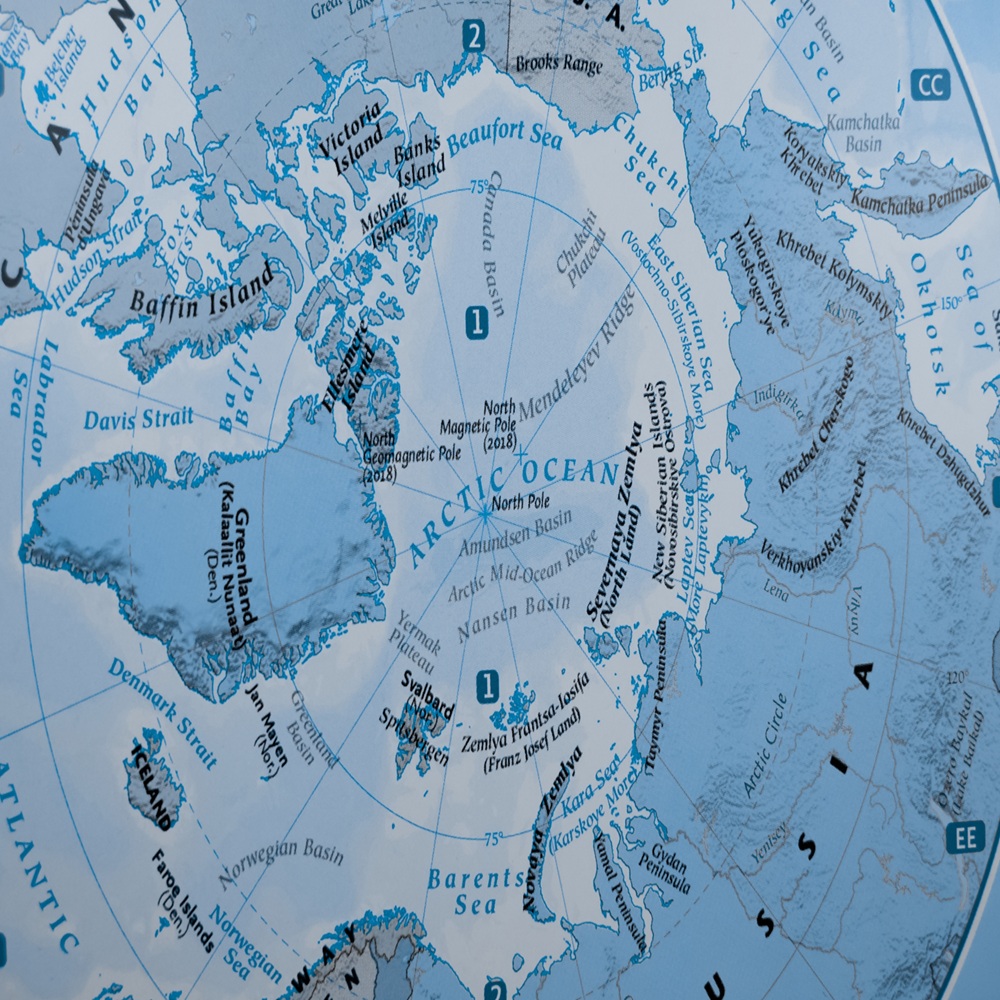
Greenland at the Center of the Arctic Power: US NSS 2025, NATO Cohesion, and the New Geopolitics of the High North.
by World & New World Journal
In the chilling expanse of the Arctic, where ice and ocean frame the edges of the known world, a geopolitical drama has quietly gathered momentum. The world’s strategic gaze is no longer fixed solely on the traditional theatres of diplomacy in Europe, the Middle East, or the Indo-Pacific. Instead, the High North — and particularly Greenland, the vast Arctic territory within the Kingdom of Denmark — has emerged as a critical arena where great-power competition, national security priorities, global trade dynamics, and climate change converge. This transformation did not occur overnight. For decades, military planners, geographers, and strategic thinkers recognized the Arctic’s latent importance. Yet only in recent years have those projections translated into urgent geopolitical reality. At the center of this shift stands the United States’ National Security Strategy 2025 (NSS 2025), unveiled in late 2025, which redefines American priorities in a world shaped by renewed great-power rivalry. While the strategy addresses multiple global theatres, its emphasis on territorial security, critical resources, strategic geography, and adversarial competition underscores why Greenland has moved from the periphery to the heart of international geopolitics. Greenland today sits at the intersection of U.S. homeland defense, NATO cohesion, Arctic militarization, global trade transformation, and the accelerating race for critical minerals. The tensions surrounding the island reveal not only disputes among allies but also deeper structural changes in the international system. This article argues that Greenland is no longer a remote outpost but a strategic fulcrum of the Arctic, whose future will shape the balance of power in the High North and beyond. America’s Strategic Recalibration in the 2025 National Security Strategy The NSS 2025 marks a clear departure from post-Cold War doctrines centered on expansive multilateralism and global institution-building. Instead, it reflects a return to strategic realism, prioritizing the protection of core national interests, territorial security, and the prevention of adversarial dominance in critical regions. The strategy defines the United States’ primary objective as “the continued survival and safety of the United States as an independent, sovereign republic,” coupled with maintaining decisive military, technological, and economic power. Although the Indo-Pacific remains central, the strategy elevates the Western Hemisphere and adjacent strategic regions, emphasizing the need to prevent hostile encroachment on areas vital to U.S. security and economic resilience. Supply chains, critical minerals, missile defense, and strategic geography feature prominently throughout the document. Within this framework, Greenland has transitioned from a peripheral Arctic territory to a linchpin of U.S. strategic defense and resource security. While the NSS does not outline a standalone Arctic doctrine, its underlying logic — securing access to essential materials, protecting strategic approaches to the homeland, and denying adversaries positional advantages — aligns directly with the intensifying focus on Greenland. Latest developments: US position over Greenland. As already mentioned, the release of the NSS 2025 made one thing clear: US foreign policy is now defined by an assertive approach towards the entire Western Hemisphere – where Greenland is part of –. Moreover, this implies that the US might claim the right to intervene in other countries’ domestic affairs in order to guarantee its strategic and corporate interests. Therefore, after Venezuela – in addition to its rhetoric towards Cuba and Mexico – Greenland has become a hot topic, due its geopolitical, economical and strategical position and of course as part of the US “national security” and interest. The interest from the US over Greenland is not new, during Trump’s first administration an attempt to buy Greenland occurred and even at the beginning of his second administration there were comments to obtain the island. Next are presented the developments that occurred until January 22nd: - The US-Greenland-NATO crisis escalated when Trump’s desire to have Greenland either “by hook or by crook” sparked the global debate, while Europeans, Greenlanders and Danish rejected his ideas and showed support for Greenland and the Kingdom of Denmark itself. - A later diplomatic meeting between Danish, Greenlandic and US officials in Washington ended up in a “fundamental disagreement” over the sovereignty of the island on January 14th. - A joint statement of several European countries supporting the idea that “Greenland belongs to its people, and only Denmark and Greenland can decide on matters concerning their relations” was released on January 18th. - Launch of “Operation Arctic Endurance” and the initial deployment of a small number of troops from the European allies plus Danish soldiers. By January 18th there were over 100 troops in Nuuk and another 100 in Kangerlussuaq. (numbers could be increased in a short time). - Worries within Europe and the NATO allies. In addition, China urged the US to stop using the so-called “China threat” as a pretext for pursuing its own interest. - General concern for Greenlanders and several protest in Denmark, and Greenland against the US actions. - The imposition of 10% tariffs from the US over Denmark, Norway, Sweden, France, Germany, Finland, the UK and the Netherlands that would increase by 25% on June 1st if there is no deal reached. After Trump’s speech in the World Economic Forum, he confirmed that tariffs threats were off the table as there was a “framework of a future deal” for Greenland. In summary, in January 2026, Washington’s posture toward Greenland has sharpened into a high-profile mix of strategic urgency and political brinkmanship, framed publicly as an Arctic and homeland-security imperative. Recent reporting describes President Donald Trump repeatedly arguing the U.S. “needs” Greenland for security, while also signaling limits on how far he would go — saying at the World Economic Forum in Davos that he would not use military force to acquire it. At the same time, the episode has clearly strained allied politics: coverage indicates Denmark has insisted Greenland’s sovereignty is not negotiable even as the U.S. debate escalated, and Greenland’s own authorities have taken the moment seriously enough to urge practical preparedness at home. The most concrete “near-term” direction emerging in January 2026 is not annexation but a NATO – and alliance-linked security bargain. Multiple outlets report Trump backing away from threatened tariffs after announcing a “framework” tied to future Arctic security cooperation with NATO leadership — suggesting the administration is trying to convert its Greenland pressure campaign into expanded defense access, posture, or burden-sharing rather than an immediate territorial transfer. Even where details remain vague, the logic is consistent: Greenland’s geography — especially its role in Arctic air/sea lanes and missile-warning architecture — makes it a leverage point for U.S. deterrence and homeland defense planning, and U.S. officials appear to be testing what they can gain diplomatically inside the alliance system when outright sovereignty change is off the table. This posture also lines up with the 2025 National Security Strategy (NSS), which elevates the Western Hemisphere as the top priority region and argues the U.S. will “deny non-Hemispheric competitors” the ability to “own or control strategically vital assets” in the hemisphere, while calling for readjusting military presence and “establishing or expanding access in strategically important locations.” While the NSS text excerpt does not name Greenland in the lines above, its framework — reasserting hemispheric primacy, blocking external footholds, and expanding access — maps neatly onto a Greenland approach that treats the island as a critical node in Arctic security competition and infrastructure control. European Parliament analysis likewise characterizes the NSS as a “pivot” toward a Monroe Doctrine–style sphere-of-interest logic in the Western Hemisphere, reinforcing the idea that Greenland is being handled less as a narrow Denmark dispute and more as part of a broader hemispheric strategy. Greenland’s Geographic Centrality: The broader US security interest of the Island. Figure 1: Arctic states, counties and other administrative regions with capitals. Source: Map by Arto Vitikka, Arctic Centre, University of Lapland. Credit for the border data: Runfola, D. et al. (2020) geoBoundaries: A global database of political administrative boundaries. PLoS ONE 15(4): e0231866. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0231866e. Figure 2: Arctic Population Centers. Map by Arto Vitikka, Arctic Centre, University of Lapland. When viewed from a polar perspective, the Arctic is not a distant fringe but the shortest connective space between North America, Europe, and Eurasia. The Arctic as seen in Figure 1 is composed of several administrative areas, including Canada, Alaska (USA), Russia, Norway, Sweden, Finland, Iceland and Greenland (Denmark). The latter can be said to be located at the center between North America and Europe and Eurasia, underscoring its geopolitical importance. In other words, Greenland occupies the central Atlantic–Arctic axis, the shortest air and missile trajectories between Russia and North America and a pivotal position between the Canadian Arctic Archipelago and the Russian Arctic coast. This geography carries deep strategic implications. First, Greenland is part of the so-called GIUK (Greenland-Iceland-UK) Gap, a crucial corridor for monitoring naval and air activity in the North Atlantic. The GIUK Gap played an important role during the Second World War and the Cold War and nowadays it has become crucial in securing air and sea surveillance through radar stations, while securing the sea lines of communication (SLOCs) as well as supply lines making them uninterrupted between NATO’s European members and the USA. The GIUK Gap can assist in ensuring maritime visibility and assist anti-submarine warfare (ASW) in case of conflicts. The presence of Russian submarines in the Arctic is a central pillar of Russia’s military strategy and nuclear deterrence, making the region one of the most militarized maritime spaces in the world. Russia views the Arctic as both a strategic sanctuary and a launch platform. In consequence, its Northern Fleet – headquartered on the Kola Peninsula –, is the most powerful of Russia’s fleets and operates a large share of its nuclear-powered ballistic missile submarines (SSBNs), such as the Borei and Delta IV classes. These submarines carry submarine-launched ballistic missiles (SLBMs) and are designed to remain hidden under Arctic ice, ensuring a second-strike capability in the event of a nuclear conflict. The ice cover, combined with Russia’s familiarity with Arctic waters, provides concealment and operational depth. In addition to SSBNs, Russia deploys nuclear-powered attack submarines (SSNs) and guided-missile submarines (SSGNs) in the Arctic. These vessels conduct intelligence gathering, protect ballistic missile submarines, and pose threats to NATO naval forces and undersea infrastructure, including communication cables. Russian submarines regularly transit through key chokepoints such as the GIUK Gap, bringing them into strategic relevance for Greenland, Iceland, and NATO’s anti-submarine warfare (ASW) posture. In addition, the Arctic also supports Russia’s broader bastion defense concept, which seeks to create heavily defended maritime zones where submarines can operate safely. Air defenses, surface ships, icebreakers, and coastal missile systems complement submarine operations. As climate change reduces sea ice and increases accessibility, Russian submarine activity in the Arctic is expected to remain intense, reinforcing the region’s importance for NATO surveillance, early warning systems, and transatlantic security — especially for locations like Greenland that sit astride critical Arctic–Atlantic routes. Second, Greenland’s high latitude makes it an ideal place for early detection of long-range missile launches. Russia has long-range intercontinental ballistic missiles (ICBMs), if ever launched from Russia toward the United States, the total flight time would be roughly between 25 to 35 minutes – depending on the launch location and target. But because of the Earth’s curvature, the shortest path from Russia to the continental US goes over the Arctic which is why Greenland is so strategically important for early detection and missile defense. In practical terms, US decision-makers would have only minutes to assess the threat and respond after a launch is detected. Establishments such as the U.S. Pituffik Space Base underscore how Greenland functions as a first line of surveillance against possible ballistic missile threats from the Eurasian landmass. Therefore, Greenland is indispensable to early-warning and missile-defense systems. Sensors, radars, and space-tracking infrastructure based on the island form a crucial layer of “U.S. homeland defense”. Finally, Greenland is the only large Arctic landmass under Western democratic control outside Eurasia. Russia dominates the Eurasian Arctic coastline, while Alaska and Canada anchor North America. Greenland bridges these spaces, serving as a keystone for transatlantic Arctic security. Its isolation does not diminish its importance; rather, it magnifies it. – making Greenland a linchpin of US homeland defense and NATO’s northern security architecture. Greenland and NATO: The Fragile Architecture of Arctic Security Figure 3: NATO’s and Russia’s militarization in the Arctic. Figure 3 exposes a stark asymmetry in the Arctic militarization between NATO and Russian. The latter maintains a dense, continuous network of military bases stretching from the Kola Peninsula to the Bering Strait. These installations support air defense, naval operations, missile forces, and surveillance — forming an integrated arc of control along Russia’s northern frontier. On the other hand, NATO’s Arctic posture is fundamentally different. It relies on discrete strategic nodes rather than territorial saturation, interoperability over mass and coordination among multiple sovereign states. Within this fragmented architecture, Greenland is NATO’s most critical node. Nonetheless, the US has presence in Greenland, specifically with the Pituffik Space Base (formerly Thule Air Base), which is located in northwest Greenland. This base – as mentioned before – is indispensable for early missile warning, space surveillance and tracking adversary launches across the polar region. While the UK has presence in Norway in the logistic Camp Viking site. Without Greenland, NATO’s Arctic posture would fracture into disconnected segments — North America on one side, Scandinavia on the other — with no central anchor. This reality explains the sharp European response in 2025–2026 to U.S. rhetoric suggesting unilateral action or coercive pressure regarding Greenland. The deployment of European troops under Operation Arctic Endurance was not merely symbolic; it was an assertion that Greenland is a collective NATO concern, not a bilateral bargaining chip. Greenland’s Resources: Strategic Minerals in a Fragmenting World Beyond military geography, Greenland’s subsoil wealth significantly enhances its geopolitical importance. The island holds substantial deposits of rare earth elements (REEs), lithium, graphite, niobium, titanium, uranium and zinc. As it is well known these strategic materials are indispensable and critical for renewable energy systems, electric vehicles, advanced electronics, missile guidance and radar technologies and space and defense infrastructure. Last but not least there is also oil and gas, but the conditions and viability to extract them make them an economic challenge. In the context of the control of natural resources, the NSS 2025 repeatedly stresses the need to reduce U.S. dependence on adversarial supply chains — an implicit reference to China’s dominance in rare-earth processing. Therefore, US eyes are on Greenland, as it represents one of the few politically aligned alternatives with large-scale potential reserves – ironically not under Chinese or Russian influence, but under US “allies” control. Yet resource abundance does not automatically translate into strategic advantage. Mining in Greenland faces severe challenges: extreme climate conditions, environmental risks, limited infrastructure, and strong local opposition to environmentally destructive projects. As a result, Greenland’s mineral wealth is strategically valuable but politically sensitive. Its development requires local consent and long-term cooperation, not coercion — a fact often overlooked in external strategic calculations. The Arctic Trade Revolution: Melting Ice, Shifting Routes Figure 4: Arctic Seaways (Northern Sea Route, Northwest Passage and Transpolar Sea Route). Source: Map by Arto Vitikka, Arctic Centre, University of Lapland. Climate change is transforming the Arctic faster than any other region on Earth. As sea ice recedes, new maritime routes are becoming seasonally viable, with potentially transformative consequences for global trade. The Northern Sea Route (NSR) along Russia’s Arctic coast already reduces transit times between Europe and Asia by up to 40%, even though some parts are free of ice for some months per year. On the other hand, a future transpolar route, cutting directly across the Arctic Ocean, could bypass traditional chokepoints such as: The Suez Canal, The Panama Canal or The Strait of Malacca. Therefore, Greenland importance relies on its geographic position that places it adjacent to these emerging corridors. Potential roles for the island include: the search-and-rescue hubs, refueling and logistics points, maritime surveillance and communications infrastructure. This elevates Greenland from a military asset to a potential gatekeeper of future Arctic trade, linking regional security directly to global economic flows. Icebreakers and Power Projection: Mobility as Sovereignty Figure 5: Major Icebreakers and Ice-Capable Patrol Ships highlight a decisive but underappreciated imbalance. Source: generated with Chat GPT using Routers Nov 2022 data. The transit in the Arctic can be defined by the possibility to move freely without any inconvenience due its extreme conditions – or at least with the least inconveniences. In consequence major ice breakers and ice-capable patrol ships became very important assets for the countries in the region. In a simple comparison, Russia possesses more icebreakers than NATO combined, as shown in Figure 5, including nuclear-powered vessels capable of year-round Arctic operations. These ships are instruments of sovereignty, enabling continuous military presence, escort of commercial shipping, enforcement of Arctic regulations and rapid crisis responses. By contrast, the United States has long underinvested in icebreaking capacity. NATO relies on a patchwork of national fleets, with Finland and Sweden contributing significantly but still lagging behind Russia’s scale. The strategic implication is clear: Russia controls mobility while NATO controls nodes. In such an environment, fixed strategic anchors like Greenland become even more critical. Competing Arctic Visions Russia Russia views the Arctic as a core strategic and economic priority, central to its national identity, security, and long-term development. Its Arctic vision emphasizes sovereignty, military security, and the exploitation of vast natural resources, particularly hydrocarbons and minerals. Moscow sees the Northern Sea Route as a critical shipping corridor that can enhance Russia’s control over Arctic navigation and generate economic revenues. To support this vision, Russia has invested heavily in Arctic infrastructure, icebreaker fleets, and military modernization, positioning itself as the dominant Arctic power and framing the region as vital to its great-power status. The Arctic is not an extension of Russian power; it is central to it. Figure 6: Cargo volume in Russia’s Northern Sea Route (1933-2023) China China approaches the Arctic as a “near-Arctic state,” framing its vision around scientific research, economic opportunity, and global governance. Beijing emphasizes participation in Arctic affairs through international law, particularly the UN Convention on the Law of the Sea, and promotes cooperation rather than territorial claims. Its strategy emphasizes long-term access to resources, influence over Arctic governance norms, and participation in future trade routes. Its concept of a “Polar Silk Road” reflects an interest in future shipping routes, energy projects, and digital connectivity, linking the Arctic to China’s broader Belt and Road Initiative. Even though China presents its Arctic engagement as peaceful and mutually beneficial, while gradually expanding its strategic and economic footprint in the region, it also has interest in Greenland’s mining sector, for example, which has heightened concerns about strategic leverage rather than direct control. Figure 7: Map of China’s Polar Silk Road. Source: Map by Arto Vitikka, Arctic Centre, University of Lapland. United States The U.S. approach, as reflected in the NSS 2025, is reactive but intensifying. Greenland crystallizes American concerns about strategic vulnerability, supply-chain dependence, and alliance credibility. Yet pressure tactics risk undermining the very alliances that make Arctic stability possible. The United States views the Arctic as an increasingly important region for national security, environmental stewardship, and economic opportunities. At the same time, it recognizes the strategic implications of growing Russian and Chinese activity in the region. Arctic States The European Arctic states emphasize sustainability, human security, and regional cooperation as the foundation of their Arctic vision. Their policies prioritize environmental protection, responsible resource management, and the rights and livelihoods of Indigenous peoples, while balancing economic development in sectors such as fisheries, renewable energy, and limited resource extraction. These states strongly support multilateral governance through institutions like the Arctic Council and stress adherence to international law. Collectively, they view the Arctic as a region where stability, cooperation, and climate leadership are essential, especially amid rising geopolitical tensions and accelerating environmental change. Canada Canada’s Arctic vision centers on sovereignty, Indigenous partnership, and sustainable development, reflecting the region’s importance to national identity and security. Ottawa emphasizes the protection of its northern territories and views the Northwest Passage as internal waters, while supporting a rules-based Arctic order. A core pillar of Canada’s approach is its collaboration with Indigenous peoples, recognizing their rights, knowledge, and role in governance and stewardship. Canada also prioritizes climate change adaptation, environmental protection, and responsible economic development, seeking to ensure that increased Arctic activity benefits northern communities while maintaining peace and stability in the region. India India’s Arctic vision is primarily science-driven and climate-focused, reflecting its broader emphasis on environmental security and multilateral cooperation. Through its Arctic research station, Himadri, and active participation in the Arctic Council as an observer, India seeks to understand the Arctic’s impact on global climate systems, particularly the Indian monsoon. New Delhi also recognizes the long-term economic and geopolitical significance of the Arctic but approaches the region cautiously, prioritizing sustainable development, international collaboration, and respect for Arctic states’ sovereignty. Strategic Futures: Cooperation or Fragmentation The future of Greenland and the Arctic more broadly will hinge on whether the region evolves toward structured cooperation or strategic fragmentation. In a cooperative scenario, Greenland becomes a stabilizing anchor within a renewed Arctic security framework, where the United States, Denmark, and NATO align their defense priorities with Greenlandic self-determination and environmental safeguards. Such an approach would emphasize multilateral governance, transparency in resource development, confidence-building military measures, and shared investment in infrastructure, search-and-rescue capabilities, and climate resilience. Cooperation would not eliminate competition, particularly with Russia and China, but it would establish rules, norms, and mechanisms to prevent escalation and miscalculation in an increasingly accessible Arctic. By contrast, a fragmented Arctic would be characterized by unilateral actions, coercive diplomacy, and the erosion of trust among allies. Pressure tactics aimed at securing access, influence, or control over Greenland could weaken NATO cohesion, fuel local resistance, and open political space for external actors to exploit divisions. In such a scenario, the Arctic risks becoming a patchwork of contested zones rather than a managed strategic commons. Therefore, fragmentation would increase the likelihood of militarization without coordination, resource development without legitimacy, and crisis dynamics without effective communication channels — conditions that historically precede instability rather than security. Conclusion Greenland’s transformation from a remote Arctic territory into a strategic fulcrum reflects deeper shifts in the international system. The United States’ National Security Strategy 2025 captures a world defined by renewed great-power rivalry, supply-chain vulnerability, and the reassertion of geography as destiny. In this context, Greenland sits at the intersection of homeland defense, NATO credibility, critical resource security, and emerging Arctic trade routes. Its importance is not a product of any single factor, but of the convergence of military, economic, and environmental dynamics reshaping the High North. Yet Greenland’s strategic value does not grant external powers unlimited leverage. Geography may confer importance, but legitimacy, consent, and alliance cohesion determine whether that importance translates into durable influence. Attempts to treat Greenland as a transactional asset risk undermining NATO unity, destabilizing Arctic governance, and alienating the very population whose cooperation is essential for security and development. The Arctic’s future must not be decided solely by military deployments or mineral deposits, but by the political relationships that sustain them. Ultimately, Greenland illustrates the central paradox of the new Arctic geopolitics: the region’s growing accessibility increases both opportunity and risk. Stability will depend not on dominance, but on restraint, not on unilateralism, but on partnership. Whether the Arctic becomes a zone of managed competition or strategic fragmentation will shape not only the balance of power in the High North, but the credibility of international order adapting to a rapidly changing world. Also, it is important to highlight Greenland’s voice – referring to sovereignty and identity. Usually under great-power maneuvering, Greenland’s own population has often been sidelined. Yet Greenland is not merely an object of strategy; it is a political community with a strong Indigenous identity, environmental concerns, and aspirations for greater autonomy. Therefore, it is important to keep in mind its constitutional status within the Kingdom of Denmark, their principle of self-determination and the political costs of alienating local consent. Paradoxically, the more external powers push, the more Greenlandic society resists — complicating both security arrangements and resource development. Finally, the Arctic is not only Greenland, the US or the NATO, there are other authors involved, Russia for instance appears as the main one, while, China and India are increasing their interests in the region Moreover, climate change seems to be game changer as new Arctic seaways gain importance in terms of trade and mobility, which in consequence are and will redefine sovereignty. For instance, either icebreakers or minerals would become as strategic as missiles. The Arctic transformation is already happening, and who will lead and what will happen in the region in the future are questions to be solved in the near future. References Agneman, G. (2025, February 04). Trump wants Greenland – but here’s what the people of Greenland want. Retrieved from The Conversation: https://theconversation.com/trump-wants-greenland-but-heres-what-the-people-of-greenland-want-248745 Aljazeera. (2026, January 15). European troops arrive in Greenland as talks with US hit wall over future. Retrieved from Aljazeera: https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2026/1/15/european-troops-arrive-in-greenland-as-talks-with-us-hit-wall-over-future Aljazeera. (2026, January 18). Trump announces new tariffs over Greenland: How have allies responded? Retrieved from Aljazeera: https://www.aljazeera.com/news/2026/1/18/trump-announces-new-tariffs-over-greenland-how-have-eu-allies-responded Arctic Centre University of Lapland. (n.d.). Arctic Region. Retrieved from https://arcticcentre.org/en/arctic-region/maps/polar-silk-road/ Bassets, M. (2026, Enero 11). “Por las buenas o por las malas”: así puede Trump conquistar Groenlandia. Retrieved from El País: https://elpais.com/internacional/2026-01-10/por-las-buenas-o-por-las-malas-asi-puede-trump-conquistar-groenlandia.html Bateman, T. (2026, January 14). Danish minister says 'fundamental disagreement' remains after 'frank' Greenland talks with US. Retrieved from BBC: https://www.bbc.com/news/live/cn824zzp670t BBC News. (2026, January 21). Trump drops threat of tariffs over Greenland after Nato talks in Davos. Retrieved from BBC News: https://www.bbc.com/news/live/cjrzjqg8dlwt Bierman, P. (2025, February 19). Greenland’s melting ice and landslide-prone fjords make the oil and minerals Trump is eyeing dangerous to extract. Retrieved from The Conversation: https://theconversation.com/greenlands-melting-ice-and-landslide-prone-fjords-make-the-oil-and-minerals-trump-is-eyeing-dangerous-to-extract-249985 Bierman, P. (2025, February 19). Greenland’s melting ice and landslide-prone fjords make the oil and minerals Trump is eyeing dangerous to extract. Retrieved from The Conversation: https://theconversation.com/greenlands-melting-ice-and-landslide-prone-fjords-make-the-oil-and-minerals-trump-is-eyeing-dangerous-to-extract-249985 Bierman, P. (2026, January 14). US military has a long history in Greenland, from mining during WWII to a nuclear-powered Army base built into the ice. Retrieved from The Conversatiion: https://theconversation.com/us-military-has-a-long-history-in-greenland-from-mining-during-wwii-to-a-nuclear-powered-army-base-built-into-the-ice-273355 Bonsoms, J. (2025, Dececmber 16). ‘Extreme melting’ episodes are accelerating ice loss in the Arctic. Retrieved from The Conversation: https://theconversation.com/extreme-melting-episodes-are-accelerating-ice-loss-in-the-arctic-272114 Brincat, S. (2026, January 18). Trump has threatened European countries with higher tariffs if he doesn’t get Greenland. Will it work? Retrieved from The Conversation: https://theconversation.com/trump-has-threatened-european-countries-with-higher-tariffs-if-he-doesnt-get-greenland-will-it-work-273698 Brincat, S., & Naranjo Cáceres, J. Z. (2026, January 07). Trump wants Greenland. Europe’s tepid response is putting NATO and global security at risk. Retrieved from The Conversation: https://theconversation.com/trump-wants-greenland-europes-tepid-response-is-putting-nato-and-global-security-at-risk-272819 Brooks, J. (2026, January 20). Pro-Greenland protesters mock Trump’s MAGA slogan with ‘Make America Go Away’ caps. Retrieved from AP: https://apnews.com/article/denmark-greenland-maga-trump-protest-cd1213dd73e9ea1e4da43285704c95ea Bryant, M., & Sabbagh, D. (2026, January 15). Greenland's defence is 'common concern' for Nato, Danish PM says as European troops fly in. Retrieved from The Guardian: https://www.theguardian.com/world/2026/jan/15/greenland-defence-nato-denmark-prime-minister-european-troops Burrows, E., Ciobanu, C., & Niemann, D. (2026, January 16). European troops arrive in Greenland as talks with US highlight 'disagreement' over island's future. Retrieved from AP: https://apnews.com/article/greenland-united-states-denmark-trump-vance-rubio-meeting-b10f5151008f1f18a788dc0751473c0e CNN. (2026, January 21). Trump says he’s formed a ‘framework of a future deal’ on Greenland. Retrieved from CNN: https://edition.cnn.com/politics/live-news/trump-administration-news-01-21-26 Davies, M. (2026, January 19). Starmer holds phone call with Trump over Greenland tariff threat. Retrieved from BBC: https://www.bbc.com/news/articles/cwyn90l1dneo Dodds, K. (2026, January 09). As the Arctic warms up, the race to control the region is growing ever hotter. Retrieved from The Conversation: https://theconversation.com/as-the-arctic-warms-up-the-race-to-control-the-region-is-growing-ever-hotter-273118 Dunbar, M. (2026, January 18). Trump's calls to seize Greenland ignite fresh criticism from Republican party. Retrieved from The Guardian: https://www.theguardian.com/us-news/2026/jan/18/trump-greenland-republican-party FitzGerald, J. (2026, January 19). Why does Trump want Greenland and what could it mean for Nato? Retrieved from BBC: https://www.bbc.com/news/articles/c74x4m71pmjo Fleck, A. (2025, January 24). NATO’s and Russia’s Militarization of the Arctic. Retrieved from statista: https://www.statista.com/chart/33824/military-bases-in-the-arctic-belonging-to-nato-and-russia/?srsltid=AfmBOoqwc5PmGe6_JB6mYjQSP9pr9fIZE_LcEtMOo_rtnCD86zMcQpwn Gjedssø Bertelsen, R. (2025). Divided Arctic in a Divided World Order. Strategic Analysis, 48(Issue 6: Changing Dynamics in the Arctic: Actors and Alliances), 568-577. doi:https://doi.org/10.1080/09700161.2025.2453322 Government Offices of Sweden. (2026, January 18). Statement by Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, the Netherlands, Norway, Sweden and the United Kingdom. Retrieved from Government Offices of Sweden: https://www.government.se/statements/2026/01/statement-by-denmark-finland-france-germany-the-netherlands-norway-sweden-and-the-united-kingdom/ Grillo, F. (2026, January 08). As the US eyes Greenland, Europe must turn a global problem into an opportunity. Retrieved from The Conversation: https://theconversation.com/as-the-us-eyes-greenland-europe-must-turn-a-global-problem-into-an-opportunity-272872 Gupta, P. (2024, September 18). Understanding the potential of the Northern Sea Route. Retrieved from ORF: https://www.orfonline.org/expert-speak/understanding-the-potential-of-the-northern-sea-route Harvey, L. (2026, January 16). European nations send additional troops to Greenland as US annexation threats escalate. Retrieved from CNN: https://edition.cnn.com/2026/01/15/world/europe-troops-greenland-trump-nato-intl-hnk Hastings Dunn MBE, D., Webber, M., & Wolff, S. (2026, January 07). US action against Greenland would undermine Nato, but now is not the time to panic. Retrieved from The Conversation: https://theconversation.com/us-action-against-greenland-would-undermine-nato-but-now-is-not-the-time-to-panic-272911 Holland, S., Mason, J., & Erickson, B. (2026, January 07). Trump discussing how to acquire Greenland, US military always an option, White House says. Retrieved from Reuters: https://www.reuters.com/world/trump-advisers-discussing-options-acquiring-greenland-us-military-is-always-an-2026-01-06/ huaxia. (2026, January 19). China urges U.S. to stop using so-called "China threat" as pretext for pursuing selfish gains. Retrieved from Xinhua: https://english.news.cn/20260119/57899ee8d43345ddbfa222828ec1d0a4/c.html Jakes, L., Tankersley, J., & Kanno-Youngs, Z. (2026, January 22). Trump Touts Greenland Framework as NATO Mulls U.S. Sovereignty Over Bases. Retrieved from The New York Times: https://www.nytimes.com/live/2026/01/21/us/trump-davos-greenland-news Karjee, M. (2025, August 20). Russia’s Arctic Corridor: Between Ice and Isolation. Retrieved from E-International Relations: https://www.e-ir.info/2025/08/20/russias-arctic-corridor-between-ice-and-isolation/ Katila, A. (2026, January 15). As US and Denmark fight, Greenland’s voices are being excluded once again. Retrieved from The Conversation: https://theconversation.com/as-us-and-denmark-fight-greenlands-voices-are-being-excluded-once-again-273131 Kennedy-Pipe, C. (2026, January 14). Whether or not US acquires Greenland, the island will be at the centre of a massive military build-up in the Arctic. Retrieved from The Conversation: https://theconversation.com/whether-or-not-us-acquires-greenland-the-island-will-be-at-the-centre-of-a-massive-military-build-up-in-the-arctic-273301 Khanna, M. (2025, March 19). China and the Arctic: An Overview. Retrieved from ORF: https://www.orfonline.org/research/china-and-the-arctic-an-overview Kirby, P. (2026, January 16). European military personnel arrive in Greenland as Trump says US needs island. Retrieved from BBC: https://www.bbc.com/news/articles/cd0ydjvxpejo Kotak, S. (2025, September 08). Leveraging India’s Arctic Observer Status: Scientific Diplomacy as a Lever for Climate, Resource and Security Advancement. Retrieved from World & New World Journal: https://worldandnewworld.com/india-arctic-observer-status/ Kottasová, I., & Edwards, C. (2026, Enero 19). Trump le dice a Noruega que ya no se siente obligado a "pensar únicamente en la paz" en carta sobre el Nobel y Groenlandia. Retrieved from CNN Español: https://cnnespanol.cnn.com/2026/01/19/eeuu/trump-paz-noruega-nobel-reux Kumar, A., & Haldar, S. (2024, October 2024). An evolving partnership in the Arctic between China and Russia. Retrieved from ORF: https://www.orfonline.org/expert-speak/an-evolving-partnership-in-the-arctic-between-china-and-russia L. Montgomery, S. (2026, January 14). 4 reasons why the US might want to buy Greenland – if it were for sale, which it isn’t. Retrieved from The Conversation: https://theconversation.com/4-reasons-why-the-us-might-want-to-buy-greenland-if-it-were-for-sale-which-it-isnt-246955 Lebowitz, M. (2026, January 18). Treasury secretary defends Greenland tariffs: 'The national emergency is avoiding the national emergency'. Retrieved from NBC News: https://www.nbcnews.com/politics/trump-administration/treasury-secretary-bessent-tariffs-national-emergency-greenland-eu-rcna254650 Levison, J., & Russell, L. (2026, January 19). Why Trump says the US 'needs' Greenland - and what the fallout could be. Retrieved from Sky news: https://news.sky.com/story/why-trump-says-the-us-needs-greenland-and-what-the-fallout-could-be-13285350 Lubold, G., Kube, C., Williams, A., & Alba, M. (2026, January 14). Buying Greenland could cost as much as $700 billion. Retrieved from NBC News: https://www.nbcnews.com/politics/white-house/buying-greenland-cost-much-700-billion-rcna253921 Manners, I. (2026, January 09). Four ways to understand what’s going on with the US, Denmark and Greenland. Retrieved from The Conversation: https://theconversation.com/four-ways-to-understand-whats-going-on-with-the-us-denmark-and-greenland-272873 Nicholas, P., & Smith, A. (2026, January 20). Trump won't say whether he would use force to seize Greenland. Retrieved from NBC News: https://www.nbcnews.com/politics/trump-administration/trump-greenland-use-of-force-nobel-norway-europe-tariffs-ukraine-rcna254786 Passi, R. (2018, February 21). One belt, one road, and now one circle. Retrieved from ORF: https://www.orfonline.org/expert-speak/one-belt-one-road-and-now-one-circle Paul, J. (2026, January 08). Greenland is rich in natural resources – a geologist explains why. Retrieved from The Conversation: https://theconversation.com/greenland-is-rich-in-natural-resources-a-geologist-explains-why-273022 Reuters. (2021, July 16). Greenland ends unsuccessful 50-year bid to produce oil. Retrieved from Reuters: https://www.reuters.com/business/energy/greenland-puts-an-end-unsuccessful-oil-adventure-2021-07-16/#:~:text=Naaja%20Nathanielsen%2C%20Greenland's%20minister%20of,profits%20or%20make%20a%20loss Rønberg, N., Gjerding Nielson, E., & Haugaard, M. (2026, January 06). Kampen om Grønlands fremtid. Retrieved from Nyheder: https://nyheder.tv2.dk/live/2025-01-06-kampen-om-groenlands-fremtid/over-200-soldater-i-groenland-lige-nu?entry=c342b2d3-e01d-4f60-b1dc-8df98fdac85b Sergunin, A., & Konyshev, V. (2025, April 21). The Arctic Great Game: The Need for Cautious Optimism. Retrieved from ORF: https://www.orfonline.org/expert-speak/the-arctic-great-game-the-need-for-cautious-optimism Sheftalovich, Z., & Jack, V. (2026, January 07). How Trump gets Greenland in 4 easy steps. Retrieved from Politico: https://www.politico.eu/article/donald-trump-greenland-easy-steps-nato-policy-deal-military/ Shetty, K. (2023, June 06). The Northern Sea route: A gamechanger or a road to hegemony? Retrieved from ORF: https://www.orfonline.org/expert-speak/the-northern-sea-route Slothuus, L. (2026, January 12). Why Greenland’s vast natural resources won’t necessarily translate into huge profits. Retrieved from The Conversation: https://theconversation.com/why-greenlands-vast-natural-resources-wont-necessarily-translate-into-huge-profits-273137 Soufi Burridge, T., Gardiner, C., & Pereira, I. (2026, January 16). France, other NATO countries send troops to Greenland for exercises after meeting with Vance and Rubio. Retrieved from ABC News: https://abcnews.go.com/Politics/france-nato-countries-send-troops-greenland-exercises-after/story?id=129241103 Talmazan, Y. (2026, January 15). European troops arrive in Greenland as Trump throws another curveball. Retrieved from NBC News: https://www.nbcnews.com/world/greenland/european-troops-arrive-greenland-trump-throws-curveball-rcna254166 Tanno, S., & Waldenberg, S. (2026, Enero 10). Trump dice que Estados Unidos tomará Groenlandia "por las malas" sino puede hacerlo por las buenas. Retrieved from CNN Español: https://cnnespanol.cnn.com/2026/01/10/eeuu/trump-groenlandia-malas-trax Testoni, M. (2026, January 16). US-Greenland negotiations have hit a wall. Here are three ways the crisis could end. Retrieved from The Conversation: https://theconversation.com/us-greenland-negotiations-have-hit-a-wall-here-are-three-ways-the-crisis-could-end-273629 tg24. (2026, January 16). Groenlandia, scattata la missione "Arctic Endurance": cosa sapere. Retrieved from tg24: https://tg24.sky.it/mondo/2026/01/16/groenlandia-arctic-endurance-esercitazione-militare The White House. (2025, November). National Security Strategy of the United States of America. Retrieved from The White House: https://www.whitehouse.gov/wp-content/uploads/2025/12/2025-National-Security-Strategy.pdf